After a year of trying, a diagnosis of infertility means you haven’t been able to get pregnant. If you’re a woman above 35 years, it means that you haven’t been able to get pregnant after six months of trying.
Infertility can also be diagnosed in women who are capable of conceiving but not bringing a pregnancy to term.
Primary infertility can be diagnosed by a woman who has never been able to get pregnant. With secondary infertility, a woman who has had at least one successful pregnancy will be diagnosed in the past.
Infertility is not merely a woman’s problem. Men may also be infertile. Women and men can be equally likely to have fertility issues.
Causes of male infertility
Generally speaking, infertility in men is attributed to the following problems:
- Efficient sperm development
- The number of sperm, or the sperm count
- The sperm’s shape
- Sperm movement, which involves both the wiggling movement of the sperm itself and the sperm transport via the tubes of the male reproductive system
There are a number of risk factors, medical conditions, and drugs that can impact fertility as well.
Risk factors
Infertility-associated risk factors in men include, but are not limited to:
- The Elderly Age
- Cigarette-smoking
- Heavy use of liquor
- Being fat or overweight
- Toxin exposure, such as heavy metals, pesticides, and herbicides.
Medical conditions
Some medical conditions that can cause infertility for men include:
- Ejaculation Retrograde
- Varicocele, or the swelling of the testicles around the veins
- Undescended Testicles
- Having antibodies that attack and kill your sperm
- A hormonal imbalance, such as the low development of testosterone
Medications and drugs
Male fertility may also be affected by various medicines and drugs, such as:
- Radiation treatment or chemotherapy used for cancer
- For rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or ulcerative colitis, sulfasalazine (Azulfidine, Azulfidine EN-Tabs) is used (UC)
- Blockers of calcium channels used for high blood pressure
- Tricyclic antidepressant medicine
- Anabolic steroids that are used to boost athletic efficiency or hormonal problems such as postponed puberty
- Drugs for pleasure, such as cocaine and marijuana
Causes of female infertility

A number of factors that influence or interfere with the following biological processes may be caused by female infertility:
- Ovulation with the release of the mature egg from the ovary.
- Fertilization, which occurs after passing through the cervix and uterus when sperm enters the egg in the fallopian tube.
- Implantation, which happens when a fertilized egg sticks to the uterine lining, where it can then mature and develop into an infant.
Risk factors
Female infertility risk factors include:
- Getting older.
- Cigarette-smoking.
- Heavy use of liquor.
- Overweight, obese, or substantially underweight.
- Getting some sexually transmitted infections that can damage the reproductive system (STIs).
Medical conditions
The female reproductive system may be impaired by a number of medical conditions and cause infertility in women.
- Examples are:
- Ovulation disorders that may be caused by hormonal imbalances or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Endometriosis
- Fibroids in the uterus
- Premature malfunction of the ovaries
- The scarring from a previous operation
Medications and drugs
Certain medications and drugs that can cause female infertility include:
- Radiation therapy or chemotherapy
- Long-term use of high-dosage or abuse of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin (Bayer) and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin)
- Antipsychotic medications
- Recreational drugs such as marijuana and cocaine
Infertility testing

You’re probably thinking when you should expect to see a doctor if you’ve been trying to conceive and have not been able to. Read on to find out which tests they will conduct to determine your and your partner’s fertility.
Men
Men should plan to see a doctor after one year of attempting to conceive or if any of the following apply:
- Issues with ejaculation, such as delayed ejaculation or retrograde ejaculation
- Erectile dysfunction (ED)
- Low sex drive
- Having undergone surgery previously in the genital area.
- Pain or swelling in the genital area
Your doctor will use your medical history first. They’ll ask about your general health, your sexual history, and factors that could impact your fertility during this period.
They will also conduct a physical examination in which they look for any structural defects or lumps in the genitals.
A semen examination may then be carried out. Your doctor will ask to take a semen sample. In a laboratory, this sample will be tested to see how many sperm are present and whether sperm is naturally shaped and properly moving.
Your doctor might choose to conduct additional tests based on your initial examination and semen analysis findings.
These tests may include:
- Hormone testing
- Genital ultrasound
- Genetic testing
Women
The fertility of a woman begins to reduce after the age of 30. After one year of trying to get pregnant, women under 35 should visit a doctor, and women over 35 and over should visit a doctor after six months of trying.
Your doctor will use your medical history first. They will ask you about your current health status, your sexual background, and any illnesses or diseases that could lead to infertility.
To scan for irregularities such as fibroids or disorders such as endometriosis or PID, they will then conduct an examination of the pelvic region. Your doctor would like to see if you ovulate on a monthly basis. This can be determined in the doctor’s office with an at-home ovulation test kit or by blood tests.
An ultrasound can be carried out to evaluate the ovaries and uterus. For women, other common tests include:
- Hysterosalpingography, a form of X-ray used to assess the uterus and fallopian tubes,
- Laparoscopy, which examines the internal organs using a camera
- The follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) test involves ovarian reserve testing, which incorporates a combination of hormone tests to assess a woman’s ability to conceive.
Infertility treatments

