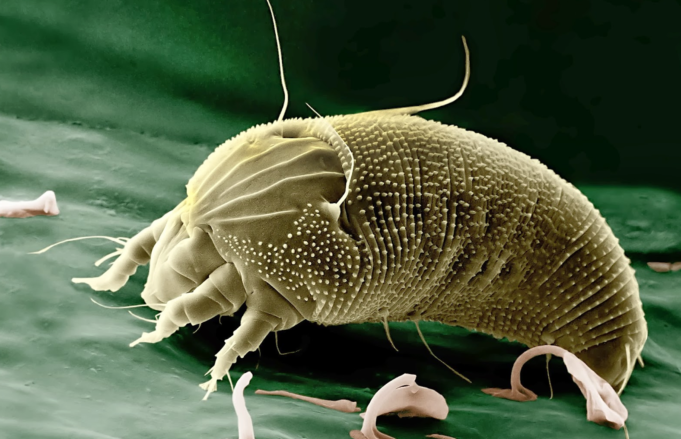
A parasite is a living organism that takes residence in another organism known as the host and often causes harms it. Parasites depend on their host for food and survival.
A parasite cannot live exclusive of a host; neither can it grow or multiply. For the sake of this dependence on a host, it is rare for a parasite to kills the host, but it is not uncommon for it to spread diseases, which may sometimes be fatal.
While some people may want to draw some similarities between other predators and parasites, one significant difference is that parasites are usually many times smaller in size than their host, and they all reproduce at a rapid rate.
What is a parasite?
A parasite is any organism that resides within another living organism known as a host.
The parasite is not capable of fending for itself; thus, it uses the resources of the host to fuel its entire life cycle. It makes use of the host’s support for self-maintenance and sustenance.
Parasites vary a great deal. While there are thousands of parasites in existence, around 70 percent of them are not visible to the physical eye, an example of such microorganisms is the malarial parasite, but there are certain worm parasites that can grow as long as 30 meters.
While it must be noted that parasites are not a disease, you must also bear in mind that they can spread infections and diseases. Different parasites have unique effects on their hosts.
Endoparasite
These are the parasites that live inside their hosts. They include tapeworms, heartworm, and flatworms. An intercellular parasite is one that takes abode in the spaces within the body of its host, within the cells of the host. They include viruses and bacteria.
Endoparasites naturally rely on a third organism, known as a carrier or the vector. The vector is what transfers the endoparasite to the host. One of the most popular vectors for several parasites is the mosquito, including the protozoan called Plasmodium, which is the cause of malaria.
Epiparasite
These are parasites that feed on other parasites in a relationship called hyperparasitism. An example of hyperparasitism is a flea that lives on a cat but with a protozoan in the digestive tract of the flea. The protozoan is this case is the hyperparasite.
Types of parasites
There are three major types of parasites.
- Protozoa: Examples of protozoa include the single-celled organism called plasmodium. It is only possible for protozoa to multiply, or divide, within the host.
- Helminths: This is another category of parasites. The creatures in this group are worm parasites. Helminths are the cause of Schistosomiasis. Other examples of such parasites are pinworm, roundworm, fluke, trichina spiralis, and tapeworm.
- Ectoparasites: These types of parasites live on, instead of inside their hosts. They include fleas and lice.
Symptoms
There are several types of parasites, as mentioned at the beginning of this article, and symptoms usually vary widely. Sometimes the symptoms caused by the presence of parasites may look like those of other conditions, such as pneumonia, hormone deficiency, or food poisoning.
Symptoms that might be displayed include:
- Increased appetite, weight loss, or both
- Skin bumps or rashes
- Abdominal pain, diarrhea, and vomiting
- Anemia
- Sleeping problems
- Allergies
- Aches and pains
- Weakness and generally feeling sick
- Fever
However, it is difficult to predict the symptoms caused by the presence of parasites because they can pass on a wide variety of conditions.
Often, there are no symptoms in manifestation, or they may appear long after infection. But even with the absence of physical symptoms, the parasite can still be transmitted to an uninfected person, who may then develop symptoms.
Human parasites
Many types of parasites can affect humans. Below are some examples of parasites, as well as the diseases they may cause.
Acanthamoebiasis
This is a tiny ameba can can cause an infection to the eye, the skin, and the brain. It can be found all over the world in soil and water. Individuals can get an infection if they have their contact lenses cleaned with tap water.
Babesiosis
This is a disease that is caused by parasites that are carried by ticks. The disease affects the red blood cells and poses a higher risk in summer around the Northeast and upper Midwest of the US.
