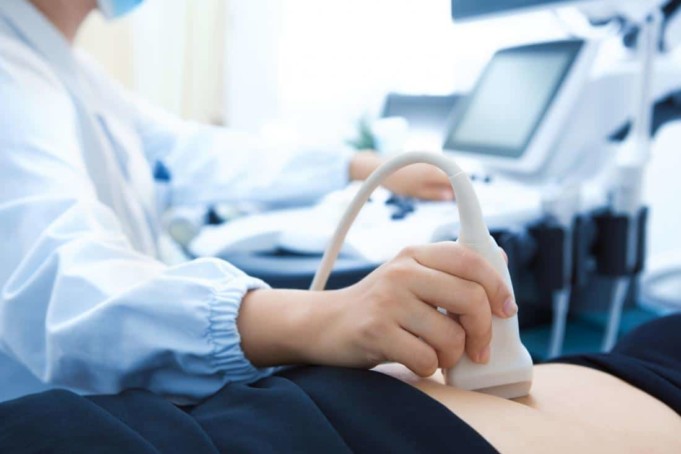
Ultrasound is a word used almost casually all the time and it is common amongst pregnant women. An ultrasound also called sonography is a medical test that is used to capture/obtain live images or pictures from within your body.
Ultrasound can be used to determine fetal development, detect a problem in the abdomen, heart, liver, pancreas, etc and unlike Xrays, it does not use radiations. Images produced by an ultrasound scan is called Sonogram.
Uses/Reasons for Performing an Ultrasound
Some people believe that an ultrasound scan is only associated with pregnancy. Although it provides expectant mothers with the first view of the unborn child. An ultrasound can also help to diagnose various conditions and also assess the damage of an organ.
An ultrasound scan can provide a view of the Brain (in children), kidneys, ovaries, pancreas, testicles, liver, uterus, gallbladder, spleen, etc
Reasons for the Use of ultrasound imaging include;
- To image breast and guide biopsy of breast cancer. Ultrasound helps produce sonograms to help doctors detect lumps and collect tissues for biopses.
- To diagnose various heart conditions such as congestive heart failure. It gives the doctor information about the size of the heart, the pumping rate and the state of the hearth valves.
- To diagnose tumors and malfunction of congenital vascular.
- To diagnose blockage of blood flow (blood clot). This type is called the Doppler Ultrasound that relies on sound waves.
- To reduce blood flow to some organs such as ovary or testes.
- Ultrasound is majorly used for detecting appendicitis in most hospitals in children. Since children may not have a way to exolain themselves clearly, ultrasound helps solve this problem by providingthe doctor with the informaton needed.
- Help physicians find a path of insertion when using an intravenous line if it is difficult to detect a vein
- Pregnancy: Ultrasound images gives lots of intricate details to the doctor about pregnancy. Thins includes the age of the developing baby, its position in the womb, its health and probably is sex.
- Abdominal Issues: Ultrasound is used when a patient has abdominal pains, loating or swelling. It also makes it easier to images if the patient is obese or difficylut to scan.
Preparation for an Ultrasound
Preparing for an ultrasound scan shouldn’t make you feel scared this is because there are no needles and injections. You may need to take off your clothes and pieces of jewelry in the ultrasound scan area.
Depending on the type of examination, your doctor may ask you not to eat for about 8-12 hours before the ultrasound especially if your abdomen is to be examined.
If the examination is to be done on the liver, pancreas, gallbladder or spleen, the doctor may ask you to eat a fat-free meal 24hrs before the procedure. For some other examination, the doctor may ask you to drink a lot of water and hold your urine so that the bladder is full.
How an Ultrasound is Performed
You will be likely asked to lay down on a table exposing the part of your body that will be scanned. A sonographer (an ultrasound technician) will then apply a special lubricating jelly that helps to transmit sound waves on your skin that will prevent friction when the ultrasound transducer is rubbed against your skin.
A transducer looks similar to a microphone and it sends high frequency sound waves through your body. When these sound waves hit dense objects such as a bone or an organ, they echo and the echo is reflected back into a computer which then creates a real-time picture on the monitor.
You may need to change position depending on the area that is being examined to enable the sonographer to have better access. The procedure lasts less than 30mins and the jelly is wiped from your skin.
In some ultrasound scan cases, the transducer is inserted into natural openings in the body. Some examples of these ultrasound scans include;
- Transvaginal ultrasound: This scan is done to view a woman’s ovaries and uterus. In this case, the transducer is inserted into the woman’s vagina.
- Transesophageal Echocardiogram: This ultrasound is done to obtain and view images of the heart. The transducer will be inserted into the esophagus in order to carry out this scan.
- Transrectal ultrasound which is done to view prostate in males (the transducer is inserted into the man’s rectum)
- Doppler Ultrasound: This type of Ultrasound uses sound waves to produce images of the body structure and organs. It is usually painless and it is a special type of ultrasound. It relies on its waves to detect movement of blood in your blood vessels. Doppler Ultrasound can produce results in Color, Graph or advanced color.
After an Ultrasound Procedure
After an ultrasound, a radiologist(a doctor who is trained to interpret radiology exam) will review the result of the scan and check if there are any abnormalities.
If the transducer was inserted into any of the body’s natural openings, it may cause minimal discomfort during and after the procedure. The doctor will call you and discuss the result/findings of the scan and depending on the findings, a followup appointment may be scheduled.
If the result of the imaging shows any abnormalities, diagnostics techniques such as MRI and CT scans may be carried out. And if the doctor was able to diagnose your condition based on the ultrasound findings then you may begin immediate treatment.
Benefits of Ultrasound
Some known benefits of ultrasound include;
- There is no need for injections and needles because ultrasound is noninvasive.
- It doesn’t use radiation so it is completely safe.
- Ultrasound scan provides you a real-time image.
- It provides clear pictures of soft tissues that may not be clearly shown on x-ray images.
- It is less expensive and easy to use among other imaging methods.
Demerits or Limitations of Ultrasound
Although standard ultrasound diagnostics do have a known harmful effect on the human body, it has a few limitations. Some of these limitations are listed below;
- It is not useful for air-filled lung imaging.
- It does not penetrate bones but can be used to image the area surrounding the bone.
- Its wave can be disrupted by gas or air.
References;
- What is Ultrasound: Overview, Benefits, and Expected Results; DOCDOC