Scabies is a skin infestation caused by a mite referred to as the Sarcoptes scabiei. When left untreated, the microscopic mites can survive and live on your skin for many months. They stay on the surface of the skin, burrow into it, and then lay eggs.
This process causes the skin to itch and form a red rash on the skin. There are approximately 130 million cases of scabies globally at any given moment.
Scabies is not a sexually transmitted disease, even though it is a highly contagious condition that can quickly be pass from one person to another via direct skin contact. Mite infestation can also be transmitted through bedding or clothing, although intimate contact isn’t completely necessary.
Although scabies can be troublesome, they aren’t untreatable. Treatment usually involves medications that can kill scabies mites and the eggs they produce.
Because scabies is easily contacted, doctors generally advise treatment for a while group of people who have had contact with a person with scabies.
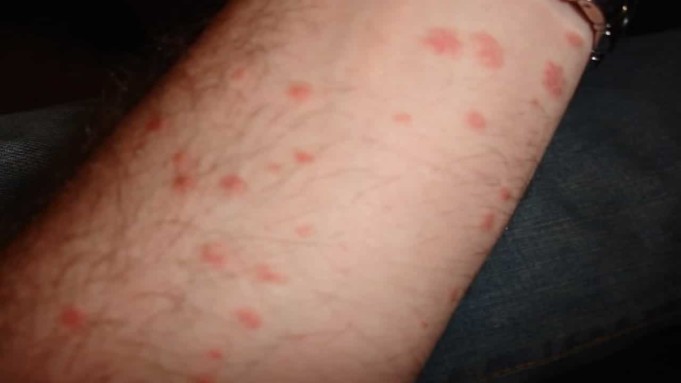
Symptoms
It can take up to six weeks or more for symptoms to manifest after the first contact with scabies. Scabies symptoms usually develop quickly in patients who have experienced scabies before.
The significant symptoms of scabies include itching and rash that can get worse at night. Continuously scratching the affected area can lead to sores that get infected.
When this happens, addiction treatment may be recommended, which includes using antibiotics for the infection.
General sites for scabies in adults and older children include the:
- Wrist
- Armpit
- Elbow
- Penis
- Buttocks
- Waist
- Nipple
- Areas between our fingers
Scabies affecting babies and toddlers, as well as the elderly or the immune-compromised, can include the;
- Face
- Head
- Hands
- Neck
- Soles of the feet
Rashes could consist of hives, tiny bumps, bumps, or pimple-like bumps on the skin. The burrow tracks caused by the mites can often be seen on the skin. They may look like tiny discolored or raised lines.
Causes
Scabies is caused by an infestation of small, eight-legged mites. These tiny bugs are so puny; it’s impossible to see them on your skin; you can only feel their effects.
They would typically burrow into the top layer on your skin tissue where they’d live and feed there. While they reproduce and pass out waste, your skin reacts and begins to develop an itchy, red rash.
Mites can be passed quickly from one person to another. Direct skin-to-skin contact is still the most common method of sharing the infestation. Infestation can also happen through;
- Bedding
- Furniture
- Clothes
Infestation can spread quickly, especially in places where people live in close contact with each other. These may include extended-care facilities or nursing homes.
Treatment
Treatment for scabies involves eliminating the infestation with creams, lotion, and prescription ointments that can be applied directly to the skin. You also have the option of oral medications.
Your healthcare provider will probably instruct you on how the medication is applied at night. This is when the mites are most active. Treatment may be done from the skin on the neck down. Any form of medicine used can later be washed off the next morning.
Ensure to follow your doctor’s advice on how to apply the treatment. Treatment may last up to seven days.
Some medications used to treat scabies May include:
- 5% permethrin cream
- 25% benzyl benzoate lotion
- 10% sulfur ointment
- 10% crotamiton cream
- 1% lindane lotion
Your medical doctor may also have to prescribe medications that can help to relieve some of the troublesome symptoms linked with scabies. Medications usually include:
- Steroid creams to relieve itching and swelling
- Antihistamines, such as Benadryl (diphenhydramine) or pramoxine lotion can be administered to help control itching
- Antibiotics to kill infections that are caused by continually scratching the skin
More intense treatment may be required for severe or widespread scabies. Oral tablets such as ivermectin (Stromectol) can be taken by people who;
- Are experiencing crusted scabies
- Aren’t seeing any improvement in symptoms after prior treatments
- Have scabies covering significant parts of their body
Sulfur is also a major ingredient that’s used in many prescriptions for the treatment of scabies. You can buy some over the counter and use it as ointment, liquid, shampoo, or soap to treat scabies.
It’s essential to note that the FDA doesn’t approve of any over-the-counter scabies treatment. Consult with your doctor to recommend the best treatment for you.
Symptoms may seem to get worse during the first week of treatment. Nevertheless, after the first week, the itching becomes reduced, and scabies should be completely healed by the fourth week. Also, note that “post-scabies” itch can last for a month.
Fix a doctor’s appointment if you are still experiencing symptoms of scabies after treatment has gone for four weeks.