Balantidiasis
This is a disease transmitted by Balatidium coli, which is a single-cell parasite that mostly infects pigs but can cause intestinal infections in humans rare cases. It can be spread by drinking contaminated water, or through direct contact with pigs.
Blastocystosis
This is an illness that affects the intestines. The blastocystis goes into the human body via the fecal-oral route. Any person can get one by eating or drinking anything that has been contaminated with animal or human feces where the parasite is present.
Coccidiosis
This is a disease that affects the human intestines. Coccidia is transmitted through the fecal-oral route. It is a condition found all over the world.
It can also affect cats and dogs, but these are different from the kinds that affect humans. Cats, dogs, and humans typically can’t infect each other.
Amoebiasis
This is a disease caused by the parasite known as Entamoeba histolytica. It attacks the intestines. It is highly unlikely to be found in places outside tropical regions and in areas with poor sanitation and high population density. It is transmitted via the fecal-oral route.
Giardiasis
Giardia, also known as “beaver fever,” is a disease that affects the lumen of a person’s small intestine. If humans keep drinking anything that has been contaminated with feces, dormant cysts may cause an infection to the body.
Isosporiasis or cyclosporiasis
This is a disease that is caused by the Cystoisospora belli, formally called Isospora Belli. It creates an infection to the epithelial cells of the small intestine.
It can be found all over the world and is both preventable and treatable. It is passed on via the fecal-oral route.
Leishmaniasis
This is a common disease that is transferred by parasites belonging to the Leishmania family. It can affect the viscera, the skin, or the mucous membranes of the mouth, nose, and throat.
It can be a fatal condition. Certain types of sandflies transmit the parasite responsible for this case.
Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM)
This is a disease passed on via a free-living ameba known as Naegleria fowleri. It affects the brain called the nervous system and is nearly always fatal within 1 to 18 days of infection.
It is transmitted through swimming pools, breathing in contaminated soil, and infected water use, but not from drinking water.
