Wilson’s disease is a disease that is very rare. It is an inherited disorder that causes the accumulation of copper in a person’s vital body organs such as the lifer, the kidney and it may even go as far as having accumulation of copper deposits in the brain. It is a disease that affects both men and women and both the young and old.
Wilson’s disease can be otherwise called hepatolenticular degeneration or progressive lenticular degeneration. Normally, in a healthy body, copper is absorbed from food and it plays a very important role in the body most especially in the development of several nerves in the body, bones and also maintenance of the melanin pigment.
Under normal conditions, a health body absorbs copper from food and is excreted through an excretory substance gotten from the liver also known as bile. The liver filters out excess copper and then passes the excess copper through urine.
When a person has Wilson’s disease, the person will experience inability to pass out and filter copper from the liver i.e. the lifer can’t filter excess copper out properly from the body.
Then this excess copper will enter into the blood stream and then go build up in other organs of the body such as the lifer, the brain and also the eyes. These three different organs are invariably the most affected organs when it comes to Wilson’s disease. Wilson’s disease is caused by gene mutation.
A mutation in the ATP7B gene which is the gene that is found on chromosome 13 essential for the encoding for the transportation of copper is what is responsible for Wilson’s disease. Wilson’s disease is an inherited disease which then means that you got it from either a parent who has the disease or a parent who was a carrier of the disease.
People with Wilson’s disease experience the accumulation of copper in all major organs of their bodies. Too much copper in the body especially in the liver cells will lead to very harmful liver conditions and eventually lead to liver failure.
Wilson disease is classified under autosomal recessive disorder. This means that a person can only get this disorder if there is an inheritance of two abnormal ATP7B genes, one from both parents (I.e. one from the mother and another from the father).
If a person should inherit just one abnormal ATP7B gene, the person is only considered as a carrier of the disease. Carriers usually don’t have this disorder, and this is because they have one abnormal gene and another normal gene.
The normal gene will end up controlling the effects of the abnormal gene and besides, one gene is enough to control the rate at which copper is absorbed by the body.
However, it is completely possible for a carrier father or a carrier mother to pass this abnormal gene to their offspring.
There are four different stages of Wilson’s disease and they include
- Stage 1: In this stage, there is severe accumulation of copper found within the hepatic binging sites in the liver.
- Stage 2: There is a redistribution of copper within the liver cells and then the excess thereby spills into the bloodstream
- Stage 3: Copper flows to the brain through the bloodstream and as well go to other organs causing fatal and severe disorders
- Stage 4: When treatments occur, the restoration of the balance of copper via chelation therapy.
There are several symptoms to be experienced at the key three organs (the liver, the kidney and the brain). At each organ, symptoms aren’t exactly the same.
For the purpose of this article, these symptoms will be described and highlights in accordance to the organ in which the symptom can be found.
Liver related symptoms
The first set of symptoms to be experienced are related to the liver. This is because the toxic effect of the copper will first of all hit the liver and then begin to cause liver problems.
When there is an accumulation of copper in the liver, the following symptoms will be experienced.
They include:
- Tiredness: The disease may begin to present as severe tiredness and weakness. The patient will get weak all the time.
- Excessive weight loss and vomiting: The patient will experience rapid and excessive weight loss and will be unable to digest food well or keep food down.
- Severe itching
- Jaundice due to liver failure
- Swelling of upper and lower extremities caused by the accumulation of copper in the muscles and also due to fluid retention
- Bloating and severe pain experienced in the abdomen
- Severe muscular cramps and muscular shocks
- The presence of a spider-web like structure made from the excessive branching of blood vessels on the skin. This is a condition known as spider angiomas
Brain related symptoms
Copper accumulation in the brain can lead to the following effects namely:
- Memory and speech impairment: The accumulation of Copper in the brain can lead to interruption of brain wave signals most especially if it gets to the speech and memory area of the brain.
- Abnormal walking due to lack of coordination
- Severe migraines
- Inability to control one’s involuntary actions.
- Inability to sleep properly or inability to sleep at all causing insomnia.
- Lack of coordination, causing clumsiness.
- Severe depression most especially when it hits the emotional center of the brain.
- Inability to concentrate on anything for long. So most especially for students, it will tend to distrust their capacity to concentrate on anything.
- Rapid personality changes.
When this condition becomes advanced without treatments, it can lead to the following more complicated brain problems:
- Muscle spasms
- Seizures
- Severe muscular pain most especially during movements.
