Laparoscopic treatment was usually carried out in diagnosing and curing diseases gynecology, gallbladder. Over the last decade, the use of this technique has also been used to cure hernia, hysterectomy, appendicitis, weight loss, achalasia cardia, anti-reflux, small intestinal and large intestinal surgeries.
In simple terms, laparoscopy is a surgical treatment in which a surgeon makes small incisions and inserts a small device known as a laparoscope in order to see inside the abdomen and the pelvis. The procedure derives its name from the use of the device “laparoscope”.
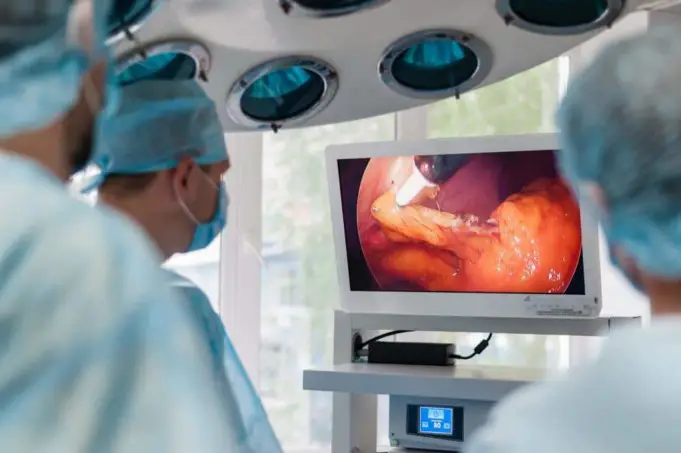
A laparoscope is a fiber-optic with a high-intensity lift and high-resolution camera at the front that is inserted into the abdominal cavity. When doctors look into the patient’s body, they view from a high- resolution monitor and diagnose accordingly.
In this type of surgery, large incisions are avoided as doctors use a laparoscope. Also known as keyhole or minimally invasive surgery, the benefits of this technique include a faster recovery, minimal pain, and reduced scarring.
Purpose of Laparoscopic Surgery
According to the healthcare website, pristyncare, doctors may recommend a laparoscopy to examine the following organs:
- Appendix
- Gallbladder
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Small intestine and large intestine (colon)
- Stomach
- Pelvic or reproductive organs
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain can be caused due to appendicitis, adhesions, intra-abdominal scar tissue, pelvic infections, abdominal bleeding, endometriosis and sometimes irritable bowel disease.
Many cases, abdominal problems can also be diagnosed with imaging techniques such as ultrasound, which uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the body or CT scan, which is a series of special X-rays that take cross-sectional images of the body or a MRI scan, which uses magnets and radio waves to produce images of the body. Laparoscopic surgeries have proven to be successful in healing both acute and chronic abdominal pain.
Abdominal mass
Lumps need to be properly examined so that doctors can recommend the appropriate treatment. Laparoscopy allows doctors to obtain tissue from the mass or lump.
Ascites
Laparoscopy is used to examine the causes of fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity, also known as ascites.
Others
Other reasons to undergo laparoscopy are liver diseases, cancer staging, etc.
Procedure of Laparoscopic surgery
Laparoscopic surgeries can be done under general or local anesthesia. Procedures under general anesthesia induce patients to sleep. It is given through an intravenous (IV) line which means it is inserted through veins.
