Complex Regional Pain Syndrome, often known as CRPS, is a type of pain, often chronic in nature that affects both the hand and leg of the patient at the same time. Sometimes, CRPS may only affect an arm or a leg; however, it may simultaneously affect both limbs in some rare cases.
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome is also known as Reflex Sympathetic dystrophy syndrome. It is said to occur when high and fast levels of nerve impulses are sent to an affected site by the brain. Generally, all impulses are sent to the brain. The brain transcribed these impulses and describes which one is pain, pleasure, and so on.
For a person who has complex regional pain syndrome, whatever impulses the brain is sending back to the body, especially to the arms and legs, is transmitted as a high level of pain even though originally it isn’t meant to be.
According to some experts, they believe that this syndrome occurs as a result of a malfunction either in the Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) or the Central Nervous System(CNS). Some scientists believe that there is an abnormal functioning of the nerves that causes the body to receive an exaggerated reaction to pain signals.
Your nervous System is divided into two; your Central Nervous System and Peripheral Nervous System. Your Central Nervous System (CNS) comprises of both your brain and the spinal cord. This part is often responsible for the generation of impulses that run along your entire nervous system.
Your Peripheral Nervous System, on the other hand, is what collects the impulses generated in the brain and spinal cord and relates it to other parts of the body such as the arms, the legs, your internal organs, and so on.
Now, the problem may not be from the CNS; it may come from an overshoot reaction that takes place in the PNS, which exaggerates pain signals to be more than what it is.
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome is commonly seen among people who are within the ages of 20-35years, and it is said to affect women more than men.
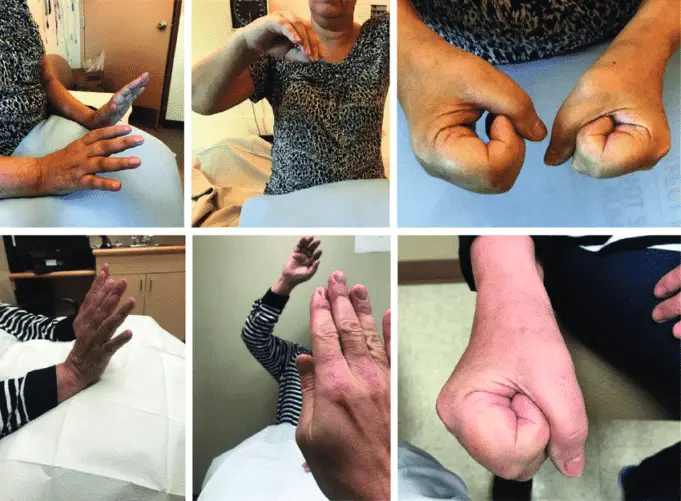
This condition causes severe pains, changes in skin color and texture, an increase in temperature, and General body weakness, amongst other symptoms to the body of the patient.
Generally, in most cases, CRPS starts out as a resultant effect of a soft tissue injury such as a fracture, sprain, or after surgery.
During the recovery of this injury, the pain the patient feels is intensified and is much more than what is generally expected during the healing process.
One problem with CRPS is that it is not a widely known condition and, as such, can be easily misdiagnosed by a doctor. This, in turn, causes the patient to receive the wrong diagnosis and treatment(in some cases, no treatment at all).
Causes of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
The causes of CRPS is not clearly understood. Some experts believe that it is as a result of the malfunctioning of nerves present in the CNS and PNS, while others believe that it is as a result of an abnormality in the formation of the nerves of the CNS and PNS.
Some scientists think that complex regional pain syndrome is caused as a result of an inflammation of the nerves coupled with several changes in the ways the patient brain and spinal cord perceives pain.
However, in a recent research, scientists have discovered the presence of inflammatory bodies such as chemicals and substances which were deposited in the affected tissue, blood, and cerebrospinal fluid of some patients who presented with CRPS.
There were also signs of pain and inflammatory compounds, as well as the presence of certain chemicals which are seen to be released in conditions where the patient has an oversensitivity of pain.
According to some doctors, they believe that the causes of this disease can be traced back to autoimmune and/or genetic factors. According to experts, CRPS can be said to occur in two forms.
These two forms present with similar symptoms and signs, but they have completely different causes. They include;
Type I CRPS
This type is known as Reflex Sympathetic dystrophy(RSD). RSD is said to occur following an injury or illness that didn’t directly damage the nerves that are present in your affected limb.
This means that Reflex Sympathetic dystrophy can occur when a person has a trauma, accident, or disease that affected a part of his brain or spinal cord, however, is now presenting as CRPS.
According to research, about 90% of people who have CRPS started out with having RSD.