Eye related problems
There are two distinct symptoms to be noticed most especially when there is an accumulation of copper in the eyes and they include:
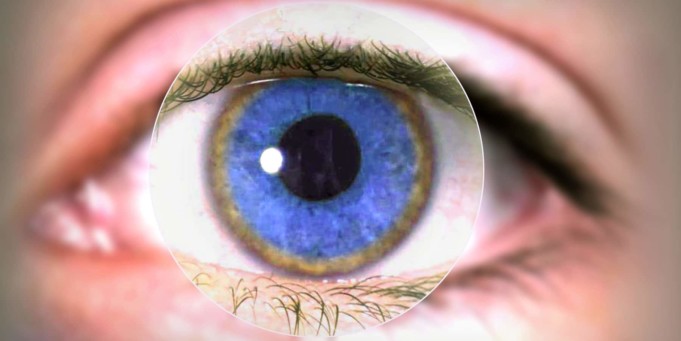
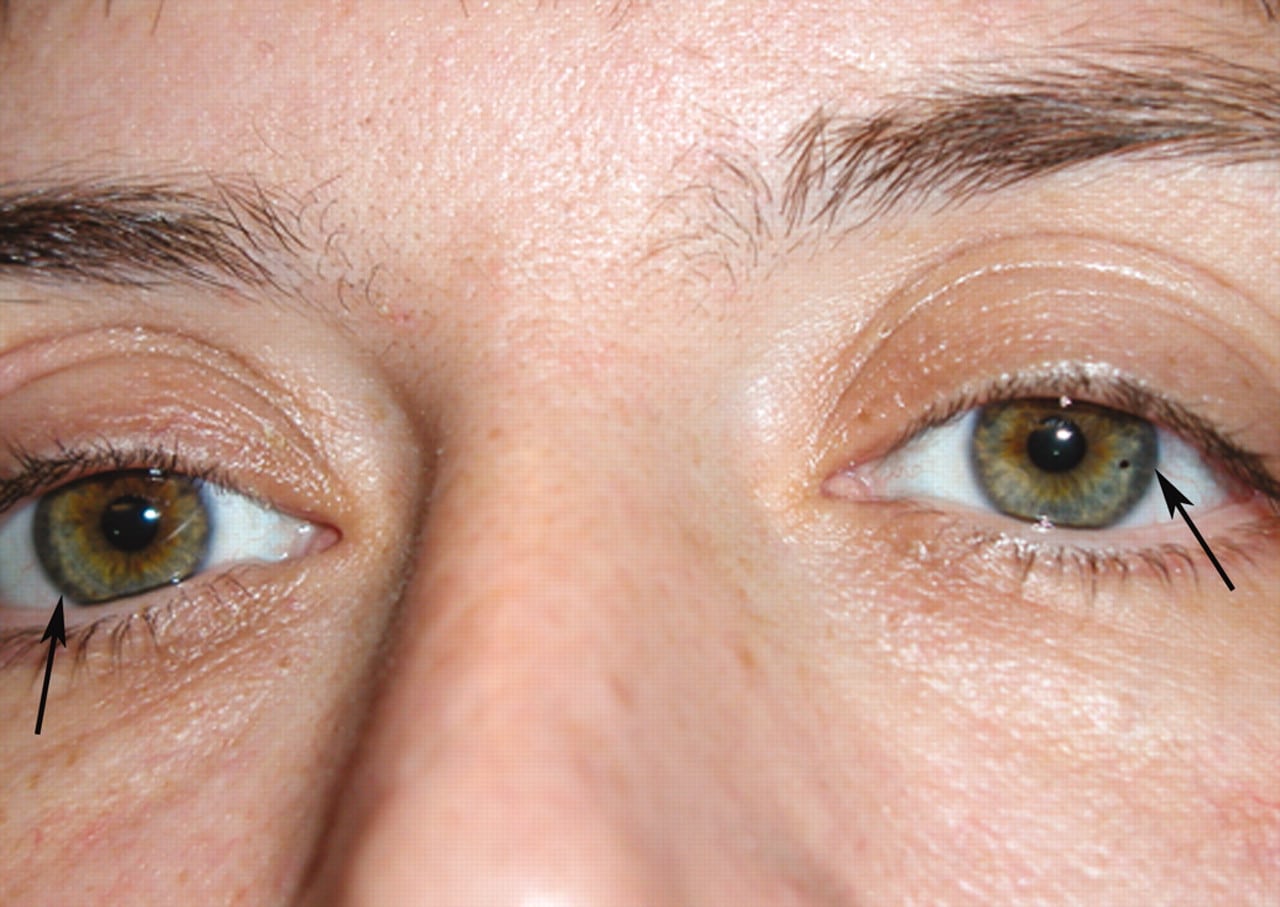
- Kayser Fleischer rings: This occurs when there is an accumulation of copper in the eyes. This is seen as an abnormally brown ring coloured pigmentation that begins to cloud the cornea of the eyes.
- Sunflower cataract: Sun flower cataract occurs when there is an appearance of a brown or green coloration on both the anterior and posterior capsule of the lens.
Asides these symptoms, there are some other symptoms that are exhibited in other parts of the body and they are kidney problems (that involves acidosis of the renal tubules which can lead to accumulation of calcium in the kidneys also known as nephrocalcinosis, brittle bones or weak bones caused as a result of severe loss of calcium and phosphorus, and a condition called amino aciduria), heart problems (severe weakness of the muscles of the heart leading to severe cardiomyopathy, heart failures and also irregularities in the heartbeats otherwise known as cardiac arrhythmia), blood problems (hemolysis might occur due to excessive flow of copper in the blood stream and this may lead to severe anaemia as well as jaundice).
Wilson’s disease can easily be diagnosed in the clinic via the conduction of a blood test to check for the levels of caeruloplasmin, a urine test to check for the levels of copper in the urine, a liver biopsy to show any traces of excessive amounts of copper within the liver and also to show if there has been any scarring of the liver as this would determine if there is an acute liver failure or not.
If there are traces of excessive amounts of copper in the body or any of these symptoms have been identified, treatments is actually better started early before any damage is done to the brain or to the liver.