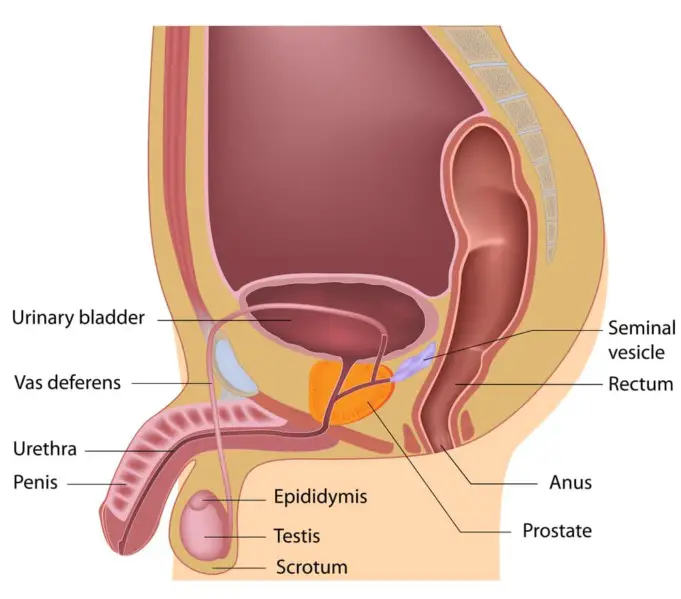
Prostatitis occurs when there is a swelling or inflammation of the prostate gland. Normally, the prostate gland has a shape of a small walnut and it is found just beneath the bladder in men. The function of the prostate gland is to produce semen; a fluid in which the male spermatozoa is found.
This fluid helps nourish the sperm and give it enough energy to swim up the female reproductive vagina to meet the female egg during sexual intercourse. Apart from this, the fluid produced by the prostate gland provides a transport system by which the sperm can swim in comfortably.
Most of the time, prostatitis is caused by bacteria strains and there are four different types of prostatitis and they include:
Acute bacterial prostatitis
This occurs when bacteria get into the prostate gland from the urinary system. When the bacteria that causes urinary tract, infections get to penetrate and enter into the prostate gland, one would develop acute bacterial prostatitis.
Most of the urinary tract organs such as the kidney, the bladder and the urethra are in close proximity with the prostate gland and there is a huge tendency that whatever bacteria that causes urinary tract infections can also get into the prostate glands too.
Acute bacterial prostatitis is a very severe but common form of prostatitis and it has the following symptoms namely;
- Severely high fever
- Elevated temperature levels
- Severe pains in the muscle.
- Pains in the joints
- Severe pains found around the base area of the penis or just beneath and behind the scrotum
- Trouble while urinating indicated by severe pains felt during urination
- Weak urine flow
Once as a man, you begin to notice these symptoms, please do seek the counsel of a medical practitioner.
Chronic bacterial prostatitis
This is usually more commonly seen in older men. This type of prostatitis can go on for a long period of time ranging from weeks to months and it usually comes on as a mild infection.
Some men may begin to experience this type of prostatitis once they have urinary tract infections or when they already have the presence of an underlying disease such as acute bacterial prostatitis.
Most of the symptoms of chronic bacterial prostatitis usually are not constant I.e. they come and go. Hence, most times it is not easily diagnosed early until it becomes severe.
It is also described as the recurrent bacterial prostatitis and it is usually difficult to treat because when the person goes for checkup, the symptoms may not appear at that point hence a misdiagnosis may occur.
There are symptoms to be expected when one begins to suspect chronic bacterial prostatitis and they include;
- An increased urgency to urinate mostly in the middle of the night
- Severe pains during urination
- Intense pain upon orgasm and ejaculation during sexual intercourse
- Pain in the lower back
- Heaviness just behind or beneath the scrotum
- Presence of an urinary tract infection
- Presence of blood or blood spots in semen
- Blockage in urinary tract leading to little or no production of urine causing the inability to urinate.
- Severe pains in the rectum.
Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome
It is otherwise known as chronic prostatitis. This is the most commonly seen among the types of prostatitis we have. However, doctors don’t have much to go on in diagnosing this type.
This is because it shares almost the same types of symptoms exhibits by acute bacterial prostatitis. It may sometimes be inflammatory and at other times, it is non-inflammatory.
This variation depends on the presence of cells that fight against infections in the urine, semen or even the prostatic fluid. Patients suffering from this disease will also not present with difficulties or specific symptoms.
It usually causes severe pains and intense swelling or inflammation in the pelvic organs, in the prostate gland and as well as the lower urinary tract.
The cause of this exact type of prostatitis is not known yet but some researchers concluded that it could be due from the result of the presence an alternative infection or as a result of external trauma causing an injury (might be very minute) which then lead to the inflammation of the prostate gland.
Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
This type of prostatitis is usually discovered during a work-up for the test of infertility in males. It can also be discovered when one does a test for prostate cancer.
Most individuals who have this type of prostatitis often don’t know that they have it simply because they don’t exhibit or show any sign and symptom that could point to this disease.
The only indicator that will point to the presence of asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis is the presence of infection-fighting cells in the either the patient’s urine or semen. There are several risk factors to consider while diagnosing for prostatitis and they include:
- Age: Men in General irrespective of the age have the tendency to develop prostatitis but it is mostly seen in young men and also middle-aged men. Men within the age bracket of 40-45 years have a higher tendency of developing prostatitis more than other men in other age brackets.
- A patients with a prior history too also has a higher chance of developing prostatitis. This could be due to a recurrent bacterial infection that entered the prostate gland through the blood.
- A patient who also had a urinary tract infection too has a risk of getting prostatitis.
- The recent use of an improperly sterilized catheter can cause the introduction of strains of bacteria into the urinary tract and invariably the prostate gland.
- People had severe trauma or injury to the pelvis also have a higher risk of getting prostatitis. Injuries too can be an entry point of bacteria into the blood and invariably the urinary tract and then the prostate gland.
- When a patient has a weakened or compromised immune system, then there won’t be enough production of antibodies to fight off infections in the body. This however will then make the patient very vulnerable to any type of infection include bacterial infection.
- Males who engage in anal sex too are likewise likely to develop prostatitis.
There are some complications which could develop in one’s body due to prostatitis and they include;
- The presence of bacteria in the blood
- Inflammation of the epididymis
- A large amount of pus found within the prostatic cavity
- Infertility can develop, and this is due to chronic prostatitis
- Obstruction of the bladder outlet leading to urine retention and hereby causing a distended bladder.
For as many men who are asking if prostatitis can be cured, yes it can. Once you are experiencing the symptoms listed above, please kindly visit your doctor for proper medical checkup. And once your medical practitioner confirms the diagnosis, then he or she should place the patient on high doses of antibiotics.
However, treatment may also depend on the type of prostatitis that is affecting the patient. For a patient suffering acute bacterial prostatitis, this infection can easily be treated.
But for patients suffering from chronic prostatitis or chronic bacterial prostatitis, there may be serious complications which can lead to life-long symptoms and severe discomfort and pain most especially from the prostatitis wasn’t properly treated.
Note: Prostatitis doesn’t lead to prostate cancer neither does it increase the risk of one getting prostate cancer in anyway.