Cushing syndrome, otherwise known as hypercortisolism, is a disorder that is caused by the presence of too much Cortisol in the body. When there is too much Cortisol in the body or when the body has been exposed to high levels of Cortisol for an extended period, then the body would likely develop this disease.
This condition may sometimes be caused as a result of the oral intake of the drug corticosteroids; however, it may also be as a result of the excess production of Cortisol in the body.
Cortisol is a hormone that is secreted by the adrenal glands. The adrenal glands are two glands that sit like a cap on the kidneys. When the body is under severe stress, the adrenal glands, after receiving a signal from the brain, secretes Cortisol to help the body adjust and maintain homeostasis.
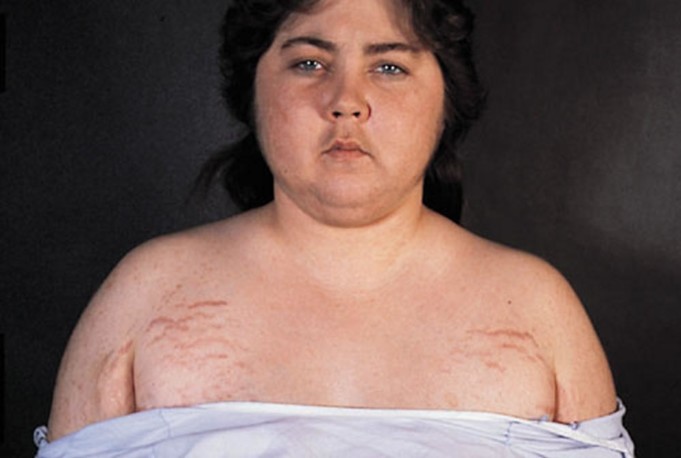
When there is too much Cortisol in the body, the body will give some signs such as the sudden development of a fatty hump which can be found in between your shoulders, the presence of pink or purple stretch marks on the skin as well as a rounded face.
Sometimes, a person who has Cushing syndrome can also have high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus type 2, and atrophy of the bones. All these signs are collectively known as the hallmark signs of Cushing syndrome.
Causes
Generally, Cushing syndrome is caused by the oversecretion of the cortisol hormone. The adrenal glands produce the cortisol hormone. Cortisol is responsible for the regulation of several processes in the body, such as blood pressure levels.
Also, Cortisol is responsible for the reduction of inflammation and helps to keep your heart as well as your blood vessels in a steady working condition. Cortisol is responsible for helping your body respond appropriately to stress.
Also, one of the functions of Cortisol is to help you convert proteins, carbohydrates, as well as fats into useable units that the body can utilize for energy and other metabolic processes.
Cortisol also helps the body to balance the levels and effects of insulin in the body.
Although Cortisol helps regulate a lot of processes in the body, when Cortisol is too high in the body, it causes the person to develop Cushing syndrome. Cushing syndrome can be caused as a result of the following:
1. The use of corticosteroids
One of the common causes of Cushing syndrome is the excessive use of corticosteroids. Some corticosteroids, such as prednisone which is an anti-inflammatory drug that is often used to treat inflammatory diseases such as lupus.
Some corticosteroids are commonly used to prevent any post-transplant problems, such as the rejection of an organ. Once these drugs are used in high doses, it can cause Cushing syndrome.
The type of Cushing syndrome, which is caused by the injection of corticosteroids, is often known as exogenous Cushing syndrome. Asides the infusion of such drugs, the ingestion through oral means over an extended period can cause several problems.
Oral corticosteroids are often prescribed by doctors to treat certain diseases lupus, asthma as well as rheumatoid arthritis. The role of prednisone and other corticosteroids is to mimic and produce the same effects that corticosteroids have on the body.
However, the body still produces Cortisol, and the required use of corticosteroids to treat certain inflammatory diseases is high. This, therefore, causes an increase in the levels of Cortisol and, as such, leads to one of the side effects of using corticosteroids, which is the development of Cushing syndrome.
2. The overproduction of Cortisol by the body
Cushing syndrome can sometimes be as a result of the malformation in your body. This means that some diseases in your body can result in the overproduction of Cortisol by the adrenal glands.
