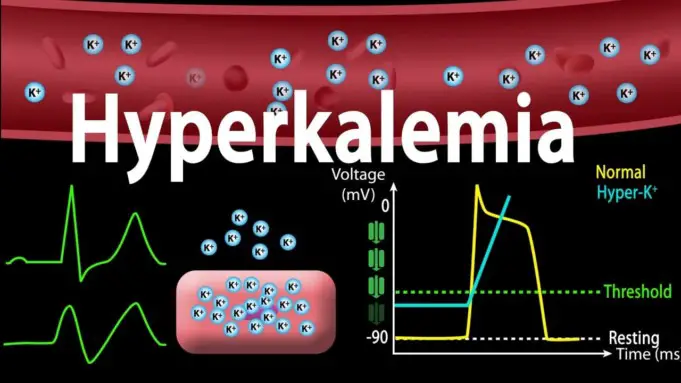
Hyperkalemia is a term that is used to describe a medical condition that arises as a result of high levels of potassium in the body. The body is generally made up of electrolytes, elements and ions.
One of the essential electrolytes in the body, mainly in the heart is potassium, and if anything goes wrong with the levels of potassium in the body, everything tends to go south.
Potassium is not only crucial for your heart, but it is also vital for your muscles, nerves and generally all the cells in your body.
Hence, when the body is having trouble balancing the levels of potassium in the body, all parts of the body gets affected. Hyperkalemia is, unfortunately, a common illness that affects most people within the ages of 30-50 years of age.
The average levels of potassium in the blood are 3.5-5.0 mEq/l. Anything outside this range begins to reflect hyperkalemia.
Causes
Hyperkalemia occurs when there is a problem with the functional process of the kidney. The kidney serves as the filtration system of the body, and if the kidney is unable to filter excess potassium from your body system.
Kidney diseases have been seen to be the leading cause of hyperkalemia globally. Generally, your kidney filters the blood for excess amounts of electrolytes and other harmful substances which we then pass out as urine.
It is, therefore, safe to conclude that the kidneys are responsible for controlling the levels of potassium in the body. There is a particular hormone known as aldosterone. Aldosterone is the hormone that is responsible for the regulation of potassium in the body.
Once an increased level of potassium ions is present within the body, the hormone aldosterone is secreted, which tells the brain to alert the kidneys to begin filtration of excess potassium from the blood.
However, when some diseases affect the level of production of this hormone, it will cause an imbalance and as such cause, hyperkalemia to occur. Asides kidney diseases, hyperkalemia also occurs when there is an increased level of potassium in one’s diet.
Once the kidneys are not functioning correctly, and you have a high intake of potassium regularly, the kidneys will find it challenging to eliminate potassium.
As such, there will be an accumulation within the bloodstream and as such hyperkalemia will occur. There are some specific conditions that can affect the functionality of the kidneys and these conditions include;
- Hormonal disorders
- Lupus: Lupus is an autoimmune disease that causes the immune system to begin to attack the tissues. This will, therefore, cause the cells to start to swell and get inflamed, severe pains and damages to the nerve endings.
- Arterial blockages which can affect the renal arteries
- Acute or chronic Kidney failure
- Glomerulonephritis
- Lupus nephritis
- Kidney transfer rejection
- Some obstructive diseases of the urinary tract such as stones in the urinary tract causing urolithiasis
Another cause of hyperkalemia can be as a result of the intake of drugs. This kind of hyperkalemia is known as Drug-Induced Hyperkalemia.
Once your body can’t properly handle and eliminate potassium regularly, taking some medicines which naturally shouldn’t pose any problems will become an issue for you.
For some drugs, one of their side effects is the high surge of potassium that is seen within the bloodstream just after the metabolism of the pill occurs.
Below is a list of some drugs that have the tendency to spike up the blood potassium levels in the body;
- Drugs that are used to regulate blood pressure such as Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, Beta Blockers and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs) can all cause hyperkalemia.
- Some herbal supplements such lily of the valley, milkweed, Siberian ginseng, Hawthorne berries and so on.
- Blood thinners such as heparin
- Non-Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Some potassium supplements
- Potassium diuretics including amiloride, and so on
- Antibiotics such as amoxicillin and so on.
Research has shown that the adrenal glands also has been seen to cause hyperkalemia. Generally, the adrenal glands are small glands that are seen to be sitting on the top of the kidney.
They are responsible for the production of some hormones such as aldosterone and cortisol. These two hormones are vital in the body.
Aldosterone is responsible for the regulation of the absorption of both water and sodium by the kidneys and potassium excretion out of the kidneys.
In other words, aldosterone helps regulate the kidneys to absorb water and sodium and to expel potassium out of the kidneys.
Therefore, any disease that might affect the adrenal glands such as Addison disease will cause a malfunctioning of the production of this hormone and as such, will cause a decreased in the levels at which the kidneys expel sodium out of the body.
Once this occurs, it will lead to the retention of potassium in the body, inevitably leading to hyperkalemia.
Symptoms
Some symptoms of hyperkalemia include;
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Lethargy
- Fatigue
- Tingling sensations in both the arms and the legs
- Muscle weakness
- In severe cases, the symptoms experienced by the patient include
- Slow heartbeat
- Weakened pulse rate
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Sudden cardiac arrest
Treatment
Treatment of hyperkalemia occurs after appropriate diagnosis has been made. Diagnosis shows the real cause of the disease, and as such treatment is usually based on the individual’s health and the underlying cause.
If the patient has mild hyperkalemia, the patient might be given an outdoor treatment based on the following reasons.
- If the ECG of the patient is normal
- If there are no related disease conditions such as acidosis and declining renal function
- If the blood pressure is not high
On the other hand, if the patient has severe hyperkalemia, he/she will need emergency treatment in the hospital. Treatment will include any of the following either in a combination or singly.
- A diet that is low in potassium
- Stop all medications that may be causing hyperkalemia
- Intravenous drugs which are rich in glucose and insulin. This is because glucose and insulin have the tendency to drive potassium from the external cellular environment back into the cells
- Calcium drugs are to be administered intravenously. This is in order to protect the heart from the harmful effects of high potassium levels.
- Administration of sodium bicarbonate which is a compound that has the ability to stop acidosis and also has the power to drive potassium back into the cells.
- Drugs such as beta-2 adrenergic receptor stimulants can also be used to push potassium into its cellular environment
- Use of diuretics. This is because diuretics causes frequent urination and as such will cause the kidneys to excrete the excess potassium
- Dialysis, especially in cases where kidney failure has occurred.