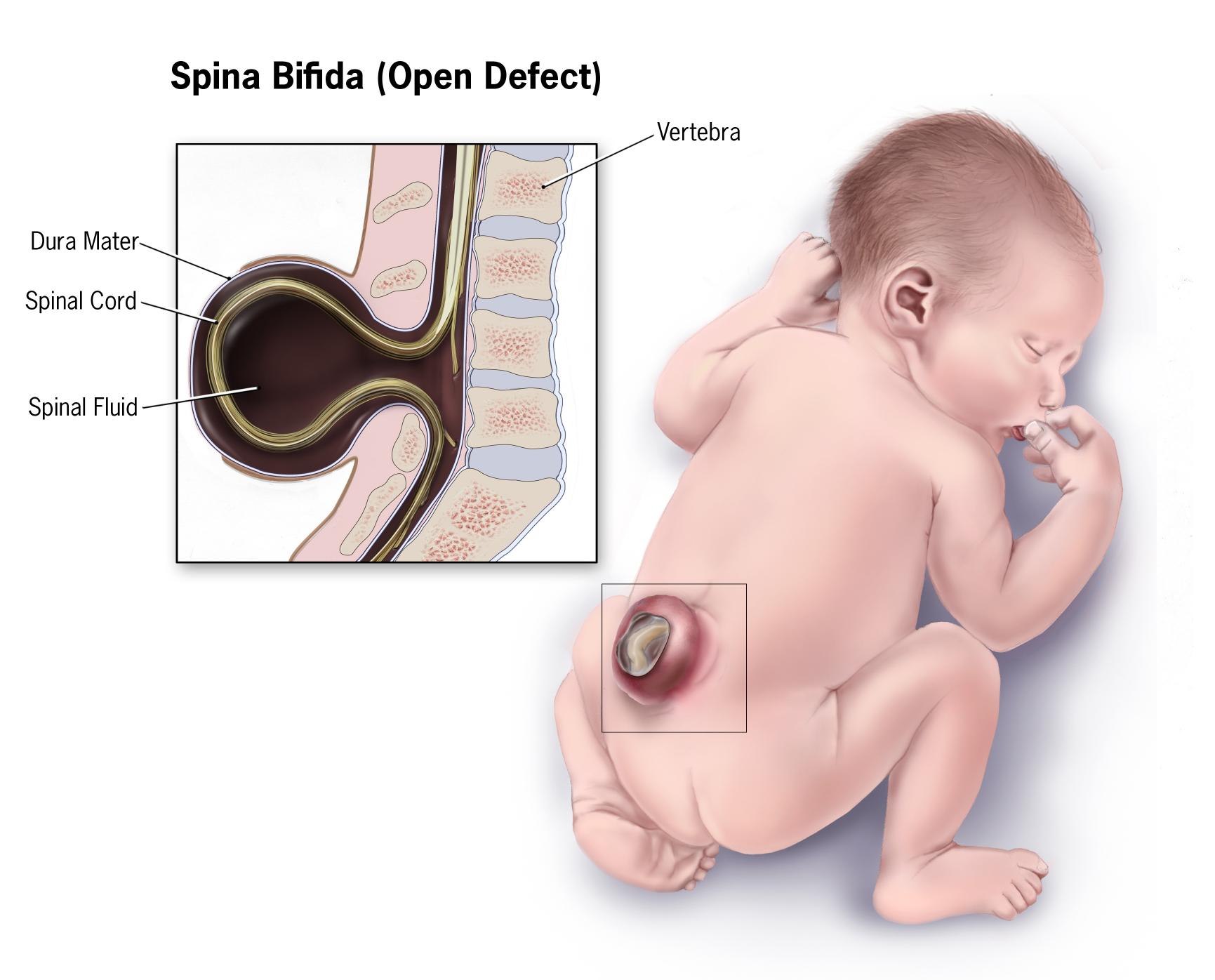
Spina bifida is a relatively common developmental defect that occurs during pregnancy. The word Spina Bifida is a Latin word that can be translated into English as “Split Spine.”
Generally, during pregnancy, the baby is expected to be entirely formed before delivery. The Spinal cord is not left out as it is formed during the 3rd and 4th week of pregnancy.
However, when there is a problem that causes the spine not to close during the third and fourth weeks of pregnancy altogether, then there is a problem.
Generally, there is a group of cells that are known as the neural crest cells which come together to form the neural tube. These cells, during the developmental formation of a child, closes up to form both the brain and the spinal cord.
