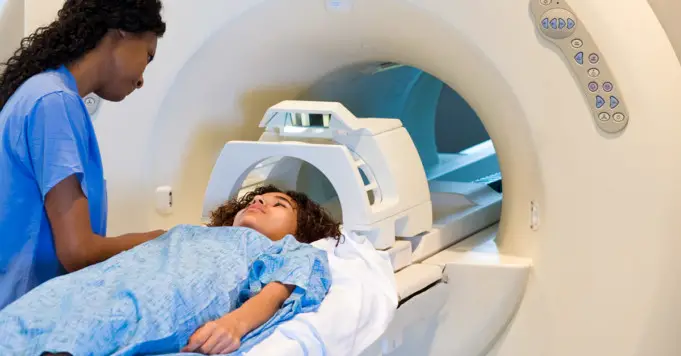
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan is a popular procedure all over the world. MRI uses radio waves and a strong magnetic field to form detailed imaging of the tissues and organs within the body.
Since MRI was invented, researchers and doctors continue to redefine MRI use to assist in medical research and procedures.
The introduction of MRI revolutionized the medical world. This article focuses on the use of MRI, how the scan works, and how doctors handle the machine.
MRI Scanning Facts
- MRI scanning is a painless and non-invasive procedure.
- Raymond Damadian created the first MRI scanner (full-body), and it was nicknamed the “Indomitable.”
- The most MRI scanner per capita is owned by Japan, with 48 MRI machines per 100,000 citizens.
- A basic MRI scanner could cost at least $150,000 but may exceed some million dollars.
What is the MRI scan?
The MRI scanning machine uses radio waves, a large magnet, and a special computer that helps to project a detailed image of internal structures and organs.
The scanner can be characterized by its tube-like structure with a table that patients can slide in. An MRI scan is different from X-rays and CT scans, as it doesn’t use potentially dangerous ionizing radiation.
Use of MRI
The invention of the MRI scan represents a breakthrough in the medical world. Researchers, scientists, and doctors can now examine the internal structure of a human body in precise details.
Examples of conditions where MRI scanner is used are as follows;
- Anomalies of the spinal cord and the brain.
- Cysts, tumors, and other complications in various parts of the body.
- Screening the breasts for breast cancer.
- Some heart problems.
- Injuries of the joints, such as the knee and back.
- Diseases of the organs, such as liver or kidney.
- To examine pelvic pain in women, that may cause endometriosis and fibroids.
The list goes on and on, as MRI technology is continuously being improved.
Preparation
The preparation required for an MRI scan is little to none. You may be asked by your doctors to change into a gown as soon as you arrive at the hospital.
Since the machine makes use of powerful magnets, you must leave all metal object fat away from the machine. You would be required by your doctors to remove all metal accessories that may interfere with the machine functions.
If a patient has shrapnel, bullets, or any metallic item inside their body, then it may not be wise to use the machine. This may also include devices, such as aneurysm clips, cochlear implants, and pacemakers.
You should inform your doctor if you suffer from anxiety or panic attacks, especially if enclosed spaces could trigger you. Medication may then be given before the examination. This medicine is supposed to help patients relax.
Sometimes, patients would be administered an injection to improve the visibility of specific tissues that are associated with the scan. By this time, the radiologist talks the patient through the procedure and answer any questions that are asked by the patient.
Once in the scanning room, the patient is helped lay down on the MRI table. The medical staff would ensure that the patient is as comfortable as possible and would even provide cushions or blankets.
Headphones or earplugs would also be provided to help block out loud sounds that the scanner produces. Anxious children can calm down by listening to music during the procedure.
During an MRI scan
Once a patient is in the scanner, the technician will use the intercom to communicate with the patient. The technicians make sure that the patient is really comfortable and wouldn’t start the examination if the patient isn’t ready.
Patients are advised to stay still so as not to disrupt the images that the machine is trying to project. It’s perfectly normal when patients hear clanging noises from the machine. Depending on what image is needed, it may sometimes be required for patients to hold their breath.