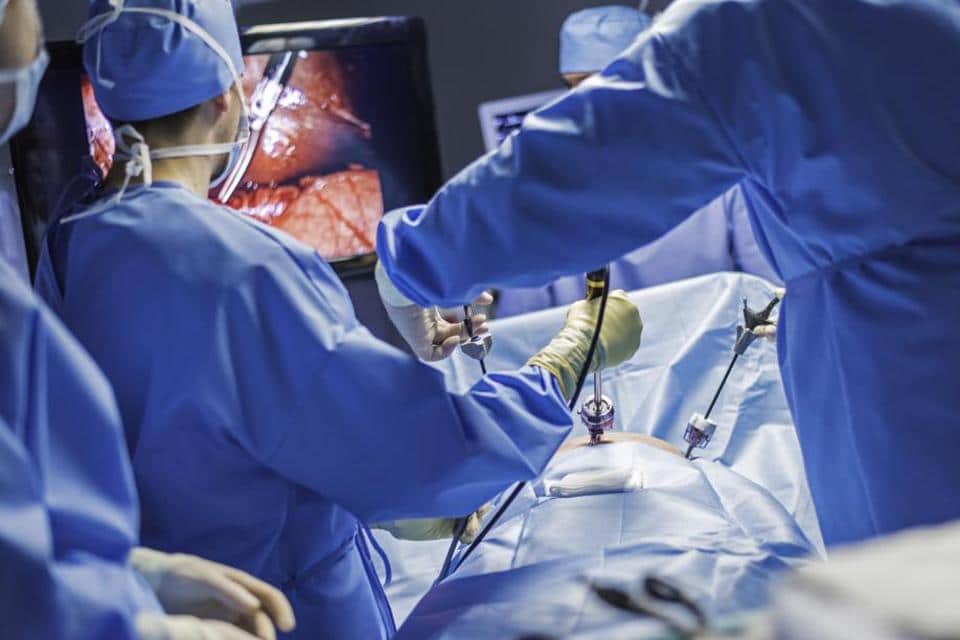
Through an IV line, doctors also provide special medications as well as fluids. Local anesthesia numbs the area to be operated and hence the patient will be awake throughout the procedure. During laparoscopic treatment, the surgeon makes an incision below the navel and then inserts a thin tube into the cavity called a cannula.
Through the cannula, the abdomen is inflated with carbon dioxide gas which allows a doctor to see abdominal organs more clearly. After inflating the abdomen, the surgeon inserts the laparoscope through the incision. The camera attached to the laparoscope displays the images on a screen, allowing the abdominal organs to be viewed in real time.
The number and size of incisions depends upon what specific diseases the patient is suffering from. Each of this incision is called a “port”. Usually, one gets from one to four incisions that are each between 0.5-1 centimeter in length.
These incisions allow other instruments to be inserted. For instance, surgeons may need to use another surgical tool to perform a biopsy in which they take a small sample of tissue from an organ to be evaluated.
After the procedure is done, the gas is let out of the abdominal cavity. After the surgical instruments are removed, the incisions are then closed with absorbable sutures, stitches or surgical tape. In some cases, laparoscopic surgeries are outpatient procedures which mean patients are discharged on the same day of the procedures.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgery
Some of the advantages of laparoscopic surgery are discussed below;
Reduced risk of bleeding
During laparoscopic surgery, the surgeon makes one or more small incisions in the abdomen. These allow the surgeon to insert the laparoscope, small surgical tools, and a tube used to pump gas into the abdomen.
This is done so that the doctor can look inside and operate easily. The size of the incision size is so small than the large incision made for open surgery reduces the risk of bleeding.
Less painful healing process
In the case of conservative methods, patients take a longer time to recover as one large incision is made. With laparoscopic surgery, the post-surgical wound is much smaller and properly bandaged with abdominal sutures. This ensures that the healing process is much less painful.
Reduced chances of scarring
Traditionally, before the emergence of this treatment, a surgeon had to cut a patient’s belly that was 6-12 inches long. This allowed doctors to see inside the abdominal or pelvic cavity and operate accordingly. Particularly in overweight and obese patients, there is a high risk of infection in the scar tissue, specifically if the surgical wound is larger.
Reduced risk of infection
The risk of post-operation infection is significantly reduced to a minimal in laparoscopic surgery as there is minimum exposure of internal organs to external contaminants. As laparoscopic surgeries are day-care procedures, patients are generally discharged the same-day. They can return to their daily activities much more quickly.
Patients who suffer from a lung or heart disease, laparoscopic treatment is carried out without general anesthesia. Individuals who have previously gone several operations are not ideal candidates for minimally invasive surgery due to the development of scar tissue and creates obstructions for laparoscopic procedures. Surgeons guide their patient for traditional or laparoscopic surgery, accordingly after thorough diagnosis.