Athletes are some of the most successful people in the world. So successful that people do not think about the risks that they put themselves through to make so much money and entertain their audience at the same time.
For movie lovers, the movie Concussion tells us a story that goes beyond mere entertainment to expose the world to the secret pains and hidden truths in the lives of American football players.
Will Smith played the role of an able forensic neuropathologist who discovered a football-related brain trauma called Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE). Despite the opposition he faced from the NFL in the movie, he tried harder to see that awareness was created on the risks that the football players were exposed to.
However, after the film was released, will smith reported feeling disappointed at the reception the movie got from the public saying “I thought Concussion would have a bigger impact”. But he realised that people loved the game of football so much that they overlooked the message behind the movie.
In this article, you will discover what Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy is and the dangers it poses to sufferers.
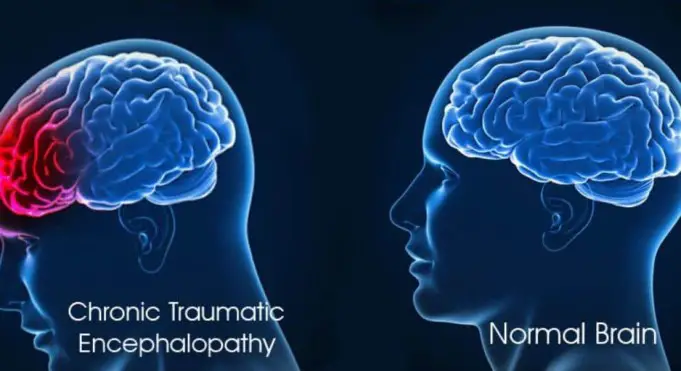
What is Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE)?
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy is a dangerous degenerative brain disease caused by repetitive brain trauma. CTE is mostly found in Athletes, soldiers, and other people who get engaged in activities that cause them to hit their heads on a regular basis.
When Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy happens, clumps are formed around the brain by a kind of protein called Tau. These clumps spread around the brain slowly and kill brain cells.
Unlike some other medical conditions, CTE might not be noticed early as it takes a long time to manifest and cannot be diagnosed on living people. It takes years after the brain hit for symptoms of this medical condition to manifest.
While it is possible for people as young as 15yrs of age to experience CTE, it takes until their early 20’s for signs and symptoms to show up.
History of CTE
What can be easily described as the first case of CTE was in 1928 when Dr Harrison Martland talked about a group of boxers who he tagged to be suffering from what he called the “punch drunk syndrome”.
Years after that, other fighters were discovered to have the same problem and some military folks suffered from the similar condition. In 2005, a pathologist identified as Bennett Omalu ( whose character was played by Will Smith in the concussion movie) documented the first case of Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy in a football player known as Mike Webster, in the United States of America.
Not long after Dr Mike Webster’s documentation, there was a partnership between the Boston University, the United States Department of Veterans Affairs, and the Concussion Legacy Foundation to form a brain bank.
The brain bank had about 500 brains donated voluntarily, and it was discovered that 300 of the donated brains had CTE.
What exactly is the cause of CTE?
From studies and researches, it has been gathered that CTE is caused by consecutive head hits that are accumulated over a period, and might not necessarily lead to concussions.
People with CTE have been discovered to have had hundreds or thousands of brain hits in their lives as a result of the sports they engage in, military work, or victims of continuous domestic violence (This is, however, the rarest cause of CTE discovered).
Are Athletes the only ones at risk of CTE?
Pretty much everyone is at risk of CTE. Every person who has ever been diagnosed with CTE has a history of repetitive head hits, and anybody can have that.
Children with the habit of hitting their heads on the wall when they are upset , Individuals with developmental disabilities that cause them to regularly beat their heads on things, rugby player, baseball players, soccer players, wrestlers, people in the military, and victims of domestic violence are all vulnerable to the condition called CTE.
But, it is noteworthy that not everybody who gets many head hits will suffer from CTE. There are risk factors that make some people more prone to having CTE than others.
What are the risk factors?
1. The age of the victim’s first exposure to head hits
Children who are sports lovers and engage in sports activities at ages earlier than 12years are at risk of having CTE when the sports activity involves head contacts. But children who participate in the same sporting activities after the age of 12 are at lower risk of getting a CTE.
2. The Length of exposure to head contact
The longer the experience of head hits the more at risk a person is when it comes to contacting CTE. From research, it was discovered that the pathology of players who had longer careers in sports that exposed them to head hits was more severe than that of players who had shorter careers.
What are the symptoms of CTE?
The most common symptoms for CTE are headaches, depression, anxiety, memory loss, irritability, and mood changes. There may be other symptoms, but further research will unravel them in the process of time.
Is it possible to have a CTE from one concussion?
There is no need to fear that you’ll have a CTE from just one head concussion. Studies show that there must be a constant head contact for a person to develop CTE and even so, there are individuals who have had many head injuries from sporting activities that never had a CTE. It is yet to be discovered why the cases of exception occur but more research is being carried out to find out more.
How is CTE diagnosed?
Sadly, CTE cannot be diagnosed when a person is still alive at the time of this publication. Doctors can only diagnose CTE through brain tissue analysis on a dead person as it is not performed as part of a standard autopsy. The process of diagnosing CTE takes months, and only a few doctors know how to diagnose the condition.
Is there a cure for CTE?
Because CTE is a condition that can not be diagnosed until after death, it is difficult to have a cure for it. Maybe in the future, there will be a solution, but currently, there are only treatments for the symptoms of CTE.
When patients fear that they have CTE doctors prescribed therapy sessions and medication that are targeted at helping to reduce or treat the most troubling symptoms.