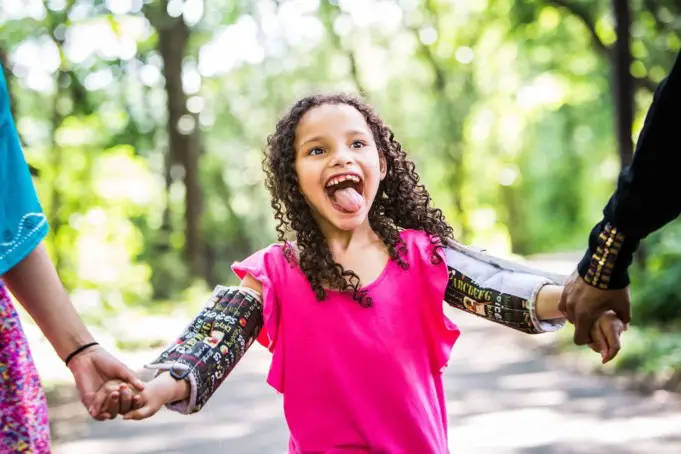
Rett syndrome is a genetic disorder that is relatively rare but occurs dominantly in girls, which are caused by a rare mutation to the X-chromosome affecting nearly all the aspects of the child’s life.
Rett syndrome affects a child’s speech, behavioral patterns, mobility, and much. By mere observation of these symptoms and genetic testing, this condition can be diagnosed.
This is not a degenerative disease, and it is not inheritable. However, it is a life-long disease with no cure but only with treatment options to manage the condition.
Rett syndrome is so rare, its occurrence globally is in 1 out of 10,000 female births, and it is very limited in male births. The symptoms manifested can be evident with disabilities ranging from mild to severe.
What is Rett syndrome?
Rett syndrome (RTT), also known as cerebroatrophic hyperammonemia, is a rare and severe genetic condition that dominantly affects girls. In 1966, a pediatrician in Vienna named Andreas Rett first described Rett syndrome, which is now popularly and officially known by his name ‘’Rett’’.
His works and writings were not widely known in English-speaking countries at that time because they were written in German.
In 1983, a Swedish pediatrician known as Bengt Hagberg published a health-related article written in English, and he named the medical condition after Rett, and now it is widely known as ‘’Rett Syndrome’’.
In 1999, a Lebanese-American physician called Huda Zoghbi studied and found out the mutation that causes Rett syndrome.
This neurological disorder is usually evident between the ages of six months to two years because, at that stage, they begin to miss their developmental milestones as well as the physical and mental abilities that they had just started to develop.
The disorder is a result of a mutation caused by a particular gene known as MECP2 found in the X-chromosome. In the MECP2 gene, there are more than 900 distinct mutations discovered, and most of them are present in eight different “hot spots.”
Symptoms
The symptoms of this health condition are generally noticed at infancy, usually when the baby is about six months. However, this is only on average because the appearance of the symptoms varies across infants.
The majority of the cases have 6-month babies with apparent signs. In contrast, the symptoms could still be noticed from then until the baby is two years. The common symptoms evident are:
- Loss of speech: From the ages of a year to four years, speech skills begin to decline as well as their social skills. This usually results in the child developing severe social anxiety, and they are likely to stop talking. Again, this affects their interactive skills even with their toys.
- Loss of voluntary use of hands: Children develop hand-moving problems causing involuntary movements of the hand. This could cause them to wring their hands together like they are practicing washing of hands, and most of them lose their ability to use their hands.
- Breathing issues: This is one of the unpleasant symptoms of RTT, where the child develops breathing issues that are characterized by uncoordinated breathing. This could also include hyperventilation, forceful exhalation of air or saliva, and swallowing of breath, and seizures.
- Slowed growth of the head, feet and, hands: Rett syndrome severely affects the proper growth of the brain affecting their intellects, coupled with the fact that the head is typically small due to the declined growth rate of the head. This is also a condition known as microcephaly. The result in stunted growth is more evident as the child grows older.
