Nigeria is currently Africa’s most populated country. With a population of over 186 million people according to date from 2016, the country is no Though blessed with beautiful people.
Also, it is a nation with diverse ethnic groups and over 380 languages, as well as a broad range of religious and cultural beliefs and practices.
Asides, these undeniable qualities of Nigeria, it is also a developing country that is faced with several health problems. In this article, we will be discussing the most common diseases that plague Nigeria today.
Knowing the 12 most common diseases in Nigeria will equip visitors with all the health information they need to survive during their visit to Nigeria.
It will also be helpful to residents as they get to know which illnesses are widespread and the vital steps they must take to stay safe and healthy.
1. Malaria
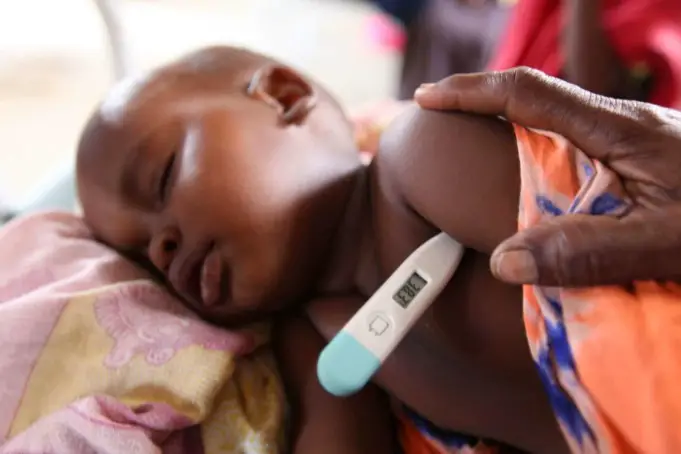
Malaria is a widespread illness in Nigeria. While there is a cure for this illness, it can still be deadly in some cases and is not restricted to any specific part of the country.
Malaria is a mosquito-borne disease that is caused by the plasmodium parasite. Just like every other condition, sickness has its symptoms, and they include:
- Headaches
- Nausea
- Chills
- Profuse sweating
- High fever
Malaria is so prevalent in Nigeria that it accounts for up to 60% of the outpatient visits in the Nigerian medical sector, 11% of maternal mortality, and an alarming 30% of childhood deaths.
As many as 100 million cases of malaria are reported annually, and more than 300,000 deaths are recorded in Nigeria per year. As earlier mentioned, malaria is a treatable condition, but it remains a fatal medical condition. Mosquitos thrive in dirty environments with bushes stagnant water.
Most rural areas in Nigeria (which is home to approximately 3% of the country’s population) are highly prone to a malaria infection outbreak.
Thankfully, the global healthcare community has taken steps to curb the spread of malaria via the Roll Back Malaria (RBM) initiative, insecticide-treated net distribution (ITN), and the topical disease research (TDR).
In spite of the efforts as mentioned above, the fight against malaria is yet to end. Several factors have contributed to the spread of disease in Nigeria, and they are:
- Presumptive treatment and self-medication by patients
- Incorrect diagnosis of patients
- Lack of access to primary healthcare facility in rural areas
- Inadequate drainage facilities and environmental hygiene
There is a need for the government to take more proactive steps to combat this common disease in Nigeria.
2. Lower respiratory infections
Lower respiratory infections are rarely discussed, but they are common in Nigeria and can be life-threatening if not treated early. The name this condition popularly goes by is pneumonia, and it includes infections like acute bronchitis and lung abscess.
The symptoms of lower respiratory include weakness, shortness of breath, sore throat, fatigue, cough, and fever. The infection is caused by smoking and infection of the lung alveoli. A respiratory infection has earned its place as the second leading cause of death in Nigeria.
3. Perinatal conditions
Perinatal conditions are the events that occur around the time of childbirth. It is no secret that birth is one of the many wonders of the world, and it is cherished by both the young and old.
However, the events and changes that occur from conception to delivery can be quite unpredictable. Out of every five hundred thousand pregnancy-related deaths that occur around the world, Nigeria records as many as forty thousand cases.
According to data from the national population commission, as many as one hundred and forty pregnancy-related deaths occur in Nigeria daily. This data makes Nigeria the country with the second-highest pregnancy-related death rate after India.
When viewed from a global standpoint, we can say this is a massive proportion. It has, however been discovered that the majority of the pregnancy-related death cases in Nigeria occur as a result of primary conditions: sepsis, hemorrhage, a complication from successful or attempted abortions, eclampsia. All of these can be prevented.
4. Cerebrovascular disease or accident stroke
The term, the cerebrovascular disease makes the sound too complicated for a condition popularly called stroke in Nigeria.
