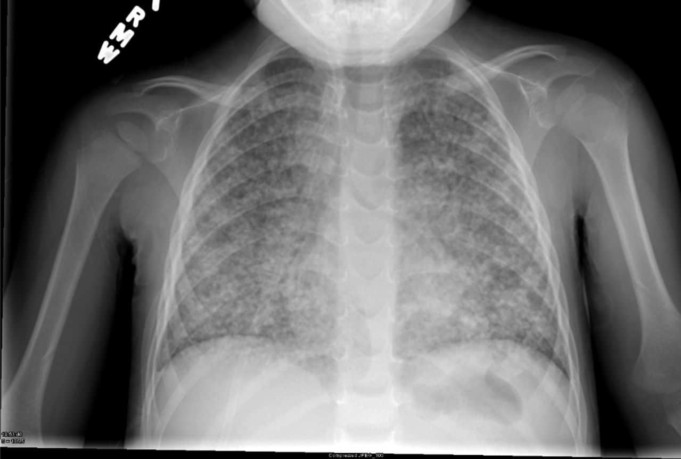
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that half of the world’s twenty-two (22) countries affected by tuberculosis (TB) are in Asia.
That means that you’ve come across someone who has been infected with TB bacteria, which according to research, only a small proportion of the affected people become sick with tuberculosis.
So, what exactly is tuberculosis? TB is simply an infectious airborne disease which is caused by different mycobacteria strains, typically Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Through fine respiratory droplets, TB can be spread from one individual to another, but you can’t get TB from sharing cigarettes, eating utensils or cups.
Basically, TB usually affects the lungs hence causing pulmonary tuberculosis, although it affects other body parts like lymph nodes, kidney, the brain, bones, and joints which is termed as extrapulmonary tuberculosis.
TB should be treated properly, otherwise, it could be a fatal disease. Keep scrolling as we tell you more about types of tuberculosis you should know about.
Active vs. latent TB
Your body can harbor the bacteria that cause TB, but you may not get sick thanks to your immune system. To have a clear understanding, let’s distinguish between latent and active TB.
Latent TB
This is a condition where people have TB infection, but the bacteria are in an inactive form. That way, it is not contagious, and the person experiences no symptoms and the result from TB blood remains positive simply because their immune system protects them from getting sick.
According to experts, there are about 2.5 billion people who carry the M. tuberculosis germ and most of them have latent TB. Unfortunately, latent TB may turn into active TB in 5-10% of people with this germ, and the risk can even be higher to people with conditions that compromise their immune systems like HIV infection.
Active TB
Active TB, also known as TB disease is an illness in which Tb bacteria rapidly multiplies and invades various organs in the body.
Even though active TB symptoms vary depending on whether it’s extrapulmonary or pulmonary, the general symptoms include unexplained weight loss, loss of appetite, fever, night sweats, fatigue, and chills.
If your lungs get infected with active TB, you may spread it to others through airborne transmission of infectious particles particularly when you cough into the air.
Pulmonary TB
Pulmonary TB occurs when Mycobacterium tuberculosis attacks the lungs and can spread to other body organs. When an infected person exhales, the germs remain active in the air for several hours and when someone else breathes in the same air, he gets infected as well.
Fortunately, the good news is that when diagnosed early, pulmonary Tb can successfully be cured using antibiotic treatment. People with pulmonary Tb usually experience the following symptoms;
- Coughing up blood
- Persistent cough that may last up to three weeks
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing up phlegm
Extrapulmonary TB
Extrapulmonary TB is simply a type of tuberculosis that affects other body parts except for the lungs. It is associated with various symptoms which basically depend on the body part affected and we will look at different parts affected.
TB lymphadenitis
Have you ever heard about TB lymphadenitis? Well, it’s among the most common types of extrapulmonary TB and affects any lymph nodes, although it commonly affects the cervical lymph nodes.
People with TB lymphadenitis complain of the swollen lymph nodes as the most prevalent symptom, but can also cause the following;
- Night Sweats
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
Skeletal TB
Skeletal TB, also known as bone TB is a type of TB that spreads from your lymph nodes or lungs to your bones. Skeletal TB is rare but has been very common in countries with high risks of diseases that weaken the immune systems such as HIV/AIDS.
It affects any bone in your body inclusive of joints and spine and even though it causes no symptoms, it’s closely associated with symptoms of general active TB as well as the following;
- Abscesses
- Bone deformities
- Swelling
- Stiffness
- Severe back pain
Miliary TB
Miliary TB occurs when tuberculosis bacteria find their way in your bloodstream which in turn affects one or several organs such as bone marrow, lungs, and liver and can spread to other body parts such as the brain, spinal cord, and the heart.
Miliary TB causes symptoms of general active TB together with other symptoms that largely depend on the part of the body affected. For instance, if the bone marrow is affected, a person may have a rash or low red blood cell count.
Genitourinary TB
Genitourinary TB affects the kidneys as well as any part of the urinary tract or genitals and spreads from the lungs through the lymph nodes or blood to the area/s aforementioned.
It can as well spread through intercourse although on very rare cases, and the affected people develop tuberculosis ulcers in the genital tract or on the penis. Symptoms of Genitourinary TB may include;
- Painful urination
- Testicular swelling
- Interrupted or decreased urine flow
- Pelvic pain
- Back pain
- Infertility
- Decreased semen volume
- Liver TB
Liver TB, also known as hepatic TB occurs when the liver is affected by TB. It is rare and out of all the TB infections, liver TB accounts for less than 1%.
Liver TB may spread to the liver from the lymph nodes, gastrointestinal tract, or the portal vein and the following symptoms are experienced;
- High-grade fever
- Upper abdominal pain
- Jaundice
- Liver enlargement
Gastrointestinal TB
Gastrointestinal TB is a tuberculosis infection that affects any gastrointestinal tract part that extends from your mouth to the anus. According to experts, Gastrointestinal TB causes symptoms that are closely linked to gastrointestinal conditions like Crohn’s disease.
Even though the symptoms depend on the infected part of the gastrointestinal tract, the following are the most common;
- Appetite loss
- Abdominal pain
- Weight loss
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Vomiting
- Nausea
TB meningitis
TB meningitis, also known as meningeal tuberculosis is a type of TB that spreads to the membranes that surround the spinal cord and the brain, famously known as meninges.
TB spreads through the bloodstream or from the lungs to the meninges and develops gradually. It causes the following symptoms;
- Fatigue
- Aches and pains
- Persistent headache
- Appetite loss
- Nausea and vomiting
- Low-grade fever
Bottom line
There are many types of tuberculosis which can be treated if diagnosed early. Well, if you work in areas frequented by people infected with TB, it could be difficult to avoid contracting it, but you should be tested regularly even if they show no symptoms.
TB can be tested through various ways such as Mantoux tuberculin skin test (TST), blood test, imaging test, and sputum test. If you’ve been exposed to TB causing bacteria, seek advice from your doctor as soon as possible because if left untreated, TB can be life-threatening.