Cat eye syndrome is a rare disorder that is caused as a result of a rare chromosomal aberration which usually occurs at birth. Typically, a human has 22 chromosomes which have two arms known as 22p (the short arm) and 22q (the long arm).
For individuals who have the cat eye syndrome, the short arm appears twice whereas the long arm doesn’t appear at all or it may appear once. This is known as partial trisomy. This defect as a result of this causes a defective abnormality with the ocular region (eyes) hence the name cat eye syndrome.
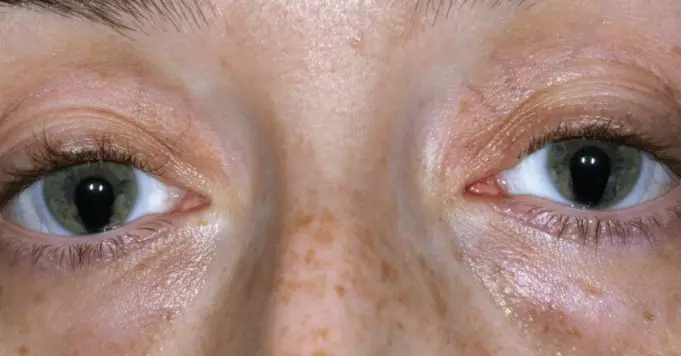
This defect which is known as coloboma usually appears as a gap or space in between the iris and the pupil as a result of this causing the elongation of the pupil thereby giving the eye a cat-eye resemblance.
Apart from the elongation of the pupil, other features are associated with the cat eye syndrome. The chromosomal aberration also affects other organs and systems of the body apart from the eyes.
These aberrations are caused during the fetal stages as well as the embryonic stages of human life. Depending on how severe the irregularities are, the Symptoms can either be acute(minute) or chronic(very severe).
While for some, the manifestations of the symptoms of cat eye syndrome may be mild, for others, the manifestations may be very chronic and severe. It can occur from person to person in a family; however, it is not a contagious disease.
Signs and symptoms to expect
The basic symptoms of the cat eye syndrome are ocular coloboma, anal atresia, and minor ear defects associated with preauricular skin tags otherwise known as pits. These symptoms are known as the classic triad of symptoms.
But because of how variable the syndrome appears to be within individuals, only about 41% of patients who have been diagnosed with the cat eye syndrome have the classic triad of symptoms.
Generally, the abnormalities which are closely associated with the cat eye syndrome always affect both eyes, both ears as well as the anal region, heart, and/or both kidneys.
When it becomes so severe, some patients tend to exhibit disabilities with the intellectual functions of their brains. The presence of the Cat eye syndrome as diagnosed in no way detects how severe the symptoms are or would be.
It is rare but not an impossible occurrence for an individual to have all the signs at once. The abnormalities associated with the cat eye syndrome include
1. Ocular Coloboma and other eye defects
A coloboma occurs when there is a partial absence of ocular tissue. This is often a bilateral problem, and this means that it always affects not just a single eye but the two eyes. It usually occurs as a result of the failure of both eyes to close a fissure in the lower part of the eye during prenatal development.
Once this fissure doesn’t close during prenatal development, it will cause the appearance of a gap or space that persists. The ocular tissues that are affected could include the iris which is the coloured part of the eyes that regulates the amount of light that enters the eyes, The choroid layer which is the middle layer or the retina which is the innermost membrane that has an abundant nerve supply.
Once the coloboma affects the iris, it gives the iris an unusual appearance that looks like a keyhole. If the only part that is affected by the coloboma is the iris, then vision won’t be impaired.
However, if the coloboma extends more than the iris such that it begins to affect other parts of the eyes, it could cause severe eye defects which may result in blindness.
Although one of the most distinctive features of cat eye disease was initially ocular coloboma, however, it has been recorded that only a few, just over half of individuals affected by the cat eye disease present with ocular coloboma.
Some patients also may present with other eye defects asides ocular coloboma. This defects may include strabismus( this occurs when the eyesight of both eyes cross each other), and unilateral microphthalmia (this happens when one eye is abnormally smaller than the other).
Other eye defects include aniridia (this refers to the absence of the iris), clouding of the cornea, absence of eye tissues, cataract and Duane syndrome. Also, this is sporadic cases; however, they are not impossible.
2. Abnormalities in the Anal region
This is a more frequently occurring symptom associated with the cat eye syndrome. This occurs when the opening to the Anal region becomes unusually narrow and small causing what is known as Anal Stenosis.
Sometimes, patients have also presented with anal atresia which is the complete absence of the Anal canal, and a fistula that runs directly from the large intestine in other abnormal places in the body.
Most times in males, when a fistula occurs as a result of this syndrome, it may form between the rectum and the bladder which is the organ that collects and stores urine, the urethra or the perineum. However, for females, the fistula could run from the rectum to the bladder and/or the vagina.
3. Abnormalities in the ear region
One of the significant signs of the cat eye syndrome is the presence of preauricular skin tags and/or pits. This is the most common sign that most patients with the cat eye syndrome must present with. According to research, history and records, over 80% of patients have presented with this abnormality as a significant sign.
Patients who have pits will present with a small depression also known as pits in front of the ears also known as the preauricular area. Apart from this trait, the patient will also exhibit an abnormally formed low set of ears which can include absent ear canals, a condition known as microtia.
For most cases, the absence of one ear canal will affect mine ear causing a mild hearing loss due to the inability of the ear to transmit hearing sounds from the outer ear to the inner ear. This condition is known as the conductive hearing loss.
4. Severe heart defects and abnormalities
More than half of the patients who present with cat eye syndrome have structural abnormalities of the heart and congenital heart defects. The most common heart defects usually introduced includes teratology of the fallot and total anomalous pulmonary venous return.
Depending on the extent of the malformation and the extent of the heart defect, symptoms may vary. Total anomalous pulmonary venous return is usually associated with abnormalities in the return of blood flow to the heart.
Infants who have total anomalous pulmonary venous return will be unable to have venous blood returned to the right atrium which is the chamber that we used for collecting venous blood.
Teratology of the fallout, on the other hand, refers to a combination of cardiac diseases. These consists of a septum that separates the two lower chambers of the heart also known as the ventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis and hypertrophy of the heart ventricle.
5. Kidney and genital abnormalities
These include malformations of the urinary system as well as abnormalities in the urogenital system. Kidney defects include unilateral or bilateral renal hypoplasia, the absence of a kidney, abnormal enlargement of a kidney, the presence of an extra kidney, accumulation of urine in a particular kidney and cystic dysplasia.
Treatment
Treatment of cat eye syndrome requires the specialty of several professional doctors such as pediatricians, cardiologists, surgeons, eye specialists, etc. There is currently no cure for this disease, however, the symptoms of this disease can be treated.