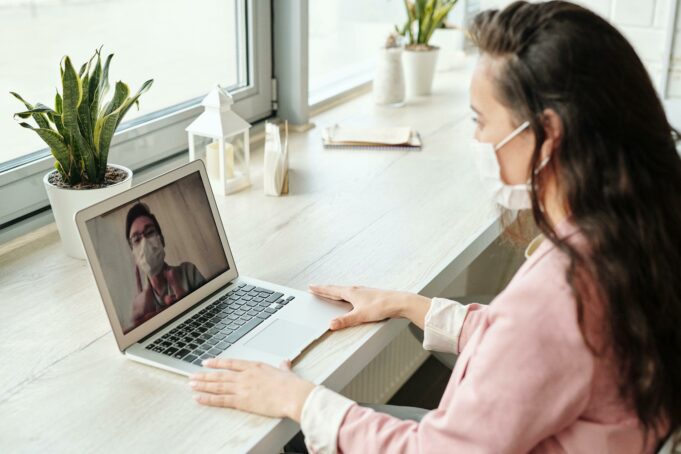
Telemedicine is revolutionizing the way we approach healthcare in a connected world. By embracing virtual consultations, remote monitoring, and advanced digital tools, medical professionals and patients are finding new ways to make healthcare more accessible and efficient. In this article, we’ll explore the advantages, disadvantages, and future implications of telemedicine for both providers and patients.
The Advantages
There is no denying that telemedicine is changing the game when it comes to healthcare. Here are some of the key benefits that it brings to the table:
- Improved access: Telemedicine has the potential to make healthcare more accessible to people in rural areas or communities with limited medical services available. By allowing patients to seek consultations remotely, they no longer have to travel long distances to visit their healthcare provider.
- Cost reduction: Virtual consultations can save both patients and healthcare providers time and money. Many routine consultations can be conducted over the phone or video call, eliminating the need for costly office visits.
- Better patient care: With telemedicine, healthcare professionals can get real-time updates on a patient’s condition, provide faster and more accurate diagnoses, and coordinate with other medical professionals where necessary.
- Increased convenience: The ability to schedule appointments and get treatment from anywhere makes telemedicine a more convenient option for many patients. They can also avoid long waiting times at doctors’ offices and receive care from the comfort of their own homes.
The Disadvantages
For all its advantages, telemedicine does have some drawbacks that are worth considering. Just a few include:
- Technical limitations: Poor internet connections can hamper telemedicine visits and make video consultations impossible in some cases. Additionally, not all patients have access to technology that can support virtual consultations.
- Loss of personal touch: While telemedicine enables virtual connections, there is still a missing element of the human touch that can be vital in the doctor-patient relationship.
- Difficulties in examining patients: In some cases, telemedicine consults may be inadequate for diagnosing certain conditions, as physicians might need to physically examine a patient or run specific in-person tests.
- Privacy concerns: As with any digital platform, telemedicine raises potential concerns over data privacy and breaches of patient confidentiality.
Utilizing certain resources that facilitate easy access to healthcare provider information can help optimize telemedicine and help with some issues. The NPI Registry is a helpful tool to find and verify National Provider Identifier (NPI) numbers of medical professionals, which can support seamless communication and coordination between healthcare providers during telemedicine consultations.
Impact on Medical Professionals and Patients
Telemedicine is benefiting medical professionals in various ways, with some of the most significant impacts on patient care being increased collaboration, streamlined patient management, and continual education opportunities. Telemedicine allows healthcare providers to share their expertise and collaborate with their peers more effectively, all without having to be in the same room. This can lead to better diagnosis and treatment options for patients. With remote monitoring and virtual consultations, doctors can manage their patients more efficiently, which can free up time for medical professionals to focus on more complex cases in person. Telemedicine creates opportunities for medical professionals to broaden their knowledge and skills through remote conferences, online workshops, and consultations with experts in different fields.
For patients, telemedicine has both its pros and cons. Telemedicine provides patients with a more interactive experience, as they can ask questions, share concerns, and get immediate feedback from their doctors. With telemedicine, patients have easier access to their medical records, test results, and care plans, which can empower them to take a more active role in their healthcare journey. On the downside, some patients might feel uncomfortable with the technology aspect of telemedicine or might not have access to the necessary resources to fully utilize it.
Disease Management and Emergency Care
Telemedicine has the potential to greatly improve chronic disease management by offering remote consultations, monitoring, and education for patients. This can help reduce hospital admissions and allow patients to better manage their conditions, improving their overall quality of life. By allowing patients to be more proactive in their healthcare, telemedicine can help reduce the burden on healthcare systems and ensure that those with chronic diseases receive the support they need to live healthier lives.
In emergency care settings, telemedicine can play a crucial role in providing rapid diagnoses and treatment plans, thereby potentially saving lives. With the support of telemedicine, emergency medical professionals can consult with specialists remotely and quickly make informed decisions, even in time-sensitive and critical situations. This can prove to be especially valuable in rural or remote areas where specialist care is not immediately available.
Addressing Health Disparities
Telemedicine has the potential to address health disparities experienced by underserved or vulnerable populations. By increasing access to healthcare services for those who might face geographic, financial, or other barriers, telemedicine can help promote health equity and improve the quality of care for all communities. This can lead to a more inclusive healthcare system and work towards reducing health disparities across the world.
Overall, the impact of telemedicine on patient care includes increased accessibility, better collaboration between medical professionals, cost efficiency, and an enhanced healthcare experience for patients. While telemedicine has its drawbacks, its potential to improve patient care is undeniable, and its future implications could further revolutionize the world of healthcare.