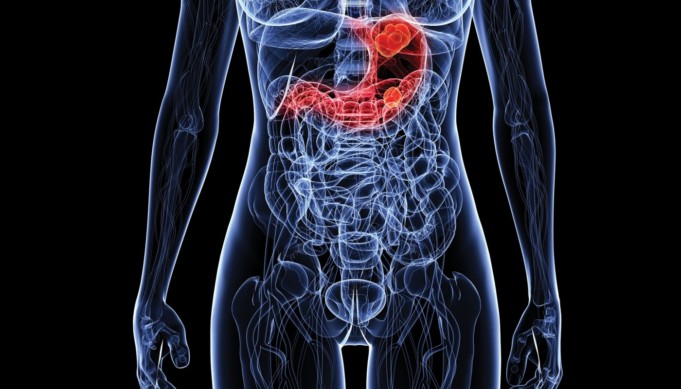
Stomach is also known as gaster. Stomach is a dilated part of gastro-intestinal tract (git) or alimentary canal which is responsible for digestion of food substances before it is being absorbed in the intestine.
Stomach cancer is also called gastric cancer. Stomach cancer is an abnormal proliferation and abnormal growth of cells in stomach lining.
This stomach cancer is due to the presence of carcinogen, malignant cells and toxic substances that act as or like a carcinogenic substance which invariably causes stomach cancer. Stomach cancer occur when normal healthy cells in the proximal digestive cell becomes cancerous and grow out of control forming tumor and becoming malignant.
This type of cancer is difficult to diagnose because most people typically don’t show symptoms at early stage. Since stomach cancer does not cause early symptoms, it often goes undiagnosed until after it spreads to other part of the body which makes it more difficult to treat.
Danger of this cancer is that it is difficult to diagnose.
Causes of stomach cancer
Stomach cancer is directly proportional, characterized or linked malignancy and Tumor in the stomach(gaster). Factors that result to growth of cancerous cell in the stomach are not easily identified.
Nevertheless, there are some factors that might increase the risk of developing the cancerous cells within the stomach. These includes the following:
- Infection by bacteria within the stomach: This bacterium is called helicobacter pylori which causes ulcer and at the same time can also increase the risk of an individual to develop stomach cancer.
- Inflammation in the esophagus(gut): Inflammation of the esophagus can cause development of cancerous cells and accumulation of malignant cells which may move down into the stomach through the gastric-esophageal junction. Ultimately, his can result into stomach or gastric cancer.
- Long lasting anemia called pernicious anemia: This is a type of anemia that is caused by deficiency of vitamin B12 which is an important factor that is required for production and development of normal size and shape of red blood cell (erythrocyte). Deficiency of vitamin B12 will lead to production of abnormal red blood cell (erythrocyte) which will ultimately be constantly destroyed before the end of it’s life span by destructive cells( phagocytic cells) as a result of abnormality in the shape of the red blood cells. Therefore, there will be shortage of red blood cell in such an individual. This condition is called pernicious anemia.
Pernicious anemia can also be as a result of lack of intrinsic factor which are responsible for the absorption of vitamin B12.
- Polyps (growth in the stomach): This is the abnormal growth of cell or tissue that forms lining of cells in the stomach.
- Lymphoma: This is malignant tumor that arises in lymph nodes or in other lymphoid tissue.
Other causes may include:
Other causes that may increase the risk factor in an individual to develop stomach cancer may include:
- Eating of salty or processed food
- Eating too much meat
- Alcohol abuse. That is, chronic alcoholism (taking too much alcohol).
- Lack of exercise
- Overweight or obesity (presence of too much fat cells or tissue in the body)
- Gastrectomy (stomach surgery)
- Certain or some genetic mutation(changes).
- Exposure to asbestos
Note: Gastric or stomach cancer is also more common among the following individual:
- Older adult (50 years above)
- Smokers
- Male are at higher than female.
Signs and symptoms
Stomach is responsible for digestion of food substances and other nutrient with other parts of the gastro-intestine part before it is being absorbed by the intestine (small and large intestine).
Therefore, if there is tumor and abnormal growth of cancerous cell in the stomach lining which is termed stomach cancer, the following may be seen as sign and symptoms.
