Arteries are blood vessels which carry oxygenated blood from the heart to the body tissues. Coronary artery or clogged arteries is caused when plaques build up in the inner walls of the heart or coronary arteries.
Plaques are mixtures of wastes which include fat, cholesterol and calcium that sticks to the wall of the arteries causing the blood vessels to become narrower.
Causes and Risk Factors of Coronary Artery Disease
Some causes and risk factors of coronary heart artery disease include;
- Smoking
- High cholesterol intake
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Unhealthy diet
- Obesity
- Constant high stress
Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease
The obvious signs of coronary artery disease usually manifest when the coronary arteries become narrows and can no longer supply enough oxygen, nutrients and blood to the heart. Some of these symptoms include;
- Shortness of breath
- Pain in the chest
- Baldness
- Pain in the calf
- Shortness of Breath: When the hearth cannot pup enough blood to meet the body needs, you become short of breath. You cannot breath properly because your heart is not functioning properly.
- Pain in the Chest: Feeling pressure or tightness in your chest like there’s something heavy pressing against your chest. This pain usually occurs on the left side or the middle of the chest and is worsened by stress. And the pain normally goes away within a few minutes of stopping the stressful activity.
- Baldness: Severe baldness is one of the symptoms of a silent coronary artery disease. If you notice early baldness symptoms, then you should check your heart health.
- Pain in The Calf: This is medically known as claudication and is caused when there is a blocked leg artery. It is more noticeable in smokers and usually happens before coronary heart disease is diagnosed
Dangers of Untreated Clogged Arteries
Clogged arteries are a step to diagnosing coronary artery disease. Some of the dangers of untreated clogged arteries and arterial plaque are listed below;
- Accumulated plaque in the arteries that carry blood and oxygen to the heart can result in heart disease and fatal heart attack that can be life threatening.
- Accumulated plaque in the blood vessels that carry blood to the legs can lead to peripheral artery disease.
- Untreated clogged accumulated in the arteries that run up on either side of the neck that supply oxygen to the brain can lead to carotid arteries disease which results in a stroke.
Testing for Clogged Arteries
If you notice or suspect any symptoms of clogged arteries, the best thing to do is to see a doctor. There are a number of test one can perform to diagnose clogged arteries. Some are;
- Ultrasound
- Chest X-Ray
- Cardiac Stress test
- Cholesterol Screening
- CT scan
Prevention of Clogged Arteries
There are ways which people can prevent clogged arteries. Following these lifestyles change one can reduce the risk of having coronary artery disease.
- Avoid eating saturated fats and trans fat
- Eat more of unsaturated fats
- Drinking herbal tea
- Regular exercising
- Dieting tips
- Avoid Eating Saturated Fats and Trans Fats: The types of fat you eat can attract plaque in the arteries. Eating food high in trans fat and saturated fat increases your chances of coronary heart disease. Food high in trans fat includes; fried foods, pastries, butter, processed canned food, cakes and pies. Saturated fats are mostly found in animal products which include; beef, pork and dairy products.
- Eat More of Unsaturated Fats: These are good fats that contain high density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol. The HDL cholesterol can help to take out bad cholesterol from the arteries before they turn plaque. Unsaturated fats are mostly found in plants and fatty fish which include; avocado, walnuts, olives, salmon, trout etc.
- Drinking Herbal Tea: Herbal teas such as green tea, black tea or ginger tea are good heart healthy substitutes for sweetened beverages — they help to lower bad cholesterols in the arteries.
- Regular Exercise: In addition to eating a heart-healthy diet, you should also exercise regularly to lose weight especially obesities. Since obesity is one of the risk factors of coronary disease, you should regularly involve yourself in cardio also known as cardiovascular exercise for at least 30mins. This will help to strengthen the heart and reduce the risks of clogged arteries. Some simple cardio exercises that can raise the heart rate include; jogging, running, swimming, cycling, aerobics, playing tennis, brisk walking etc.
- Dieting Tips: To preventing clogged arteries, you should aim at eating more of food that will help to lower the body’s low density (LDL) cholesterol and avoid or limit sugary foods, sweetened beverages and red meat. You should eat more of whole vegetables and fruits, low-fat dairy, fish and whole grains.
Other ways to prevent clogged arteries include
- Reduce stress using stress reduction techniques such as meditation and yoga.
- Stop smoking: Smoking can damage your arteries directly and make fatty deposits grow faster and larger increasing your chances of clogged arteries.
Medical Treatment Options
When prevention methods for clogged arteries are not very effective, you may need medical intervention to help alleviate clogged arteries issues. Doctors may place you on medication that will help lower your LDL cholesterol and sometimes dieting as well.
Focusing on controlling the factors that can contribute to accumulation of plaques in the arteries, medication may include;
- Drugs to lower blood pressure
- Drugs to lower your cholesterol
Depending on how severe the case is clogged arteries may require surgery. Some types of surgery that may be carried out include; Bypass surgery and Stent surgery
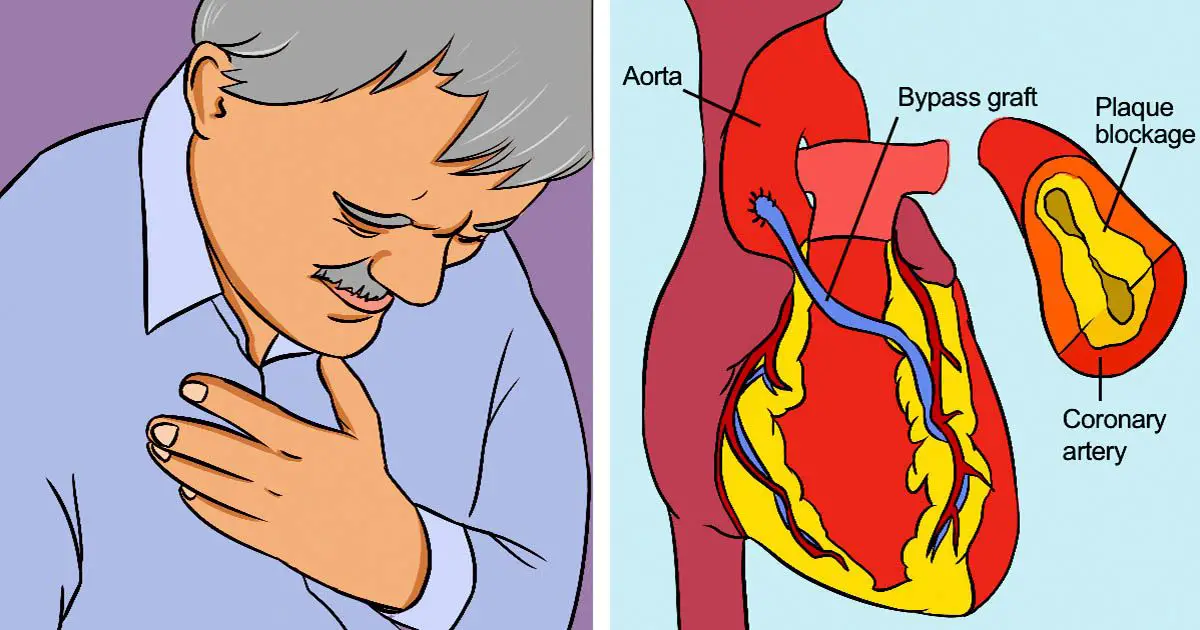
- Bypass Surgery: This surgery is done to move the arteries from other parts of the body to bypass the clogged arteries so that oxygen and food nutrients can reach their final destination.
- Stent Surgery: This surgery is done to place a small tube in an artery. This tube contains medication that helps to maintain blood flow in the body.