Is obesity a disease? How do you know if you’re obese? Should you be scared if you’re obese? What are the causes of obesity? How can you prevent it? How can it be treated?
Overview
Obesity is a medical condition defined as the state of being overweight due to excess body fat. It is a problem that can lead to an increased risk of several health complications like heart diseases, high blood pressure, and different types of cancers.
Women have a greater risk of getting obese than men and seem to have greater complications too. Obesity in women affects psychological and mental health and is associated with certain pregnancy risks like miscarriages and higher rates of caesarean sections.
It reduces life expectancy and can pose a threat to future offspring.
How can you tell if you’re obese?
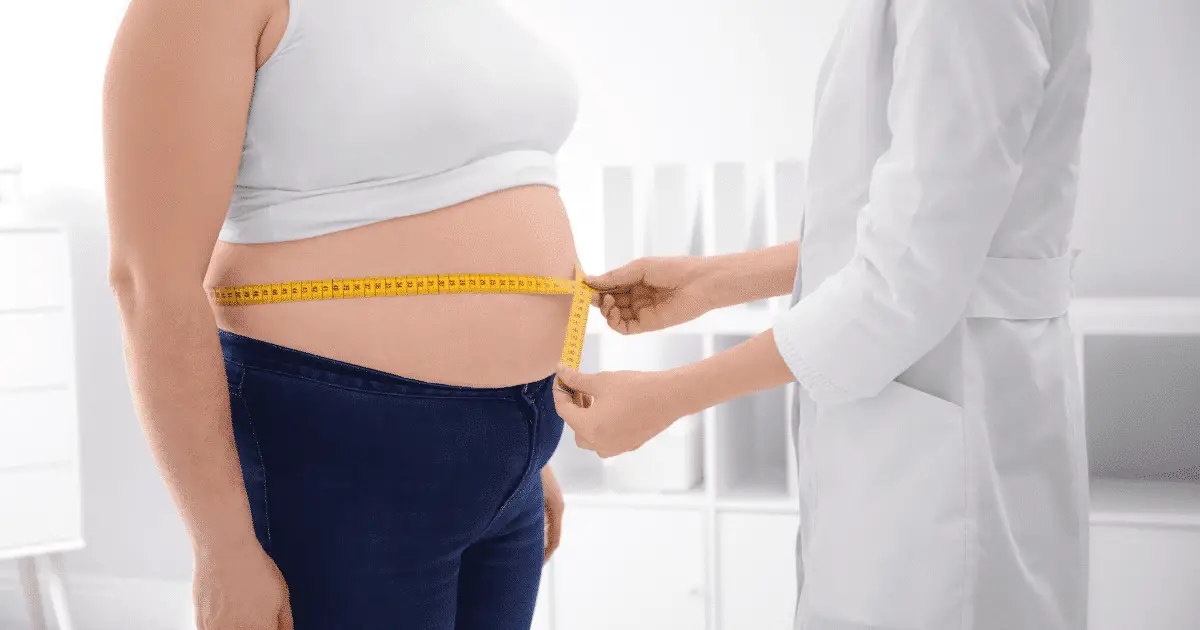
Obesity is defined by your body mass index (BMI). You are obese if your body mass index has a value of 30 and above. You can determine the value of your BMI by dividing the value of your weight in kilograms by the square of your height in metres.
If your BMI has a value of 18.5 and below, it means that you’re underweight. Values between 18.5 to 24.9 mean that you’re normal, while a value between 25 and 29.9 shows that you’re overweight. If your BMI is up to 30, it suggests that you’re obese.
It is important to note that even though the BMI provides a reasonable estimate for body fat, it has certain limitations. Other factors can influence BMI values like age, sex, and muscle mass. A muscular athlete may have a high BMI value due to high muscle mass.
When in doubt, you should see your doctor.
Causes
Obesity occurs when you take in more calories than you burn as you carry out your daily activities. These extra calories, over time, become responsible for unwanted weight gain.
The following are some of the causes of obesity:
- Poor dieting: Eating foods that contain too much fat and calories. These contribute to belly fat and may lead to abdominal obesity.