You may want to seek help if you and your wife have been trying to get pregnant and have not been able to. A number of factors may depend on the type of treatment that is recommended, including:
- The cause, if known
- How long have you been trying to conceive of a
- The ages of you
- Both you and your partner’s general wellbeing
- After consultation about your care choices, the personal interests of you and your partner
Men
Depending on the cause, male infertility can be treated in a number of ways. Surgery, medication, and assisted reproductive technology can be treatment choices for men (ART).
Surgery can repair obstructions that prevent the presence of sperm in the ejaculate. Terms such as varicocele can also be right. Sperm can be directly extracted from the testicles in some cases, after which it can be used in therapy with ART.
Medications may be used to treat conditions such as hormonal imbalances. They can also be used to treat other diseases, such as ED or infections affecting sperm count, that can affect male fertility.
ART refers to procedures outside the body in which eggs and sperm are administered. It may include therapies such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) and injection of intracytoplasmic sperm. For ART therapy, sperm may be collected from ejaculate, testicular extraction, or from a donor.
Women
Surgery, medicine, and reproductive aid such as Sculpture may also be part of female infertility care. To help resolve female infertility, many forms of treatment are often needed.
While surgery may still be used to treat female infertility, it has become rarer now due to developments in other fertility therapies.
Surgery can enhance fertility through:
- Correcting an abnormally shaped uterus
- Unblocking fallopian tubes
- Removing fibroids
Methods like intrauterine insemination (IUI) and ART may be involved in reproductive assistance. During IUI, near the time of ovulation, millions of sperm are inserted into a woman’s uterus.
IVF is one type of ART that requires the removal of eggs that are then fertilized in a laboratory with the sperm of a man. The embryo is inserted back into the uterus after fertilization.
The drugs used to treat female infertility work to either stimulate or control ovulation, like hormones that are naturally present in the body.
Infertility and natural treatments
Methods, including acupuncture and yoga, may involve natural therapies. One 2018 analysis found that some form of natural or alternative infertility treatment was attempted by at least 29 percent of couples, either alone or to supplement conventional treatments.
Acupuncture
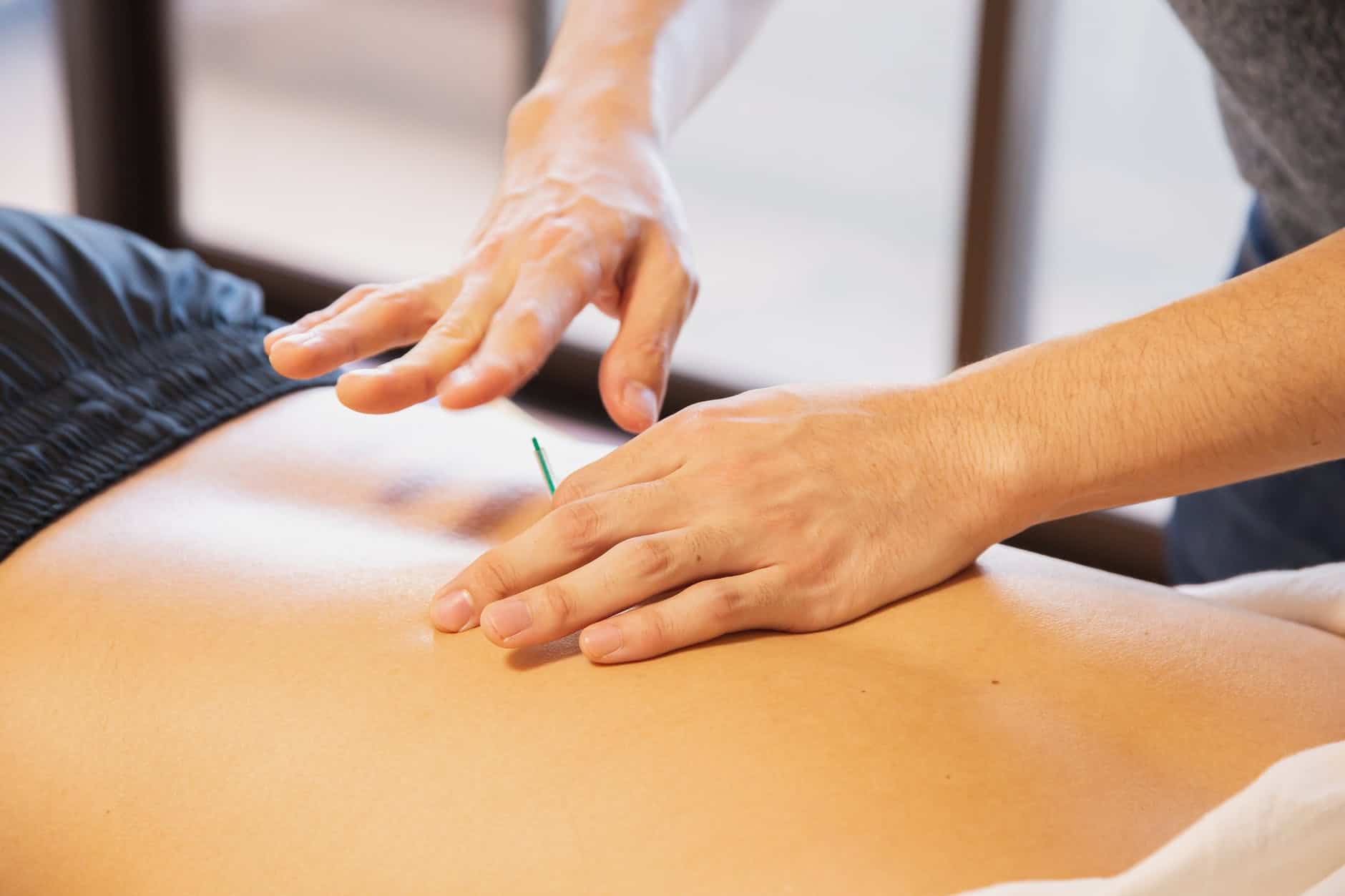
Acupuncture entails the insertion into different points of the body of short, thin needles. It is assumed that these points will help to enhance the energy flow of the body. As a cure for infertility, there is no definitive evidence to support acupuncture.
A recent analysis of several clinical trials found insufficient evidence that acupuncture could stimulate both ovulation and menstruation in women with PCOS.
Yoga