This condition occurs as a result of blocked blood supply to a specific part of the brain due to blood vessel rupture called hemorrhagic or Ischaemic stroke, respectively.
If there is an interruption in the blood flow, for more than a few minutes, the brain cells start to experience irreparable damage which could cause permanent damage.
5. Diarrhoeal Diseases
Diarrhoeal is a prevalent disease that has led to the death of thousands of people in third world countries.
It is also the second major cause of death in children below the age of one worldwide. According to data by the WHO, the number of deaths caused by Diarrhoeal disease has cumulated to 173,878, which is 10.19% of the total reported death cases.
The age-adjusted rate is a total of 101.48 per every 100,000 people in Nigeria. This data puts Nigeria on the 19th spot of countries around the globe with the highest mortality rate due to Diarrhoeal disease.
6. Measles
A lot of people are not aware that measles is a contagious respiratory disease. Measles is known to affect as high as 90% of people who share the same living space with an infected person at any given time.
Measles kills as many as 22 people per hour or up to 197,000 individuals around the globe every year. Measles remains one of the leading cause of death in children below the age of 5. The availability of vaccines may seem like a lasting solution to the spread of this condition.
However, this disease continues to spread as a result of poverty, lack of information, and poor education, and also lack of access to primary health facilities.
Nevertheless, there has been a recorded drop in the rate of measles spread by up to 74% in the last one and a half-decade. Thousands of lives in Nigeria as lost to measles despite the drop in spread rate.
7. Tuberculosis (TB)
We mostly see cases of people with tuberculosis on television, but this disease caused by a bacterium known as Mycobacterium tuberculosis is more common than you can guess.
According to the WHO, an estimated one-third of the world’s population had TB. Also, one person in the world gets a new TB infection per second, especially in Africa. Nevertheless, getting a TB infection does not mean that there will be a manifestation of the disease.
An infected person will become symptomatic if he or she has any debilitating condition or illness that suppresses the immune system such as HIV/AIDS, poorly managed diabetes, or malnutrition. TB stands next to HIV/AIDS in terms of the number of deaths it has caused around the world, and in Nigeria.
8. HIV/AIDS
The first case of HIV/AIDS was recorded in the 1980s, and it has continued to cause several deaths around the world until today.
While several studies have been carried out in search of a cure for this deadly disease, no treatment has been approved and made assessable to the public. Thankfully, there have been sensitizations and free clinics for patients and the general public, as well as the distribution of ARDs to help people manage the condition.
There have been as many as 239,700 recorded HIV/AIDs deaths in Nigeria so far. This accounts for more deaths than any Ebola outbreak in the world.
9. Yellow fever
Yellow fever is an illness caused by a virus of the flavivirus genus. Just like malaria fever, yellow fever is carried by mosquitoes, but a specific type of mosquitoes.
An unusual tropical mosquito spreads the yellow fever condition with its nasty bites, injecting the virus into a victim’s blood which then takes abode in the person’s lymph nodes.
The virus is later released into the blood after 3-6 days, making the person fall sick and manifest symptoms such as reddish rash, headaches, fever, and a cold.
In about half cases of yellow fever, it is impossible to save a victim. A yellow fever vaccine is available, and immunity to the disease can last up to 10 years once vaccination is done.
10. Dengue fever
Dengue fever is an acute transmissible condition that is also known to be viral. Nigeria, unfortunately, has to deal with the existence of this condition amongst some of its citizens.
The symptoms of dengue fever include rash, fever, lethargy, arthralgia, myalgia, and even enlarged lymph nodes. There are cases of dengue fever that transform into a Haemorrhagic condition
At present, there is yet to be a way to combat or treat this medical condition, neither is there a vaccine for it, but it remains non-life-threatening.
However, note that a tropical hemorrhagic fever may be deadly as it is an acute form of the dengue fever illness and can lead to severe bleeding that affects both children and young people.
11. Meningitis
Just like tuberculosis, meningitis is a fatal disease if not treated early enough. Meningitis is responsible for up to 5% of the total deaths recorded in Nigeria annually.
Meningitis is transmitted easily in densely populated places and can lead to severe brain damage in patients. Although there is a vaccine for meningitis, it is very costly, and low-income earners cannot afford it. Also, it is difficult to find hospitals with the vaccine readily available.
12. Polio
Polio is one disease that Nigeria can boast of overcoming. There was an outbreak of this deadly disease in 2016, but with free vaccination and public awareness, the spread was contained, and the plague was eradicated from the country. Polio was one of the most common diseases in Nigeria
There are 12 of the most common illnesses and diseases in Nigeria. Do not hesitate to leave a comment below if you found this article helpful.