Once a baby has a disruption in the closing of the neural tube such that it doesn’t close all the way, this will cause the spine also known as the backbone of the body to incompletely form and as such, causing defects in the formation of the spinal cord as well as the vertebrae. This, in turn, causes mental as well as physical problems to the baby.
According to research, this congenital disability is quite common as it has been seen that about 2000 babies out of 4million babies that are born every year are born with this congenital disability.
The effects of Spinal Bifida can differ, ranging from mild to extremely severe, depending on the type of defect that caused it, the location of the abnormality, how large the defect is as well as complications that are as a result of the defect.
Types of Spinal Bifida
Spina bifida has been seen to not only occur in one particular way but several ways. These ways have been noted to cause three significant types, and they include:
1. Spina bifida Occulta
This type of spina bifida is also referred to as “Hidden spina bifida.” In this type, it is seen that both the spine and the spinal cord of the baby are healthy.
The nerves which come out of the spinal cord are also seen as normal. There is likewise no opening at the back, and sometimes, it is difficult to detect.
However, there is a problem as there are tiny spaces that are present within the vertebrae. Generally, the vertebrae are small bones that come together to form the spine collectively.
Usually, there aren’t supposed to be gaps within the vertebrae, and when those gaps form, it causes a type of deformity known as Spina Bifida Occulta.
In so many reported cases, the child goes on to live a healthy, perfect life without any form of disturbances in the spinal function. Most times, it goes on undetected, and as such, most people aren’t aware they have it unless they, for one reason or another, go to have an Xray.
However, in rare cases, people with this kind of defect may experience some problems.
Symptoms like neurological disabilities, lack of coordination, bladder dysfunction, lack of control of bowel movement, back pain, weakness of the lower limbs, as well as scoliosis are often experienced by people who have Spinal Bifida Occulta.
2. Spinal Bifida Meningocele
Spinal Bifida Meningocele, commonly referred to as Meningocele, most times occur as a result of the inability of the bones around the spinal cord to properly close up and, as such, cause the meninges to be pushed out via the opening hence resulting into the formation of a big fluid-filled sac.
The meninges are the coverings that are found around the brain and spinal cord, and they are divided into three, namely, the pia mater, the dura mater, and the arachnoid mater.
In the cases of Meningocele, only the meninges are affected; the brain and the spinal cord are left intact. The spinal nerves also are not damaged or severely affected.
This type of Spinal Bifida is often regarded as the rarest form of spinal Bifida, and it can be corrected through surgery.
3. Spina Bifida Myelomeningocele
Myelomeningocele is the most common type of spina bifida. According to research, it accounts for almost 75% of patient cases. In addition to it being the most common type of spina bifida, unfortunately, it is the most severe type.
Myelomeningocele occurs when the spinal cord gets out of the spinal canal as well as the meninges and ends up protruding through the back.
In some cases, the spinal cord may be covered in a sac; however, more often than not, the nerves are exposed as well as the spinal cord and, as such, complicating the case.
The extent of the disability that is formed by this type of congenital disability depends on the location of the defect as well as how severe the deformation is.
According to the cases reported and the doctors’ assessment of this type of condition, if the disability occurs in such a way that only the bottom part of the spinal cord is affected, it may only result in bladder malformation and bowel dysfunction,
However, in more severe cases, it often affects the entire length of the spinal cord, causing total paralysis of the lower limbs as well as bladder and bowel dysfunction.
Causes
The exact cause of this congenital disability hasn’t been discovered yet by doctors and researchers. However, some doctors speculate that spina bifida could be as a result of a combination of genetic factors as well as a host of environmental disturbances.
Factors such as Vitamin B9 deficiency, as well as a history of neural tube defects in the family can play a vital role in causing Spina Bifida.
Symptoms of Spina Bifida
The symptoms of Spina Bifida vary based on the type which has caused the condition.
Also, the symptoms may vary based on individual differences as well as the severity of the congenital disability. Based on the type of Spina Bifida that occurs, the symptoms can be classified as follows
1. Based on Spina Bifida Occulta
Generally, there are typically no signs or symptoms that are associated with this kind of spinal defect. This is because often, the spinal nerves are not affected or deformed. Some people go through life without having any worries or troubles.
However, in some cases, on a newborn who has this spinal defect, one would notice the presence of an abnormal turf of hair, or a dimple or birthmark just around the lower vertebrae.