Malaria
There are different types of plasmodium that affect red blood cells. This disease exists in warm tropical regions and is majorly transported and transmitted by the Anopheles mosquito.
Rhinosporidiosis
This is a disease caused by Rhinosporidium seeberi. It primarily affects the mucous of the conjunctiva, nose, and urethra. It is more common in Sri Lanka and India but can occur elsewhere
. Polyps cause nasal masses that can only be removed by surgery. Taking a bath in natural ponds can expose your nasal mucous to this parasite.
Toxoplasmosis
This is a form of parasitic pneumonia that is caused by the parasite Toxoplasma gondii. It affects the eyes, liver, heart, and brain. It can occur anywhere in the world.
People can become infected with this parasite after ingesting raw or undercooked lamb, pork, goat, milk, or even though contact with soil or food that is contaminated with cat poop.
A person that has a healthy immune system usually will not show any physical symptoms, but it can pose a serious for people with weak immune systems and during pregnancy.
Trichomoniasis
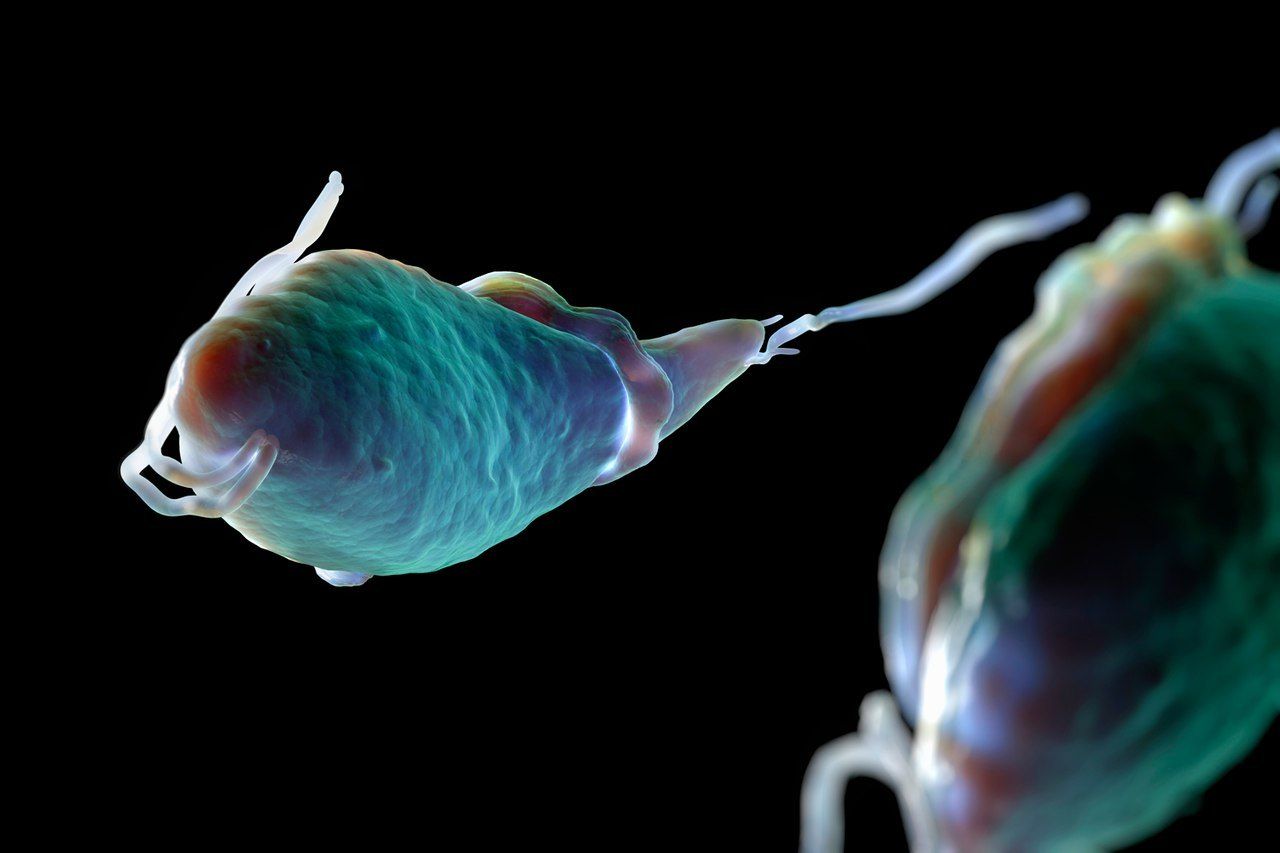
This condition is also known as “trich” and is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that is caused by the parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis. It can affect males but will display no symptoms. It mainly affects the female urogenital tract.
Trypanosomiasis (Sleeping sickness)
Also called the African sleeping sickness, Trypanosomiasis is a disease that is passed on when a tsetse fly transmits a parasite belonging to the Trypanosoma family. The parasite affects the blood, central nervous system, and lymph.
It causes a change in sleep pattern or behavior, among several other physical symptoms, and it is considered fatal without immediate treatment. It can cross the placenta and even infect a fetus during pregnancy.
Chagas disease
This is a disease that affects the muscle, blood, nerves, esophagus, heart, and colon. It is transferred through an insect bite. More than 300,000 people in the United States have the parasite that causes this disease.
Worms
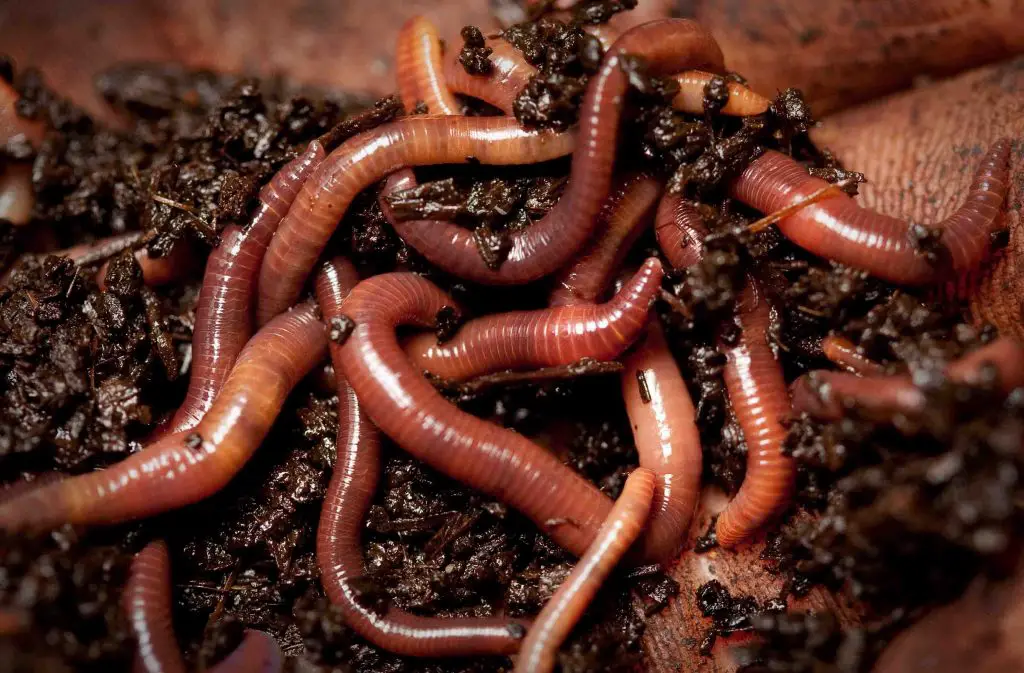

Worms, or helminth organisms, may affect both animals and humans.