- Loss of mobility or gait disturbances: The development of muscle coordination issues and loss of muscle tone is a common issue associated with Rett syndrome. This may result in awkward gait and mobility of the sufferer, and loss of specific body movements.
- Overreaction: As children with this medical condition get older, they also tend to get more tense and irritable. They may overreact to situations and cry or scream out loud for a long time, and sometimes, they laugh hysterically for a long time too.
Other symptoms include:
- Impaired sleep patterns
- Growth retardation
- Small cold hands and feet
- Diminished response to pain
- Intense eye communication (eye pointing)
- Bruxism (teeth grinding)
Complications
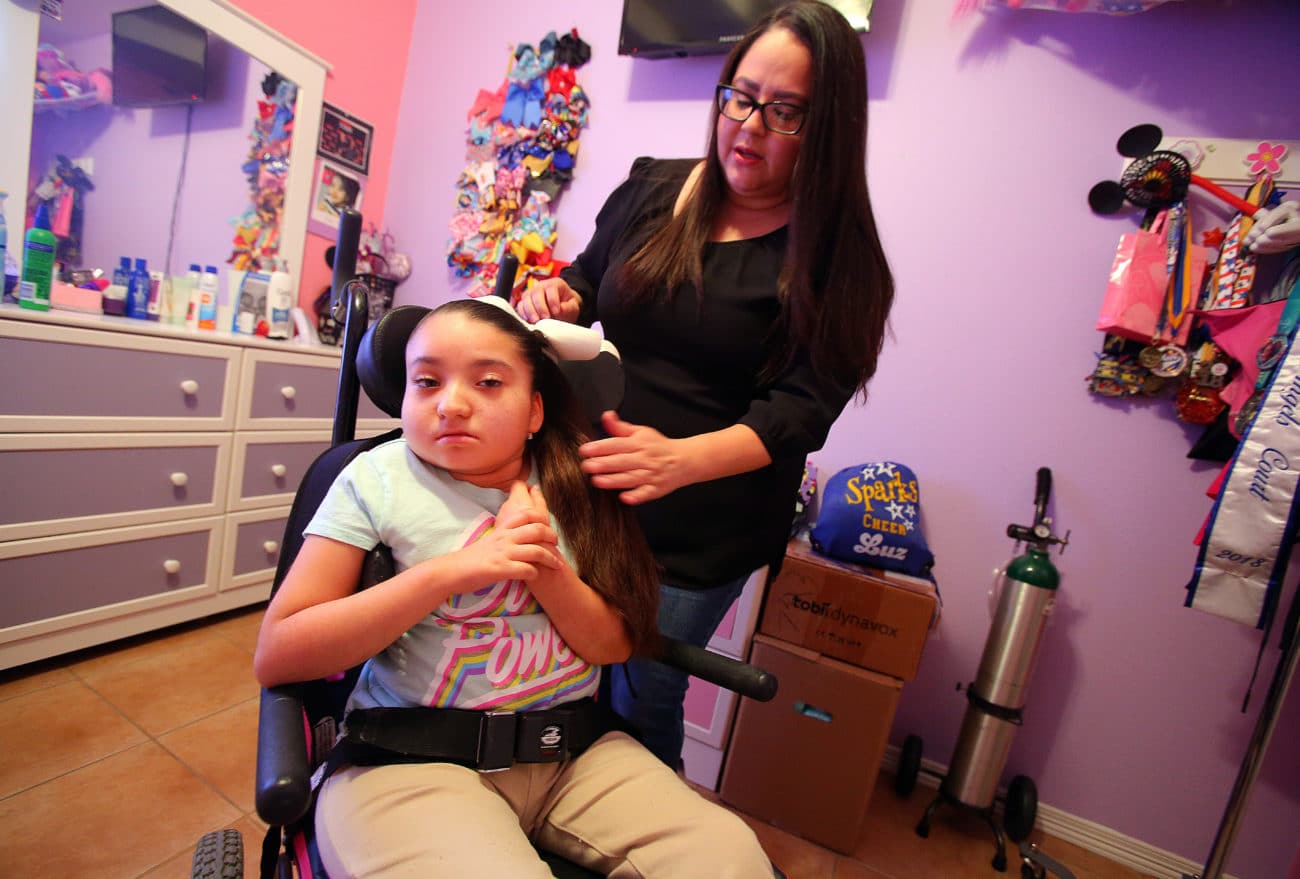
There are complications which may arise if Rett syndrome worsens and some of them include the following:
- Seizures or Rett “episodes”: Episodes of epileptic seizures (apnoea) are manifested in severe cases of Rett syndrome, and in some individuals, these seizures are relatively frequent.