Sometimes, the baby may experience skin marks, which is maybe a result of an underlying spinal cord defect. This defect is only noticed when the child is taken for a spinal ultrasound or an MRI scan.
2. Based on Spina Bifida Meningocele
In this case, both the spinal cord as well as the meninges which cover them are healthy, however, the child will experience protrusion of the spinal cord through the opening, which in turn will cause the formation of a sac.
However, through the protrusion, the spinal cord is kept safe by the meninges, which also are not affected.
3. Based on Spina Bifida Myelomeningocele
This is the severe form of Spina Bifida, and the symptoms that may be experienced by the child include:
- The opening of the spinal cord which remains along the vertebrae in both the middle and lower backs.
- The newborn will experience the protruding of both the spinal cord as well as the membranes covering it. This protrusion often occurs at birth and, as such, will form a fluid-filled sac.
- There is a tendency for both nerves and tissues to become exposed; however, in most cases, skin always covers the pouch.
Risk factors associated with Spina Bifida
There are some factors that put one at the risk of developing this congenital disability, and these factors include:
1. Race
According to research, Spina Bifida has been seen to occur mostly among the whites and Hispanics than in other races, such as blacks and Asians. The reason for this is not known, but it has been speculated that this is a result of environmental factors.
2. Gender
Females mostly develop this congenital disability. According to research, in every 1000 children that are born, 50 children are affected, and 30 are most likely to be females. Hence, females are seen to be more affected than men.
3. Folate Deficiency
A folate is a natural form of Vitamin B9. It is one of the vitamins that are very vital and are needed for the healthy development of a newborn.
However, when this vitamin is lacking, then there could be congenital disabilities such as Spina Bifida. Folic acid, which is often found in food supplements as well as fortified foods, is the synthetic form of folate.
Once either folate or folic acid is deficient, the likelihood of developing congenital disabilities increases by 50%.
4. Family History
Once there is an underlying family history of neural tube defects, there will be an increased chance of the baby developing Spina Bifida.
Research has shown that parents who gave birth to their first child having a neural tube defect will most likely have their other children with the same congenital disability.
The risk of the third child having neural tube defects increases if the other two children also developed neural tube defects.
However, the increased number of children who have spina bifida are born to parents who have had no kids or no family history of neural tube defects.
5. Drugs
Some medications that have been taken in when the mother was pregnant can put the child at the risk of developing congenital disabilities such as Spina Bifida.
For example, some anti-seizure drugs such as Depakene(Valproic Acid) have been seen to cause neural tube defects in pregnancy.
This sometimes occurs because the drug has the ability to dampen or hinder the baby’s ability to use folate as well as folic acid for its development. As such, this drug is highly recommended to women who aren’t pregnant.
6. Diabetes
Women who already have diabetes, especially type II diabetes, have a higher risk of giving birth to babies with Spina Bifida.
7. Obesity
Obesity before pregnancy, which is otherwise known as Pre-Pregnancy Obesity, is always associated with increased chances of the baby having neural tube defects, including Spina Bifida.
8. Untreated Increased body temperature
According to research, some evidence has shown that hyperthermia, which is also known as increased body temperature during the early weeks of pregnancy, can increase the chances of the baby developing Spina Bifida.
If, as a pregnant woman, you enjoy visiting the saunas and using the bathtub to elevate your body’s core temperature or you have an untreated fever, which increases your body temperature, then you are possibly increasing the chances of your baby developing Spina Bifida.
Complications associated with Spina Bifida
Spina Bifida Occulta may cause minimal problems as well as minor physical disabilities. However, generally, the other types of Spina Bifida may cause major physical complications.
The severity of the difficulties that can arise as a result of Spina Bifida can be due to the following reasons;
- The location of the defect
- The size of the defect
- Does skin cover the affected area or not?
- Do spinal nerves come out of the affected area? If yes, which spinal nerves?
There are different types of complications that can result as a result of Spina Bifida, and this list may seem overwhelming; however, it is not all these complications that can happen to one child all at once, and more often than not, these complications can be corrected.
1. Motility and walking disturbances
If the lower end of the spinal cord is affected, then the nerves that control the muscles of the legs may be damaged and, as a result, may cause walking problems as a result of muscle weakness or complete paralysis depending on the severity of the nerve damage.
For your child to be able to walk properly will depend on the location of the defect, how large the defect is, as well as the type of care they receive to correct the deformity.