- Indigestion that does not resolve: one of the functions of the stomach is to digest food. After that, it moves the food down to the intestine, then the food is absorbed to the body. If there is stomach cancer, the cells that are inside the stomach have become cancerous (enlarged). Instead of the cells to secrete the normal digestive enzymes to make the food digest (breakdown), it will be unable to secrete the acid that will help to breakdown the food. This symptom now leads to sensation of being very full during meal. The food in the body can not digest and cannot move to the small intestine. So, indigestion that does not resolve means that food will not be digested because the cells that are responsible for digestion of food in the stomach have become abnormal.
- Trapped wind: The junction at which the esophagus connects with the stomach is called gastro-esophageal The windpipe is also known as the esophagus(gut). When we eat food, it moves down from the mouth to the esophagus(gut), then the food moves from the gut through the gastro-esophagus junction which then enters the stomach. In a case whereby the food has refused to digest, it leads to constant increase of air inside the stomach due to undigested food substances. This can pressurize the air in the stomach to enter back into the esophagus. Hence, when the air moves back into the esophagus, it will come back to the mouth. This makes air to be trapped between the stomach and gastro-esophagus junction which connects the stomach and the esophagus down to the esophagus itself.
- Hematemesis (vomiting of blood): As a result of accumulation and presence of cancerous cell, malignant cell and abnormal proliferation of stomach cells may lead to injury or damages in the stomach which invariably may also cause gastro-esophageal-reflux-disease(GERD) causing vomiting of blood in a stomach cancer patient.
- Nausea: This is an irritation in the digestive tract as a result of stomach cancer.
- Frequent heart burn: Stomach cancer can lead to gastro-esophageal-reflux-disease (GERD). This means that food substances that are present in the stomach may move back into the esophagus as a result of gastro-esophageal-reflux-disease. This can cause heart burn because the food substances that is moving from the stomach to the esophagus already contain some digestive enzymes which already result in heart or chest burn.
- Bloody stool: Due to presence of carcinogenic cell, injury or damages may be done to the stomach which may result to the present of blood in stool.
Other symptoms may include:
- Sensation of being very full during meal
- Swallowing difficulty
- Feeling bloated after meal
- Loss of appetite
- Stomach pain or ache
- Jaundice
- Excessive fatigue
Prevention of stomach cancer
Stomach or gastric cancer does not have a specific or generally accepted preventive procedure. This can, however, be prevented by avoiding the following:
- Avoid eating too much meat
- Avoid excess alcoholic intake
- It can also be prevented by constant exercise
- Avoid smoking
- Avoid taking salty food
- Avoid Exposure to asbestos
Note: Stomach or gastric cancer can be prevented by trying as much as possible to avoid all the above-mentioned factors that can increase the risk of stomach cancer.
Diagnosis of stomach cancer
Doctors and physicians would first perform or conduct physical examination on patient to ascertain or know any abnormality. Similarly, certain diagnosis can be conducted.
- Test for presence of helicobacter pylori bacteria.
- Endoscopy: This is a means or procedure that is carried out for diagnosis of stomach cancer by the use of an instrument called endoscope. The endoscope presents a camera that can be used to view the internal organ after the instrument is inserted into the individual.
- Biopsy: This is a diagnostic procedure that involves the collection of living cells and tissue from a stomach cancer patient for laboratory analysis to ascertain if the cancerous cells are malignant cells or tumor cell.
- Imaging test such as C.T (computerized tomography) scan and x-ray. This involve visual imaging if cancerous cell and tissue as a diagnostic procedure for stomach cancer.
Treatments of stomach cancer
Prompt and instant treatment of cancer cells in the stomach is very essential in order to prevent the spread of such cancerous cells. If the stomach cancer is left untreated, it may spread to other vital organ of the body.
That is, the lungs, liver, esophagus, bones, lymph nodes. However, stomach cancer can be treated by one or more of the following
- Chemotherapy: This is a procedure that involves the use of chemical therapy or treatment in order to convert stomach cancer. It is either to prevent further spread or to manage the condition.
- Gastrectomy: This is also known as stomach surgery. It is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the stomach part that is being affected by the cancerous cell.
- Immunotherapy: This involve the use of medication, drugs or vaccine.
Conclusion
Stomach or gastric cancer is a medical condition characterized by abnormal proliferation of cells, and presence of tumor or malignant cells including cancerous cells.
This condition has several medical implications which may include indigestion, feeling feed after taking little quantity of meal and other detriment impact.
Therefore, if an individual is showing any of the above-mentioned signs and symptoms, such individual is advised to seek a medical help immediately. This is because, if stomach cancer is untreated, it can lead to further medical complications.