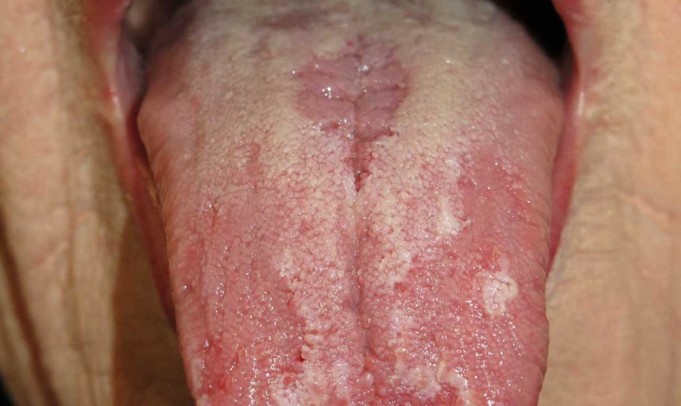
Glossitis is generally characterized by tongue inflammation. It can also lead to changes in the color and texture of the tongue.
Another visible sign of glossitis is swelling of the tongue. Extreme cases of glossitis can be very painful and can affect the way a person eats or talks.
There are various types of glossitis, and they include;
- Acute glossitis: This typically develops suddenly, and extreme symptoms may manifest.
- Median rhomboid glossitis: A Candida yeast infection often causes this glossitis.
- Chronic glossitis: A clear sign of this underlying condition is chronic tongue inflammation.
- Atrophic glossitis: Also known as Hunter’s glossitis, is characterized by the shrinking of several tongue bumps (papillae). This shrinking effect can change the surface of how the tongue looks, giving it a glossy appearance.
Symptoms
Glossitis symptoms vary from person to person. They may also manifest differently depending on the underlying cause of the condition.
General symptoms of glossitis include:
- Swollen tongue
- Itching or burning tongue
- Painful tongue
- Difficulty swallowing
- Difficulty eating or speaking properly
- Colored tongue
- Change in texture of the tongue
Causes
Several things could lead to glossitis, and some of them include the following;
– Injury to the mouth
Mouth injuries caused by burns from hot food or cuts from braces, can cause inflammation or swell to the tongue. Due to the repeated injury caused by dental braces to the tongue, a person is more at risk of having chronic glossitis.
– Allergic reaction
When glossitis is triggered due to an allergic reaction, a person can develop acute glossitis. This can cause a person’s tongue to swell, causing extreme pain. Allergies to particular drugs, foods, or specific irritants can result in this kind of reaction.
– Diseases
Some diseases can cause glossitis, mainly when they are caused by nutritional deficiencies, such as protein-calorie malnutrition, celiac disease, and pernicious anemia.
When diseases like Sjögren’s Syndrome that affects the immune system affects a person, it can affect the mouth and lead to glossitis.
– Infections
Fungal, bacterial, and viral infections can all lead to glossitis. Nonetheless, oral herpes, which is a fungal yeast infection, and viral infection, are among the possible cause of glossitis.
– Nutritional deficiencies
When there isn’t enough iron in the blood, then we can say a person is deficient in iron. Iron deficiency can trigger glossitis as reduced levels of iron causes a reduced level of myoglobin.
Myoglobin is a substance present in the blood that improves the health of all the muscles in a person’s body, especially the tongue.
Another cause of glossitis is the deficiency of vitamin B12.
Diagnosis
A person must visit a doctor once they notice the symptoms of glossitis. The medical expert would access medical history. A doctor or dentist would thoroughly examine the mouth and tongue.
Tongue abnormalities would be noted. They would check for blisters and bumps on the tongue and around the mouth, especially the gum.
A swab of saliva may also be taken for testing. Blood work may also be done to check for any underlying diseases or nutritional deficiencies.
Treatment
Treatment for glossitis is based on its cause. Typically, patients with glossitis respond well to treatment once the underlying cause or causes has been detected.
Doctors may administer medications to people with glossitis that is caused by infections or diseases. Anti-fungal, antibiotic, or antiviral drugs may help clear up a fungal, bacterial, or viral infection.
In cases where glossitis was caused by nutritional deficiency, doctors may prescribe dietary supplements to help elevate the nutrient. Doctors may also advise patients on ways to improve the missing nutrient in the patient’s diet.
Nutritional deficiencies caused by an underlying health complication, like celiac disease, can be tackled with treatment and some dietary adjustments.
Prevention
Preventing glossitis may not always be possible. Nevertheless, a person can minimize their risk of developing the complication by doing the following:
- Maintain a healthy diet
- Minimize or do away with irritants, like cigarettes, spicy and acidic foods
- Practice good oral hygiene with consistent brushing, mouthwashes, and flossing
Outlook
People with glossitis can naturally expect to make a full recovery, even though this would take some time, coupled with the right treatment.
Foods that may irritate the tongue should be avoided, especially during treatment. Maintaining good oral hygiene is also compulsory to guarantee an overall recovery.
Immediate medical attention should be sought after if symptoms persist. In cases where the patients’ tongue is severely swollen, and in some cases, starts to clog the airways, he or she should seek emergency medical attention as the condition may become fatal.
Do you know anyone who’s suffered from glossitis? Do you have any idea how they treated the disease? Care to share your opinions or thoughts on the topic? Feel free to use the comments section below.