When the body is the one responsible for the overproduction of Cortisol, it causes a type of Cushing syndrome, which is known as endogenous Cushing syndrome. When one or both of the adrenal glands starts to malfunction or when the body overproduces the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which is responsible for the regulation of the cortisol hormone, it causes Cushing syndrome.
There are certain conditions that can result in the overproduction of Cortisol by the body. They include:
1. Pituitary Adenoma
Pituitary Adenoma occurs when there is a tumor on the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland, which is usually known as the master gland, is situated at the base of the brain is a small pea-sized gland that is mostly responsible for the regulation of many body processes.
When there is a benign (non-cancerous) tumor that presses against the pituitary gland, it causes the excess production of the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). ACTH is what is responsible for the stimulation of the adrenal glands, which in turn causes the production of Cortisol in the body.
When there is an excess production of ACTH, the adrenal glands will become overstimulated and, as a result, causes the over-production of Cortisol, causing the levels in the body to increase, causing Cushing syndrome.
Pituitary Adenoma is mostly seen in women, and it is the most common form of endogenous Cushing syndrome.
2. An ACTH secreting tumor
Typically, only the adrenal glands produce Cortisol, and only the pituitary gland produces the adrenocorticotropic hormone. However, in some rare cases, there are some tumors that can cause other organs to begin to produce the ACTH hormone, which in turn stimulates the adrenal gland to produce excess Cortisol cause Cushing syndrome.
The tumors which are often called ectopic tumors can be both benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous), and they are usually found either in the thymus gland, the thyroid gland, the pancreas or in the lungs.
3. Presence of a primary Adrenal disease
In this case, the problem son coming from a disorder with the pituitary gland or with the production of adrenocorticotrophic hormone(ACTH). Instead, the problem is with the adrenal glands.
In this case, people who have this kind of condition are known to have adrenal adenoma. People who have adrenal adenoma have Cushing syndrome, which isn’t as a result of the overproduction of ACTH; instead, the adrenal cortex is where the tumor is located.
These tumors can be benign or non-cancerous, which are known as adrenal adenoma, or they may be cancerous, causing adrenocortical carcinomas, although the cancerous ones are rarely seen. Adrenocortical Carcinomas are rare and can cause Cushing syndrome.
4. Familial Cushing Syndrome
Although it is rare to inherit Cushing syndrome directly, however, it is entirely possible to develop tumors that affect the endocrine glands. Some people can have tumors in more than one of the endocrine glands.
Once this occurs, it can cause a spike in the levels of Cortisol, resulting in Cushing syndrome.
Symptoms
The signs and symptoms experienced by a person who has Cushing syndrome are based on how much Cortisol the person’s body has been exposed to. This means that the severity of signs experienced differs from one person to another.
However, the most common symptoms experienced by patients who have Cushing syndrome include;
- Increase in weight
- Deposits of fats, especially around the abdomen and the upper portion of the back. Also, the patient may see deposits of fats around the face causing the person to have what is called moon face, as well as deposits of fats around the shoulder forming shoulder humps(also called buffalo humps)
- Presence of purple or pink stretch marks visible on the skin of the thighs, the abdomen, arms as well as the upper portion of the breast.
- Fragile skin causing the skin to break easily, forming injuries
- The patient will experience slow healing of cuts and bruises, as well as insect bites and infections
- The presence of acne
- Muscle weakness
- Severe fatigue
In addition to these common symptoms, there are other signs that a patient might experience, which is not common among others. These symptoms are severe, and they include:
- Increased blood glucose levels
- Severe dehydration
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Osteoporosis: This means that the patient is experiencing severe bone loss, which can lead to unusual bone fractures.
- Hypertension characterized by an increase in the patient’s blood pressure
- Mood swings
- Severe anxiety
- Frequently occurring headaches
- The patient becomes easily irritable.
- An increased rate of frequently occurring infections
- Depression.
The symptoms in children are slightly different than those in adults. Research shows that children also develop Cushing syndrome, although it isn’t as common as in adults. Records of a 2019 study show that every one in ten adults develops Cushing syndrome every year.
Children who have Cushing disease will experience unexplainable weight gain and possible obesity, as well as an increase in blood pressure and a reduced growth rate.
