PPE is an acronym that stands for personal protective equipment. It is an equipment that is designed to protect the user against safety or health risks at work.
It can include essential items such as gloves, safety helmets, eye protection, safety footwear, high-visibility clothing, and safety harnesses. Respiratory protective equipment (RPE) is part of PPE.
Why is PPE necessary?
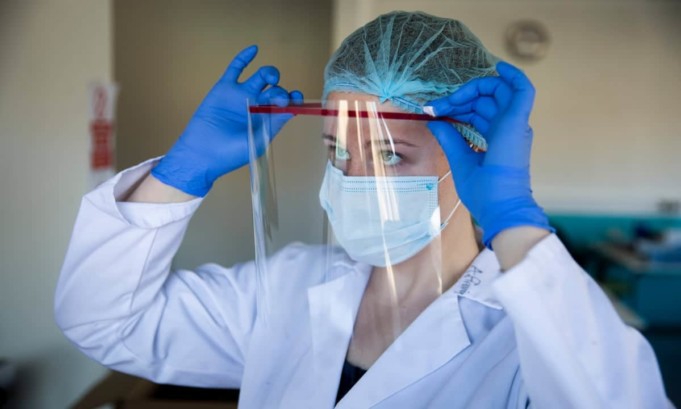
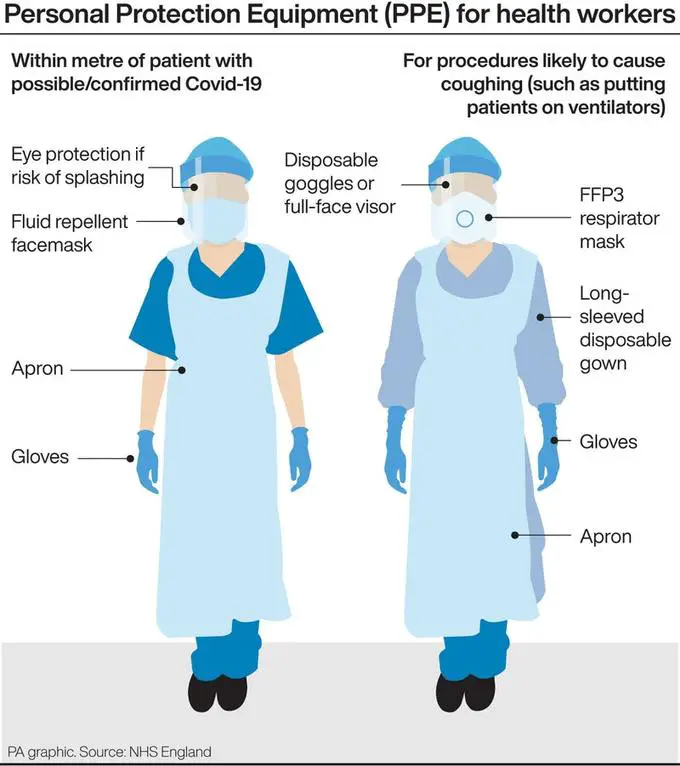
For health workers, PPE is essential in cases of highly infectious diseases such as Ebola and COVID-19. It is crucial for health workers to protect themselves while handling patients and working in high-risk environments so as not to get infected.
It is essential to make the workplace safe, and that includes providing easy to follow instructions, procedures, training as well as supervision to encourage individuals to work both safely and responsibly.
Even where the right engineering controls and safe networks of work have been applied, there are some hazards that might remain. These include injuries to places like:
- The lungs, as a result of breathing in dangerous or contaminated air
- The head and feet, as a result of falling materials
- The eyes, due to splashes or harsh or corrosive liquids or flying particles
- The skin, due to contact with corrosive substances
- The body, as a result of extremes of cold or heat
Attorneys from the Spar and Bernstein law office agree that, in the above cases, PPE is required to reduce the risk.
What do I have to do?
As a health worker, PPE is the only option for self-protection when it comes to cases of highly infectious diseases.
