Meningitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cords; this rare infection affects the delicate membranes that cover and protect the brain and spinal cord. There are several types of meningitis:
Bacterial meningitis is caused by bacteria; it happens when bacteria enters the bloodstream and travel to the brain and spinal cord and cause acute bacterial meningitis.
It can also occur when bacteria directly invade the meninges (that is the membranes around the brain and spinal cord); a skull fracture, surgeries, an ear or sinus infection can cause this.
There are several strains of bacteria that can cause acute bacterial meningitis and blood poisoning and the common ones are:
- Listeria monocytogenes (listeria): This bacterium is found everywhere, it can contaminate food and when taken in can cross the placental barrier and cause complications for both the mother and the baby.
- Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus): This is the most common cause of bacterial meningitis and it is caused by pneumonia, ear or sinus infection.
Haemophilus influenzae (haemophilus): This is the leading cause of bacterial meningitis in children but the cases have been reduced due to Hib vaccines.
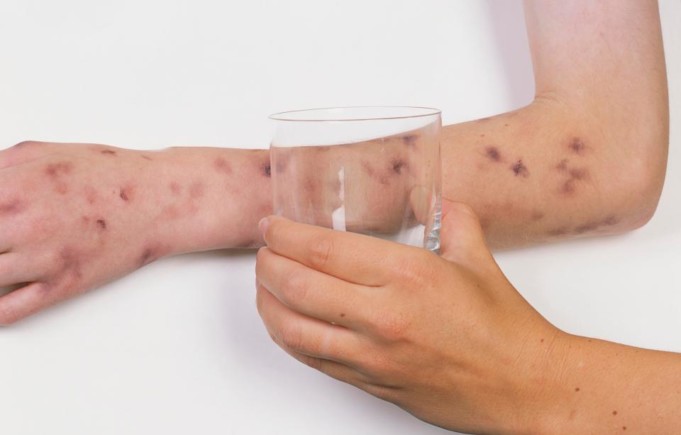
Neisseria meningitidis (meningococcus): This is another leading cause of bacterial meningitis; this same organism is also responsible for infection of the upper respiratory tract; meningitis caused by this microbe is highly contagious, this is the type of meningitis infection that affects mainly teenagers and young adults. It may cause local epidemics in college dormitories, boarding schools and military bases.
It spreads among people that are in close contact with one another and it can be life threatening.
Viral meningitis is caused by a group of virus called enteroviruses; patients can recover completely without treatment and it is less severe than bacterial meningitis. It is common in late summer and early fall. Other viruses that can cause meningitis are simplex virus, HIV, mumps, West Nile virus.
Amebic meningitis is a rare and devastating type of meningitis; this type is characterized by infection of the brain, it is caused by the microbe Naegleria fowleri, which is a free living microscopic ameba that lives in the soil and warm water.
Fungal meningitis is a rare form of meningitis; it often mimics acute bacterial meningitis and it can cause chronic meningitis, it happens in people who have weakened and compromised immune system like adults over the age of fifty five.
Parasitic meningitis is caused by parasites and it is assumed or diagnosed when eosinophils are predominant in the cerebrospinal fluid. Parasites responsible for these are Angiostrongylus, cantonensis, Gnathostoma, spinigerum and Schistosoma.
Other meningitis are caused by chemical reactions, drug allergies, some types of cancer and inflammatory diseases such as sarcoidosis.
Symptoms of meningitis are sudden high fever, stiff neck, severe headache that is different from normal, nausea and vomiting accompanied by headache, difficulty concentrating and confusion, seizures, skin rash, lack of thirst and appetite, light sensitivity, hypersomnia or difficulty waking.
Meningitis can also affect newborns and signs of meningitis in newborns are high temperature, constant crying, stiffness in a baby’s body and neck, poor intake of food, sluggishness or inactivity, and a bulge in the soft spot on top of the baby’s head, excessive sleepiness or irritability.
It is highly advisable to see a doctor immediately any of these signs and symptoms is noticed if not it can lead to undesirable health complications like hearing loss, memory loss and difficulty remembering, learning disability, seizures, shock, kidney failure, brain damage, gait problems and death.
Meningitis can be prevented by
- Regular washing of hands to help prevent the spread of germs. Children should be taught to wash hands before and after eating, after using the toilet, after petting animals or being in public and crowded place; they should also be taught how to vigorously and thoroughly wash their hands.
- Covering the mouth and nose when you cough or sneeze; because these viruses and bacteria that cause meningitis can spread through coughing and sneezing.
- Practicing good hygiene; straws, eating utensils, lip balms or toothbrushes should not be shared with anyone, kissing or sharing a cigarette can also spread meningitis.
- Eat healthy foods, with lots of fruits and vegetables to help your system fight and overcome any infection or germs that enters your body.
Those at risk of meningitis are children under the age of five and adults over the age of 55 due to a weak immune system.
If reported early to a medical doctor, meningitis can easily be controlled and arrested and stopped from spreading and causing further harm or destruction in the body, especially blood poisoning when it is caused by a bacterium.
Recently, the Minister of Health Isaac Adewole has warned Nigerians to protect themselves against meningitis as the federal government has no enough vaccine to go round for everybody.