Natural treatment
Several traditional scabies treatments can cause unneeded side effects like redness, burning sensation on the skin, swelling, tingling, or even numbness. While these side effects are temporary, they can be very uncomfortable.
Some natural treatments for scabies may include:
Tea tree oil
Some studies show that tea tree oil may be used in the treatment of scabies, and at the same time, easing itching and eliminating rash. Unfortunately, it doesn’t work so well on mites that are burrowed deep into the skin.
Aloe vera
Aloe Vera gel is known to have properties that help with burning and skin irritations. But still, Aloe Vera was as successful as a prescription treatment at treating infections like scabies. Ensure to buy pure Aloe Vera and not Aloe Vera-infused products.
Essential oils
Natural bug killers like clove oil can be be used to kill mites. Other essential oils, including lemongrass, lavender, and nutmeg, could be useful in treating scabies.
Capsaicin cream
Although this doesn’t kill mites, capsaicin creams may help to relieve itching and pain by desensitizing your skin to the bothersome bugs and bites.
Soaps
The neem tree has active properties that can be gotten from its bark, leaves, and seeds, and can be used to kill scabies-causing mites. Creams, oils, and soaps made with the neem tree’s extract may be used to kill stubborn mites.
Using home remedies in treating scabies has shown some promise for both killing mites and relieving symptoms of infestations. But be sure to do some research on these natural remedies before trying out any.
Is scabies contagious?
Yes, scabies is very contagious. The spread of scabies can occur in the following ways:
- Prolong contact of the skin
- Sharing towels, clothing, or bedding that have been used by people with scabies infection
- Intimate contact with a person with scabies infection
Because the transmission of scabies is mostly through direct contact, the infestation is easily passed on to sexual partners, friends, family members. Places that scabies can quickly be spread also include;
- Prisons
- Schools
- Nursing homes
- Sport locker rooms
- Rehabilitations facilities
Types of scabies
The only type of mite that causes scabies infection is known as Sarcoptes scabiei. Nevertheless, Sarcoptes scabiei can create many types of infestations.
Typical scabies
This is the most common type of infestation. Typical scabies causes an itchy rash on the wrists, hands, and other areas on the body. It, however, doesn’t affect the face or scalp.
Nodular scabies
This may develop as severe itching, raised bumps, or lumps, mostly in the genital areas, groin, or armpits.
Norwegian scabies
This is another form of scabies that’s very severe and can be very contagious. It is also known as crusted scabies, as people with this type of infestation have thick crusts formed on that skin. These crusts have several thousands of kites and eggs in them.
Norwegian scabies can also appear as:
- Gray
- Thick and
- Crumbles easily when touched
This usually develops in individuals with weakened immune systems. This can include people with HIV or AIDS, people who are on steroids or specific medications, or people undergoing chemotherapy.
Scabies causing mites not only overpower the immune system, but they can multiply very quickly. Crusted scabies is able to increase at the same rate as normal scabies.
Prevention
The most effective way of preventing scabies is by avoiding direct skin-to-skin contact with people who have scabies. You would also want to avoid unwashed clothes that have been worn by people with scabies.
Scabies mites can survive for three to four days away from their host, so certain precautions need to be taken to prevent another infestation.
Ensure to wash all bedding, clothing, pillows, towels in hot water, reaching up to 122°F (50°C). Then they need to be dried for at least 30 minutes on an increased heat in the dryer.
Items that can’t be washed would have to be properly vacuumed. After vacuuming, expel the vacuum bag using hot water and bleach. Hot water and bleach can also be used to clean areas that contain scabies mites.
Who can be infected by scabies infestation?
Anyone can be infected by scabies. Mites don’t distinguish between races, sex, income levels, or social classes.
Mites infestations don’t have anything to do with a person’s level of personal hygiene either. Mites simply need a place to stay, and they can burrow into any skin.
Individuals who stay in close, crowded places, like prisons or dormitories, can be easily infected by scabies. This is because the infestation is easily contagious and can be transmitted through contaminated surfaces, such as furniture.
This is why babies and toddlers may quickly contact scabies. Crusted scabies can easily affect older adults, especially people with a weak immune system.
Diagnosis
By performing a simple examination and inspecting the affected parts of all the skin, your doctor will be able to diagnose scabies accurately. In most cases, doctors may need to confirm the diagnosis by extracting more using a needle.
Your doctor would have to scrape off a small portion of the skin to get some tissue sample if finding a mite is difficult. After that, the sample would be examined using a microscope to check for the presence of scabies mites.
How long does scabies last?
Scabies mites can survive on a person’s skin for up to two months. When the mites are outside a person’s body, they commonly die within three to four days.
If a person is treating scabies, burning, and itching caused by the rash can last for many weeks after treatment commenced.
This is because the mite wastes and eggs are still buried in the skin after the mites are dead. A person may still experience irritation and rash until a new layer of skin is grown.
If you notice any odd-looking patches on your skin, then you have to go see your doctor. Try as much as possible to complete your medications if given any, and ensure to take necessary measures in spreading the mites.
Have you ever experienced scabies infestation? What measures did you take in controlling the spread? What treatment methods did you use in controlling the infestation? Share with us in the comments below.