It should not be considered a last resort but the only resort if you must care for patients, or handle the corpse of people who died from diseases like Ebola and COVID-19.
Hospitals and centers of disease control in different parts of the work makes sure that these equipment are always available to health workers.
For construction workers and others who do not work in the health sector, only use PPE as a last option.
If there is still a need for PPE after you have implemented other controls (and there must be situations when it is, like head protection on many construction sites), PPE must be provided for your employees at no cost
You must choose all PPE very carefully and ensure that your employees are well trained to use it in the proper way, and know-how the best ways to detect and report faults
How to select and use PPE?
Before a contractor or medical facility buys PPE, it is essential to ask and answer the questions below:
- Who is exposed, and what are they exposed to?
- How long are they exposed to such dangers for?
- How much are they exposed to such dangers?
When you decide to select the PPE and use them
Choose only PPE products which are marked CE in accordance with the 2002 Personal Protective Equipment Regulations – suppliers also have the right to advise you
Choose only equipment that suits the user perfectly – consider the fit, size, and weight of his PPE. If you involve the user in the process of choosing a PPE, they will have a higher chance to use it
If you must wear more than a single PPE item at the same time, make sure that they all can be used together, for example putting on safety glasses may bother the seal of a respirator, and that will cause air leaks
Conduct training sessions on why people will be instructed and trained on how to use it. For example, you can teach people to take off their gloves without getting their skin contaminating.
Tell them why it is vital that they use it when to make use of it, and what its possible limitations are.
Other relevant advice on PPE
Never take the risk of allowing exemptions from using PPE for those jobs that do not take longer than a few minutes
Do well to check with your supplier on what options of PPE is appropriate for a specific task – explain the job to them
If you are in doubt, do well to seek more advice regarding PPE from a specialist adviser
PPE Maintenance
When not in use, it is vital that all PPE is adequately looked after and kept when they are not in use, like in a dry and clean cupboard. In some cases, you have to dispose of some PPE mainly when used by health care workers in high-risk environment.
If it is a reusable PPE, it must be thoroughly cleaned and appropriately kept in good condition.
Think about
- Making use of the correct replacement parts which fit the original, such as respirator filters
- Always ensure that you keep replacement PPE readily available
- who is responsible for the maintenance of PPE and how it is supposed to be done
- having a supply of the right disposable suits which are best for dirty jobs that require high laundry costs, eg, for visitors who have to use protective clothing
- Employees are required to always make proper use of their PPE and report any loss, destruction, or fault.
Types of PPE that you can use
PPE for Eyes
- Hazards: Metal or chemical splash, gas and vapor, dust, radiation, projectiles
- PPE for Eyes Options: Safety spectacles, face screens, goggles, face shields, visors
Important Note: Make sure that all eye protections selected has the perfect combination of impact/splash/dust/molten metal eye protection for the required task and adequately fits the user
Head and neck PPE
- Hazards: the impact from flying or falling objects, risk hair getting tangled in machinery, of head bumping, climate or temperature, chemical drips or splash.
- Head and neck PPE Options: bump caps, industrial safety helmets, hairnets and firefighters’ helmets.
Important Note: some safety helmets incorporate or can be paired with specially-designed hearing or eye protection
- Do not forget the importance of neck protection, like scarves for use in welding
- Always replace head protection in cases of damage
PPE for Ears
- Hazards: noise – a range of combinations of sound duration and level of exposure. When there are very high-level of sounds, it is a hazard even for a short duration
- PPE for Ears Options: Earmuffs, earplugs, semi-insert/canal caps
Note: provide the perfect hearing protectors for any kind of work, and see to it that all workers are aware of the best way to fit them
Select protectors that lessen noise to an acceptable level, while it allows for safety and communication.
We hope you have found this article useful. Kindly leave a comment below.
References;
- Risk at Work – Personal protective equipment (PPE); HSE
- Personal protective equipment; WHO