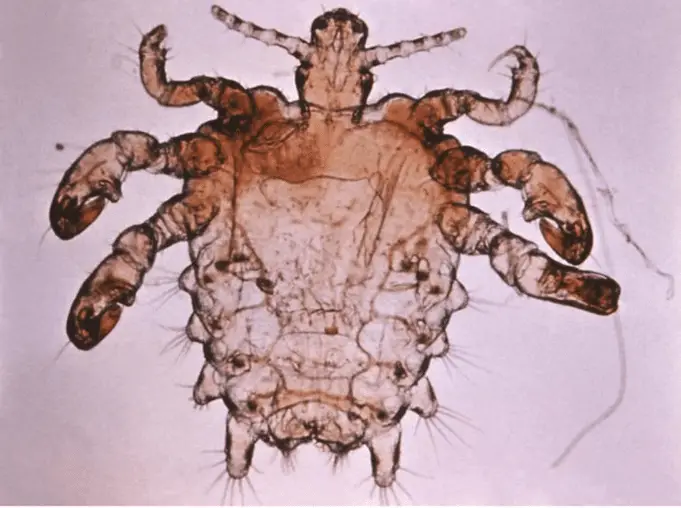
Pubic lice also called crabs or crab lice are very small parasitic insects that infest and feed on blood around your genitals. Crabs do not affect genitals only, they can also affect other hairy parts of the body which include eyebrows, beards, eyelashes, mustache and abdominal hair.
Pubic lice are visible to the eyes and can be spread from one person to another by crawling from hair-to-hair.
Pubic Lice Life Cycle
A female pubic louse can lay up to 300 eggs in her lifetime and the eggs hatch between 6-10 days. After an egg hatches it takes 2-3 weeks for it to mature and start reproduction.
A pubic louse can survive outside the human body for about 24 hours and its entire life cycle is between 6 days to 3 months.
Except crawling onto another human’s body, lice do not leave their host’s body. This is because lice feed on human blood.
Causes of Pubic Lice (Crabs STD)
Knowing that crabs can be passed from one person to another, it is important for us to know how these pubic lice spread from person to person. Pubic lice spread easily based on the following factors;
- Close body contact including sexual activities and non-sexual body contact(hugging and kissing).
- Sharing your bed with an infected person.
- Sharing towels, shaving sticks/clippers, underwears and other personal belongings with an infected person.
Signs and Symptoms of Pubic Lice
The presence of pubic lice may not be noticeable after the first contact until about 5days of infestation. Noticeable symptoms of pubic lice include;
- Itching in pubic regions that are caused by a reaction to crab bites.
- Presence of small bugs in your pubic hair when you look closely.
- Pubic lice lay eggs on the bottom part of your pubic hair.
- Irritation and feeling feverish.
- Sometimes you may see blood in your underwear although this is as a result of scratching from intense itching.
Diagnosis of Pubic Lice
Since pubic lice are visible to the eyes, you can diagnose it yourself by examining your pubic region or by using a magnifying glass.
To confirm an infestation, you will spot the lice/crab moving from hair to hair in your pubic area.
Lice eggs can also indicate an infestation. The eggs are laid at the bottom or root of your pubic hair and are not visible to the naked eyes because they are very tiny.
Complications of Pubic Lice
When pubic lice infestation is not treated, it can result in some minor complications such as bacterial skin infection and boils(furunculosis) due to intense scratching which can cause the skin to flake off.
Continuous feeding of lice in a particular spot may lead to the development of a pale blue spot. Sometimes untreated pubic lice infestation can also make you feel unwell.
How to get rid of pubic lice
Getting rid of pubic lice from your body is easy and does not calls for panic if you follow these instructions.
- Decontaminate yourself, bed and clothes.
- Shave off pubic hair and apply over-the-counter creams and shampoo which are available at the pharmacy and are mostly applied once.
- Avoid close contact and sharing personal belongings with others until it is certain that the lice are gone.
- Wash pubic hair if the infestation is mild.
- Check for nits(lice eggs) after treatment and remove leftovers that may cling to your hair with tweezers.
- If you share your bed with some members of your family then you should extend the treatment to them as well.
- Decontaminate your home by cleaning your bathroom with a bleach solution, wash all bedding, towels, and clothes in hot water.
Stronger medicine is needed if lice survive after these efforts. Some of these products include;
- Ivermectin: This is a pill that is taken orally.
- Malathion: A lotion that is applied to the affected area for about 8 to 12 hours before washing it off. This process should be repeated after 7days.
- Lindane: A lotion applied on the affected area for only 4mins before washing it off. This is the most toxic product used for pubic lice treatment and it is not to be used on infants, pregnant women or breastfeeding mothers.
Prevention of Pubic Lice Infestations
If you are already infested with pubic lice, you can prevent others from being infested by pubic lice refraining from sexual activities and sharing of personal items until your treatment is successfully completed.
If you are not yet infested then avoiding multiple sex partners and sharing of personal items will help you stay safe from pubic lice infestation.