- Anisakiasis: This is a disease caused by worms that can invade the stomach wall or the intestines. The worms are transmitted through contaminated fresh or undercooked squid and fish.
- Roundworm: A roundworm or ascariasis infection does not usually show any physical symptoms, but the worm may be noticed in feces. It enters the human body through the consumption of contaminated food or drink.
- Raccoon roundworm: Baylisascaris is a disease that is transmitted through raccoon stools. It can affect the liver, brain, lungs, and intestines. It is common in North America. For this reason, people who love to keep exotic pets are advised not to adopt q raccoon as a pet.
- Clonorchiasis: Also called the Chinese liver fluke disease, clonorchiasis is a disease that affects the gall bladder. A person can become infected by this disease after eating raw, preserved, or poorly processed freshwater fish.
- Dioctophyme renalis infection: The is a giant kidney worm that can move comfortably through the wall of a person’s stomach, all the way to the liver, and finally, the kidney. People can get infected by the disease after accidentally eating the eggs of the parasite together with raw or undercooked freshwater fish.
- Diphyllobothriasis tapeworm: This disease affects the blood and intestines. Humans can get infected by the illness after eating raw fish that live fully or partly in freshwater. The prevalence of this disease has increased in certain parts of the developed world, most likely as a result of the growing popularity of salted fillets, sushi, ceviche, and other dishes that involve raw-fish.
- Guinea worm: This is a disease that affects subcutaneous tissues and muscle and is known to cause ulcers and blisters. The worm may be apparent in the blister. As the worms are removed or shed, they enter the water or soil and are transferred on from there.
- Hookworm: These are common causes of intestinal disease. These parasites lay their eggs in the soil, and their larvae can easily penetrate the human skin. Early physical symptoms of hookworm include a rash and itching. Hookworms are most common in damp places and places with poor sanitation.
- Hymenolepiasis: Humans can get infected by this disease when they ingest material contaminated by cockroaches, rodents, flour beetles, and mealworms.
- Echinococcosis tapeworm: Cystic echinococcosis can cause cysts in the lungs and liver, and alveolar echinococcosis can lead to a tumor in the liver. Humans can get an infection after direct contact with an infected animal, or from eating foods that are contaminated by the droppings of an infected animal.
- Enterobiasis pinworm: A threadworm, or pinworm, Enterobius vermicularis can take abode in the human colon and rectum. The worms lay eggs around a person’s anus while they sleep, which leads to itching. These parasites spread through the oral-fecal route.
- Fasciolosis liver fluke: This parasite affects the liver and gall bladder. It is common in countries where sheep or cattle are reared, but rare in the United States. This infection can affect the bike ducts and liver, and it also causes gastrointestinal symptoms. The parasite also passes from one mammal to another using snails as a medium of transport. A person may get this parasite from eating watercress.
- Fasciolopsiasis intestinal fluke: This I’d a parasite that affects the intestines. It can also be transmitted through the consumption of contaminated water or water plants.
- Gnathostomiasis: This parasite causes swellings under the skin, and may occasionally affect the eyes, liver, and nervous system. It is a rare infection but can be very fatal. It mainly occurs in Southeast Asia. It is transmitted by eating snails, freshwater fish, pigs, frogs, and chickens.
- Loa loa filariasis: Also called loiasis, this is an infection caused by the Loa loa worm or the African eye worm. This parasite causes itchy swellings all over the body. It happens mainly in West and Central Africa and is transmitted by deerfly bites.
- Mansonellosis: This is an infection that is passed on via the bites of midges or blackflies. Mansonellosis affects the layers under the skin surface, but it can find its way into the blood. It can lead to swellings, angioedema, fever, skin rash, and joint problems. This parasite is most common in Africa and Central America.
- River blindness: This illness is caused by a worm called Onchocerca volvulus; this affects the skin, eyes, and other body tissues. It is an illness found close to fast-flowing water and is transmitted via the bite of a blackfly. While it occurs in South America, 90 percent of reported cases are in Africa.