- A sedentary lifestyle: This is characterized by a lack of physical activities.
- Insufficient sleep: This encourages the production of ghrelin which is a peptide hormone that increases your appetite.
- Stress: You are likely to eat more junk and high-calorie foods when you’re in a stressful situation.
- Pregnancy: The weight gain associated with pregnancy is difficult to lose and may lead to obesity.
Risk factors
Certain factors can increase the risk of obesity in women. Some of them are:
- Genetics: Your genes may affect the rate at which your body breaks down fat, making it difficult for you to lose weight.
- Ageing: As you grow older, your muscle mass becomes less and there is a reduced rate of metabolism, making it easier to gain weight.
- Psychological factors: Depressed people have a higher chance of being obese because they tend to turn to food for emotional comfort.
- Environmental and social factors: Your environment may influence what you eat and how much fat you burn. If your surroundings make it difficult to exercise, or you don’t have access to healthy foods, you’re likely to gain weight.
Complications
People with obesity are more susceptible to certain health problems than those without it. Some of the complications that can arise from having a high weight to height ratio include:
- Type 2 diabetes: Being obese can affect the function of insulin in your body, increasing the risk of getting type 2 diabetes.
- Heart diseases and stroke: People with obesity tend to have abnormal cholesterol levels and high blood pressure, which may lead to heart diseases or stroke.
- Cancer: Obesity may increase the risk of certain cancers. Some of the cancers which may arise from having a high BMI value include ovary, colon, liver, prostate, cervix, and kidney cancers.
- Gynaecological problems: Obesity in women may lead to infertility and irregular menstrual cycles. It can lead to erectile dysfunction in men.
- Sleep apnea: This is a disorder characterized by brief breathing interruptions during sleep. It, alongside other breathing problems, is a possible complication for people with obesity.
- Digestive problems: Obesity increases the risk of gallbladder disease, heartburns, and liver diseases.
Obesity generally reduces the quality of life. It may prevent you from carrying out your exciting daily activities. Other issues that may arise from being obese include:
- Disabilities
- Shame
- Isolation
- Depression
Prevention
Various steps can be taken to prevent unwanted weight gain and reduce the chance of being obese. These are steps that help to make sure you don’t take in too many calories than you burn out.
Some of these practices are;
- Eating right: Your meal should consist of low-calorie foods such as fruits and vegetables. Also eat food rich in fibre like rice, beans, and oats, but stay away from excess saturated fats and sugars. Eat three balanced meals every day and avoid unnecessary snacking.
- Regular exercising: Moderate physical exercises like walking and jogging go a long way in the weight loss journey. Other activities that can help you lose weight include swimming, dancing, riding a bike, weight lifting among others.
- Reducing stress: Your body releases the cortisol hormone when you’re stressed. This hormone causes excess calories to remain in your body as fat. It is also known to lead to an increase in appetite.
- Getting quality sleep: Studies have shown that people who sleep less tend to gain more weight. Insufficient sleep makes the body release hormones that increase your appetite and you may end up taking in too many calories.
Treatment
All obesity treatments aim to reduce your weight to a healthy level. If you are unable to lose weight on your own, you should get medical help.
You may need to work with a team of health professionals. This team may consist of a dietician, a therapist, and other health staff, and they’ll help guide you through certain processes.
You’ll be expected to make some lifestyle changes, and sometimes, you may require weight loss medications or even a weight loss surgery.
Final words
Obesity in women can have adverse effects at each stage of a woman’s life cycle. It impacts the psychological health of young women, and then their reproductive health as they grow older. It also leads to some risks during pregnancy.
Even after any obesity treatment, it is common to regain weight if you continue to eat high-calorie foods and live an unhealthy lifestyle. You should pay attention to your weight, eating the right kind of food, and taking part in regular physical activities.
Author Bio:
Jude Uchella is a writer. He has a knack for writing educational content that helps people live a better, more fulfilling life. He is the founder of Health Makes You, a research-driven health blog.
















Thank you for this useful post, I found it more educative, GOD bless you