2. Orthopedic disturbances
Children who were born or developed Myelomeningocele have been seen to have a range of problems in their legs and spine due to the presence of weak leg and back muscles. The difficulties developed also is dependent on the location of the defect.
The kind of orthopedic disturbance which can occur include scoliosis(also known as the curved spine), Abnormal growth of the limbs and back, dislocation at the hip, joint and bone deformations, as well as muscle contractures.
3. Bladder and bowel malformations
Once there is a problem with the lower end of the spinal cord, the nerves that supply the bowels and the bladder, which usually come out from this area, end up becoming affecting and, as such, will not function properly.
This kind of abnormality mostly occurs when the child has Myelomeningocele.
4. Accumulation of fluid in the brain
Hydrocephalus, which is also known as fluid in the brain, is often a result of Spinal Bifida Myelomeningocele. This is a common condition that occurs, and it is associated with a build-up of pressure within the brain, which in turn causes severe swelling of the head.
5. Shunt Malfunction
Usually, when a child has hydrocephalus, shunts are placed within the brain in order to help drain the fluid and relieve the pressure that is accumulated there. However, these shunts can stop working effectively or can begin to malfunction due to infections.
There are certain signs that one would experience that will show that these shunts have stopped working effectively. They include:
- Intense headaches
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sleepiness
- Constant irritability
- Redness or inflammation present within the shunt
- Mild or severe confusion.
- Changes in the eyes such as drooping eyelids
- Troubles experienced during feeding
- Seizures.
6. Chiari Malformation Type II
Chari Malformation type II is a common brain malformation that is often associated with Spina Bifida Myelomeningocele.
This abnormality is a result of the brain stem(which is the lower part of the brain, close to the spinal cord) becoming elongated or positioned lower than usual.
As a result of this new positioning, the newborn will experience difficulties in swallowing, as well as breathing. Sometimes, compression in this area is felt, and mostly a corrective surgery is needed to relieve the pressure that is caused as a result of this compression.
7. Meningitis
Meningitis is often as a result of the presence of an infection within the meninges(coverings) of the brain. This condition is associated with babies who have developed Myelomeningocele.
This condition, if not treated immediately, can result in a potentially life-threatening situation or cause brain injury.
8. Tethered Spinal Cord
This condition is often as a result of the spinal nerves binding to the scar, which was formed where the defect was closed surgically. Once this occurs, the spinal cord is hampered form growing as the child grows.
When this tethering progresses, it causes the loss of muscle function in the legs, bladder, or bowel. Hence, the child lacks the inability to be able to use his legs properly, as well as will experience both bowel and bladder malfunctioning.
Surgery may be needed. However, it doesn’t completely cure the disability; it only helps to improve the function of life.
9. Sleep disoriented breathing
Adults and children who have Spina Bifida Myelomeningocele experience sleep disorders, especially sleep apnea.
10. Skin distortions
Children who have Spina Bifida may experience wounds or skin distortions on their legs, feet, back, or buttocks. Due to the damages of the spinal nerves, they won’t feel when they have a blister, wound, or sore.
When this occurs, they also will not know to treat the lesion. This sore can, in turn, becomes a deep wound or foot infection, which can become hard to manage over time.
11. Allergy to latex and rubber products
Children with Spina Bifida have an increased risk of having latex allergy. These allergies can cause the child to itch, scratch, sneeze, have a rash, running nose, or watery eyes when introduced to rubber and its products.
The child may also develop a life-threatening condition known as anaphylaxis in which the child will experience swelling of the airways and face resulting in difficulties in breathing.
Prevention
One question that may be running through your mind is how to prevent this kind of congenital disability. The following can be done in order to avoid Spina Bifida.
1. Ensure that when you are pregnant, you never lack Folic Acid
It is imperative for a pregnant woman to ensure that she has enough folic acid in her system, especially during the early stages of the pregnancy.
Due to the fact that some women may not be aware of their pregnancy, doctors recommend that women of childbearing age should ensure that they take 400 micrograms of folic acid daily.
This doesn’t mean you must keep popping drugs into your mouth every day. There are some foods that are rich in folic acid, and they include enriched bread, pasta, rice as well as some cereals.
2. Ensure that you plan your pregnancy
Women who want to get pregnant should ensure they plan their pregnancies as well as ensure they take in enough folate. This is so as to prevent your newborn from developing congenital disabilities such as Spina Bifida.
Sources;
- Spina Bifida; Mayo Clinic
- Spina Bifida; types and treatment options; AANS.ORG