- Lung fluke: Also called paragonimiasis, this is an infection that affects the lungs, causing symptoms that are similar to those of tuberculosis (TB). This parasite can reach the central nervous system, causing the dreaded meningitis disease. This parasite is transmitted when eating raw or undercooked freshwater crayfishes, crabs, and other crustaceans. It is almost everywhere in the world, but most common in parts of Asia.
- Schistosomiasis, bilharzia, or snail fever: There are several types of schistosomiasis known to affect humans. They can affect the skin and the internal organs. schistosomiasis results from exposure to freshwater where snails live, especially snails that are infected with the trematode or blood fluke worm. The worms are have not been found in the U.S., but they are popular in other parts of the worldwide.
- Sparganosis: Humans can get infected by sparganosis if they ingest foods that are tainted with cat or dog feces that have the larvae of a tapeworm belonging to the Spirometra family. Sparganosis is rare and can cause a migrating abscess under the skin.
- Strongyloidiasis: This is a parasite that can lead to severe and even fatal immunodeficiency. The Strongyloidiasis parasite penetrates via the human skin and affects the intestines, lungs, and skin. This parasite is passed on from direct contact with soil that has been contaminated. It mostly occurs in subtropical and tropical regions.
- Beef and pork tapeworms: Taeniasis is a disease that is caused by tapeworm belonging to the taenia family. They attack the intestines and are passed on by eating raw or undercooked beef or pork.
- Toxocariasis: This is an infection transmitted by a roundworm from animals to humans. It affects the brains, eyes, and liver. Toxocariasis is caused by swallowing the eggs of the parasite accidentally. Accidental ingestion may occur when children play with soil. Almost 14 percent of people living in the U.S. have antibodies, which suggests that millions of people have been exposed. Most never show any symptoms.
- Trichinosis: This is an infection caused by the roundworm belonging to the Trichinella family. An infection can cause fever, intestinal symptoms, and muscle aches. It is transferred from animals to humans by eating undercooked meat.
- Whipworm: Also called trichuriasis, the whipworms takes abode in the human large intestine. Its eggs are passed in feces, and it is a prevalent parasite all over the world. Humans can get infected from ingesting the eggs accidentally when consuming unwashed fruit or vegetables.
- Elephantiasis lymphatic filariasis: This is an infection that is transmitted through mosquito bites. The adult worms reside in the lymph system. Infection can lead to elephantiasis and lymphedema, in which swelling can result in disability and disfigurement. In the Americas, the parasite is transmitted by the Culex quinquefasciatus mosquito.
- Most people sometimes mistake ringworm for an actual worm, but it is a fungal infection and not a real worm.
Ectoparasites

As explained above, these parasites live on the outside of the body. An example of such parasite is fleas.
- Bedbug: These are common parasites that can affect the skin and also affect vision. They are not restricted to specific parts of the world as they are evenly spread across all geographical locations. Sharing bedding and clothing with an infected person can spread infection. You can find them in may some hotel rooms and in newly rented accommodation.
- Body lice: These are another widespread parasite that is found worldwide. A body lice infection can spread through skin-to-skin contact, sexual activity, and sharing bedding or clothing.
- Crab lice: These are a common parasite that affects the eyelashes and pubic area. They spread through skin-to-skin contact, sexual activity, and sharing clothing or bedding.
- Demodex: These are parasites that affect the eyelashes and eyebrow. They can be found all over the world and can spread quickly via prolonged skin contact.
- Scabies: This is a parasite that affects the skin. It is not specific to geographic location and can be spread through skin-to-skin contact, sexual activity, and sharing bedding or clothing.
- Screwworm: This is a parasite that is transmitted by a fly, and can affect wounds and skin. It is mostly found in North Africa and Central America.
- Head lice: These are parasites that live on the scalp and attack the hair follicles. They are not specific to geographic locations, and quickly spread through head-to-head contact. Contact with their saliva causes itching.
Prevention
You can increase your chance of staying free of parasites by:
- Finding out which kind of parasite is prevalent where you reside and locations you may visit
- Take precautions like using insect repellant in areas where flies and mosquitoes are common
- Be careful to feed on only well-cooked meat and fish
- When traveling to new places, drink only bottled water with a sealed top
- Be careful when taking a bath in fresh-water lakes or rivers
- If you notice any symptoms and suspect a parasite infection, see a doctor.
Parasites come in a variety of shapes and sizes and can cause a wide range of symptoms and medical issues. Not all parasites are treatable.
Leave a comment below if you have questions or contributions.