- Scoliosis/ kyphosis: This is a postural defect that is characterized by the abnormal lateral curvature of the spine. Severe cases of Rett syndrome often have the sufferer developing scoliosis.
- Sleep disturbances: The sufferer may also start having disturbed and unhealthy sleeping patterns, which could be a result of livid nightmares, sleepwalking, nigh-time seizures, and bedwetting characterized by night laughing, night bruxism, night screaming, and many more.
Rett syndrome is a life-long disease, and its symptoms, in most cases, do not improve over time. Unfortunately, the symptoms tend to worsen gradually or remains unchanged. It is difficult for people with this medical condition to be able to live on their own independently.
Causes
This condition is a genetic disorder that is a result of gene mutation to the MECP2 gene in the X chromosome. According to researchers, a single gene may influence the other genes involved in development.
Records show that a person living with Rett syndrome are mostly girls because most boys born with this disorder barely make it through birth. This is because boys have only one X chromosome while girls have two, therefore when the only X chromosome gets mutated, they could barely survive after being born.
However, what exactly causes the mutation of the chromosome and what the resulted mutated gene does is unknown to researchers.
Even though the disorder is genetic, infants are not known to have inherited the problematic gene from parents or ancestors, but they are known to have had the mutation occur in their DNA by chance.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing this condition is based on the behavioral patterns of the sufferer. A simple observation on the child’s behavior and by mere talking with the child’s parents about the noticed symptoms and when they became evident could be enough to diagnose this condition.
Because Rett syndrome is a rare condition, doctors will have to narrow down the symptoms to the actual cause.
To narrow Rett syndrome down, the doctor will have to cancel out all other possible conditions such as cerebral palsy, prenatal brain disorder, autism spectrum disorder, and metabolic disorders. To do this, genetic testing may be conducted to help confirm the condition.
These tests help in the diagnosis of 80% of girls suspected to have Rett syndrome, and they also predict the possible futuristic severity.
Treatments
Rett syndrome has no cure yet, but some treatments can be applied to manage the condition by controlling the symptoms. Medical assistance from a multi-disciplinary health team could give the sufferer the best medical care while addressing the symptoms.
This medical assistance team is needed throughout the patient’s lifetime.
Again, some patients may need exclusive resources and aids to help their movements and help correct certain postural defects. These types of equipment may include: Scoliosis braces to stop the progression of scoliosis, splints to modify hand movement, and more.
This multi-disciplinary medical team may include:
- Primary care physician
- Physical therapist
- Occupational therapist
- Speech-language pathologist
- Nutritionist
- Support services in academic and occupational settings.
The team offers best treatment options available for treating of Rett syndrome including:
- Standard medical care
- Physical therapy
- Speech therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Good nutrition
- Behavioral therapy
- Supportive services
The use of medicines such as anticonvulsants is applied to help in controlling episodes of epileptic seizures. The use of medication can be used to treat mobility problems. Experts believe that therapy can help both the patient suffering from Rett syndrome and their parents.
Treatments applied properly may help in stopping the condition from getting worse and allowing some girls to be able to go to school and other social places to interact and learn. Fortunately, many people with Rett syndrome can live into middle age and beyond.
Have you had to take care of a family member or friends with Rett syndrome? What were the steps you took to manage the condition? Kindly share your experience with us in the comments below.
References;