Symptoms of Cushing syndrome in women
In women, on the other hand, Cushing disease has been seen to be more prevalent. According to the National Institute of Health (NIH), women tend to have higher chances of developing the disease more than men.
In other words, every 1 in 3 women to men ratio has the Cushing syndrome. Women who have Cushing syndrome experience the overgrowth of hair on the face, abdomen, chest, neck as well as on their thighs.
The abnormal growth of hair in all these places is known as Hirsutism.
Some women may experience an abnormal menstrual cycle, while others who have the syndrome may not experience the menstrual cycle.
Symptoms of Cushing syndrome in men
In men, alongside the general symptoms they may experience, they will also experience some other symptoms such as erectile dysfunction, decreased fertility, a loss of sexual interest, or low sex drive.
Some men may also experience loss of emotional control as well as increased pigmentation on their skin as well as brittle bones causing their bones to fracture easily.
Diagnosis
Cushing syndrome can sometimes prove to be a difficult disease to diagnose. However, your health care provider may require you to undergo the following tests in order to diagnose the cause of excess Cortisol in the body.
1. Blood Adrenocorticotropic hormone levels test
This test simply measures the level of ACTH in your blood. A decreased level of ACTH and an increased level of Cortisol indicated that there is a problem with the adrenal glands. More often than not, a tumor on the adrenal cortex of the adrenal glands is usually the culprit.
2. Corticotropin-releasing hormone(CRH) stimulation test
In this test, a shot of CRH is administered to the patient, if it causes a rise in the levels of ACTH and Cortisol, it is an indication that the patient has a tumor in the pituitary gland.
3. High-Dose dexamethasone suppression test
This test is also known as the low dose test; however, in carrying out this test, a higher dose of dexamethasone is administered. If the level of Cortisol drops, then it means that you may have a pituitary gland tumor. However, if it doesn’t fall, it merely means that you may have an ectopic tumor.
4. Petrosal Sampling diagnosis
In this kind of test, blood is drawn from two veins; one from the vein close to the pituitary gland and one from the vein far away from the pituitary gland. After the blood has been drawn, a shot of Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) is then administered.
If there are increased levels of ACTH in the blood present within the vein, it indicates that the pituitary gland has a tumor present in it.
However, if the levels of ACTH are increased both in the blood present in the vein close to the pituitary gland and in the blood that is present within the veins that are far away from the pituitary gland, it indicates that you have an ectopic tumor.
5. The use of Imaging studies
This includes the use of CT scans as well as Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), which are used to check the pituitary and adrenal glands for the presence of any tumors.
Treatment
Cushing syndrome is a disease that has to do with the increase of Cortisol in the body. To treat this disease, your doctors need to reverse and lower the level of Cortisol in your body, and this can be done in several ways.
However, the treatment of Cushing syndrome depends on what is causing the rise of Cortisol in your body. Some drugs may be targeted at the adrenal glands in order to reduce the amount of Cortisol that is produced, while other drugs may target the pituitary gland where ACTH is being produced.
Some of the drugs you may be given include Ketoconazole(also known as Nizoral), Mitotane(lysodren), Metyrapone(Metopirone), Signifor, and so on. If you are on any corticosteroids, you may require a change in dosage.
If your Cushing syndrome is as a result of a tumor, you may require surgery to remove it. In some cases, the tumor may be benign, meaning it is non-cancerous. However, in cases where the tumor is malignant, and it can’t be removed, you may require chemotherapy or radiation therapy to help shrink cancer.
Complications
If one who has Cushing syndrome and doesn’t go for treatments, some difficulties may arise, such as:
- Osteoporosis: Osteoporosis is caused by unexplainable bone loss, and it can lead to unusual bone fractures such as the fractures of the rib as well as fractures of the bones of the feet.
- Hypertension which is characterized by a steady increase in blood pressure.
- Diabetes Mellitus type II
- Unusual infections which may occur frequently
- Muscle wasting and atrophy which is characterized by loss of muscle mass and well as severe muscle weakness.
References;
- Cushing Syndrome; Mayoclinic
- Cushing Syndrome; Healthline