Type II CRPS
This type is referred to as causalgia, and it is said to occur after the patient has had a significant nerve injury within the affected limb or body part.
It is easy to mistaken type 1 for type II, and this because their symptoms are the same. However, the only difference among these types is the location of the nerve injury in the body of the patient.
Although the causes of CRPS are not known, however, a forceful trauma, injury, accident, or disease can lead to its development. Also, certain conditions such as a severe heart attack, an infection, a sprained ankle, or even a surgery can cause the patient to have CRPS.
It is important to note that doctors are not yet sure why and how these injuries can cause Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. It is also essential to note that it is not everyone who has these sort of injuries that would develop CRPS.
Symptoms of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
The major symptom of CRPS is pain. However, the severity and complexity of pain differ from person to person. However, one thing that is notable about the pain is it becomes intense, continuous, and worse over time.
If complex regional pain syndrome should occur after an injury, it blows the pain and severity of that injury out of proportion. In some cases where you get to injure a toe or a finger, the pain can become so severe that it radiates throughout the arm or leg.
In general, the signs and symptoms you may experience once you develop Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) include;
- Intense and continuous throbbing and/or burning pain usually felt in your foot, legs, arms, or fingers.
- Severe sensitivity to cold and touch.
- Inflammation and swelling of the affected area.
- Alternating changes in temperature of the skin found around the affected area. Sometimes, the area may be very cold; at other times, It becomes very hot and sweaty.
- Changes in nail and hair growth.
- Swelling, stiffness, and eventual damage to the joints present in the affected area.
- Presence of muscle tremors, muscle spasms, muscle weakness, and eventual atrophy (muscle loss).
- Increasing the inability to move the affected part.
- Paleness and coldness of the affected limb
- Overtime, there may be a spread of pain and symptoms from the affected limb to the opposite limb.
Over time, in some people, the signs and symptoms of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome may end up resolving themselves such that the pain disappears. However, in others, this pain can last for several weeks, months, or even years.
How to diagnose CRPS
Just like the cause of Chronic Regional Pain Syndrome is not known, there is no specific diagnosis for CRPS. However, there are certain tests that a doctor can carry out that will help eliminate the possibilities of other conditions.
One of such is the triple-phase bone scan. This test is carried out in order to identify certain changes in the bone and how effective the blood circulation is. Another test that can be carried out is known as palpitations.
Palpitations is done by applying a stimulus(sometimes touch, cold, or heat) to determine if there is a pain in the area and its intensity.
For your doctor to diagnose CRPS, the following symptoms must be seen:
- The presence of an injury that had occurred before the pain began.
- An increased intensity of the pain(much more than the normal)from the initial injury.
- A change in the physical appearance of the area.
- No visible cause of pain or alteration of the appearance of the skin on the affected area.
Treatment
Since there is no visible cause of Chronic Regional Pain Syndrome, there is no cure available yet for CRPS. Since there is no cure, the only option the doctor has is to help manage and reduce the pain as well as the painful symptoms of the patient.
One of the significant ways of managing a patient’s symptoms is through therapy. These therapies include physiotherapy, psychotherapy, and physical therapy. Other forms of treatment may include drug therapy.
Drug treatment or therapy would involve the use of certain medications such as osteoporosis medication, antidepressants, anti-seizure drugs, corticosteroids, topical analgesics, as well as narcotics.
Other forms of treatment plans include:
Sympathetic nerve block
These nerve blocks are usually done in order to reduce the transmission of pain, as such, provide pain relief significant enough for the patient.
A sympathetic nerve block can be done using a number of methods such as placing the block(often an anesthetic) just close to the spine in order to block the transmission of impulses that are coming through the sympathetic nerves.
Surgical Sympathectomy
This method is often considered a controversial technique because it destroys the nerves that transmit pain impulses.
Some experts have considered it to be one of the best techniques because they feel it brings a favorable outcome; however, other scientists have considered it dangerous because they feel it only increases CRPS.
This technique should only be considered for those patients whose pain has been temporarily blocked using the sympathetic nerve block technique.
Intrathecal drug pumps
This treatment method is done by using pumps and catheters, which have been implanted to help send pain medications directly into the spinal fluid.
That way, the medications go directly into the nerves via the spinal fluid.
Spinal cord stimulations
This method is considered one of the best methods which can be used to manage Chronic Regional Pain Syndrome. This method is done by placing electrodes very close to the spinal cord.
These electrodes then absorbs the impulses that come from the spinal cord into the limbs.
Sources;
- Complex Regional Pain Syndrome; mayoclinic
- Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS); webmd
- Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS); clevelandclinic