Patients can use the intercom to request that the machine be stopped if they don’t feel comfortable with the scanner.
After an MRI scan
The radiologist would examine the images after the MRI scan to determine whether more images are needed. Patients are free to go home once the radiologist says the patient is safe to go.
A report would then be prepared by the radiologist, where the result of the scan would be discussed with the patient by their doctor.
Side effects
Side effects from an MRI scan are infrequent. Nevertheless, the contrast dye may cause headaches, nausea, and burning or pain at the point of injection in some individuals.
Allergies to the contrast material may include itchy eyes or hives, but this is seldom experienced. If you are feeling some form of discomfort during the scan, immediately notify the technician.
People sometimes find it difficult to undergo the procedure, especially when they are claustrophobic or get stressed in enclosed spaces.
Function
The MRI scanner has two string magnets. These are the significant parts of the machine. The human body is mainly made of water molecules that comprise oxygen and hydrogen atoms.
Right in the middle of each bit is a smaller particle known as a proton, which acts as a magnet and reacts smoothly to any magnetic field.
Generally, water molecules in the body are aligned randomly, but when molecules are exposed to an MRI scan, they are aligned in one direction, either north or south.
Running an electric current through gradient coils, which causes vibrating in the coils to vibrate, forms the magnetic field that creates knocking sounds in the scanner.
Although changes aren’t apparent to the patients, the machine can easily detect these changes and then project them as images with the help of a computer.
(fMRI) Functional magnetic resonance imaging
Functional MRI (fMRI) or functional magnetic resonance imaging uses MRI technology to calculate cognitive activity by studying the flow of blood to certain parts of the brain.
Blood flow increases in parts where neurons are most active. This gives the technicians insight into neuron activities in the brain.
This technique has helped to revolutionized brain mapping by giving researchers access to the spinal cord and brain without any drug injections or invasive examinations. Functional MRI can be used by specialists to learn about an injured, diseased, or normal brain.
Functional MRI is also used in detecting any tissue anomalies. The scanner shows what work tissues do rather than how they appear.
Doctors assess risks of brain operations with the use of fMRI to identify regions of that perform vital functions like speaking, sensing, movement, or planning.
Functional MRI is also used to determine the effects of stroke, tumors, and brain trauma, or neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does an MRI scan take?
MRI scans can take from 20 to 60 minutes, depending on what areas of the patient’s body are being analyzed and the number of images required.
The radiologist may repeat scan if they aren’t satisfied with the images they got.
Can I undergo the scan of I have fillings or braces?
Although fillings and braces are not affected by the scan, but some images may be distorted. Your doctor would discuss this beforehand, and an additional MRI scan may be required to get clearer images.
Am I allowed to move while I am in the machine’s tunnel?
Patients must stay completely still while in the MRI scanner. The scanner may be distorted by any movement, therefore causing the images to be blurry. In cases where the scan takes long, MRI technicians may permit short breaks through the procedure.
What can I do if I am claustrophobic?
Your doctor or radiologist would talk patients through the entire examination, especially when patients are claustrophobic. Doctors or radiologist ensure that patients are calm before they can proceed with the procedure.
More-so, open MRI scanners are great alternatives for certain parts of the body to help patients with claustrophobia. Medications to ease anxiety can also be taken before the test.
Should I get an injection of contrast before my MRI procedure?
A contrast dye can be used to improve the accuracy of diagnostic by targeting specific tissues. Sometimes, patients may be required to have a contrast agent administered before the scan.
Is MRI scan safe during pregnancy?
Unfortunately, there is no direct answer to that. It is best to let your doctor know you are pregnant if it’s not yet evident. There are very few studies on the side effects of an MRI scan when a person is pregnant.
In 2016 nevertheless, guidelines that shed more light on the subject was posted
The guidelines clearly state that patients exposed to MRI during the early stages of pregnancy aren’t linked to any long-term after-effects and shouldn’t inspire any clinical concerns.
Doctors would not recommend the administration of contrast material for pregnant women. Unless the information required is very important, MRI scans should be avoided during the earliest trimester.