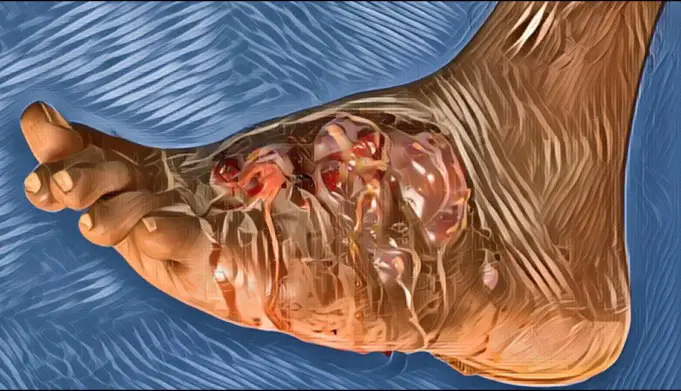
Mycetoma is a fungal disease that can be considered to be a chronic and rapidly progressive infection that affects the majority of the foot and minorly, the remaining part of the body. Sometimes, mycetoma can also be as a result of certain types of bacteria that can be found in the soil and stagnant or dirty water.
Once a person has an injury or a break on the skin and goes to an infected area (i.e., a place where these bacteria and fungi can be found), the bacterium or fungus can easily pass through the injury or break in the skin into the bloodstream resulting in the development of an infection.
According to W.H.O., this disease is a progressively morbid disease that is often inflammatory and destructive and can infect anyone. A medical doctor first described Mycetoma in the year 1694.
However, the first case of mycetoma wasn’t first experienced until the mid 19th century in a town in India called Mandura. This is why Mycetoma was initially called Mandura foot.
This infection generally affects both children and adults. However, most adults within the ages of 20 and 40 years are more at risk of developing this infection.
Once this infection enters the foot or the part of the body where it is found, it causes the formation of large masses that appear to be firm under the skin and, if not properly treated, can affect the underlying bone.
Mycetoma is caused by the bacteria actinomycetoma or the fungi eumycetoma. The most significant amount of people who have this infection are seen in underdeveloped and developing countries.
People who of the lower socioeconomic statuses as well as manual laborers such as farmers, agriculturalists, herdsmen as well as laborers are often the most affected and this is because of the nature of their job as well as the few precautions they take to protect themselves from certain diseases and infections such as this.
In a science review of articles held in 2013, it was seen that there were almost about 10,000 cases worldwide; however, there is every tendency that the number of people who have Mycetoma is more than that number.
Mycetoma is a disease that occurs much more in men than in women. This disease affects people who are mostly found in the following regions: Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
Symptoms
Both bacterial and fungal mycetoma have similar signs and symptoms. The patient will experience firm masses under the skin, which is usually painless. Initially, these masses will be seen under the foot, and after that, it will spread and be seen on other parts of the body.
Generally, the masses start as small lumps; however, over time, they grow from being lumps to large masses and begin to bring out sores. This will, therefore, lead to the deformation of the affected limb and, as such, rendering that limb unusable.
In critical cases where treatment fails or the disease isn’t properly treated, the infection can spread to other parts of the body, thereby causing further problems. If the condition goes untreated for a long time, it can eventually destroy the underlying bone and muscle.
Diagnosis
In other to diagnose this disease, your doctor will take a biopsy(i.e., taking a small portion) of the affected part of the body and send it to the laboratory for medical testing. This is mostly to confirm what kind of disease is.
Another test may be run to know what kind of microbial agent is causing it (i.e., trying to determine if it is fungal or bacterial). Once the cause of the infection is determined, it is easier to treat.
Also, your doctor will need to carry out an imaging test to determine the extent of the infection and how much damage has been done to either the muscle, bone, skin, or all three.
A patient can prevent amputation or long-term infection from occurring by detecting the disease early and seeking medical attention immediately.
Treatment
Treatment of Mycetoma basically depends on the causative agent. This is why it is essential to know what causes the disease before proceeding to treatment. An antibacterial drug can’t treat a fungal infection; likewise, an antifungal medicine can treat bacterial disease.
If the disease is caused by a bacterial agent(actinomycetoma), then an antibiotic can treat the infection. However, the specific antibiotic(s) that can treat the disease must be prescribed by the doctor else a complication may result.
If the disease is caused by a fungal agent (eumycetoma), then the course of treatment will require the long term use of antifungal drugs. However, sometimes, using antifungal drugs may not be enough, especially when the disease wasn’t detected on time.
Sometimes, in severe cases, the doctor may prescribe surgical methods or complete amputation of the affected limb to help remove the affected tissue and prevent further spread of the infection.
References;