To encourage relaxation and decrease stress levels, yoga combines postures and breathing techniques. Studies on yoga as a treatment for infertility are minimal. However, it is known that it can be helpful to practice yoga to alleviate the tension that can be associated with fertility treatments.
Vitamins
Various vitamins and minerals can be beneficial in promoting fertility. Some to look out for include:
- Folate
- Zinc
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin E
- Iron
- Other nutrients, such as probiotics, can also be considered, encouraging safe digestion and boosting overall wellness.
Tea
Commercially available for purchase are a range of fertility teas, but do they work? There are very limited studies on the impact of these tea formulations on fertility. However, one recent analysis found that by improving parameters such as sperm count and motility, antioxidant compounds found in green tea can help fertility.
Essential oils

Essential oils, usually from their roots, seeds, or leaves, are obtained from plants. They can be used to facilitate relaxation and minimize stress levels in aromatherapy.
Massaging with, bathing with, or burning essential oils may involve aromatherapy. To determine the effects that essential oils can have on fertility, more research is needed.
Fertility diet
For women, food guidelines for fertility-boosting are aimed at improving infertility triggered by ovulation issues. Therefore, infertility caused by physical problems such as a block in the fallopian tubes or uterine fibroids would not work for them.
Some fertility-enhancing dietary guidelines include:
- By concentrating on fiber-rich foods (such as vegetables and whole grains), choose carbs wisely while avoiding processed carbs that are high in sugar
- Preventing trans fats found in many fried and refined food products
- Swapping some of the animal protein against vegetarian protein sources
- Choosing high-fat dairy products (like whole milk) rather than low-fat products
It can also help men improve the health of their sperm by following these guidelines and consuming a nutrient-rich diet in general. It can help improve fertility by introducing dietary changes along with lifestyle changes, such as becoming more involved. Get more fertility-enhancing tips by improving the way you diet and exercise.
Fertility cycle
About the time when they ovulate, women are most fertile. It can increase your chances of conceiving by monitoring your ovulation and then focusing on your sexual activity at this time. One day out of the month, ovulation happens.
Your ovaries release a mature egg at this point, which starts moving through your fallopian tubes. Fertilization may occur if the egg encounters sperm during its journey.
If an egg is not fertilized, within around 24 hours of ovulation, it will die. However, for up to five days, sperm will reside inside a woman’s body, raising the chances of fertilization.
You’re actually fertile for about five or six days out of the month because of this. Ovulation does not occur every month at the same time, so understanding the signs of ovulation is essential. Body changes such as stomach cramping and a slight increase in body temperature may be found in these.
Infertility Facts and statistics
12.1 percent of U.S. women 15 to 44 years old have trouble conceiving and bringing a child to term, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). In this age group, nearly 7 percent of married women are infertile.
In addition, 7.3 million women between 15 and 44 years of age have used infertility services, according to the CDC. That accounts for approximately 12% of women in that age group.
A woman in her 30s is predicted to be half as fertile as a woman in her early 20s, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
The Office on Women’s Health reports that after the age of 35, about 20% of women in the United States now have their first child. This makes age a rising factor that contributes to infertility. Around 9 percent of men have suffered fertility problems.
While, with growing age, male fertility may still decline, it declines more slowly than female fertility.
Outlook on infertility
Being diagnosed with infertility does not mean that it has ended your hopes of having a child. It may take some time, but it will finally be possible for a number of couples who experience infertility to have a child. Others will do so on their own, and others will require medical support.
Many factors, including your age, the cause of infertility, and your personal preferences, will depend on the care that’s right for you and your partner. Similarly, several factors may depend on whether a particular infertility treatment results in a pregnancy or not.
In certain instances, it is likely that a fertility condition will not be handled. Your doctor might recommend that you and your wife consider donor sperm or eggs, surrogacy, or adoption, depending on the circumstances.
With many shifts in perceptions and cultural norms, the environment of fertility in the United States continues to be dynamic.












