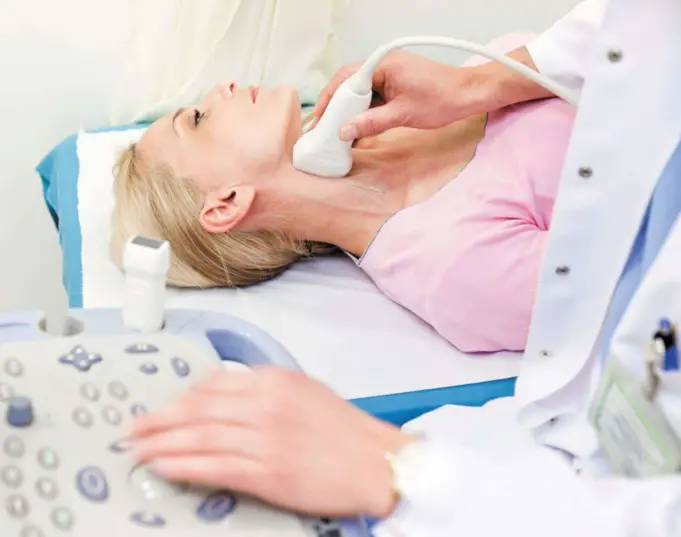
Carotid ultrasound is an imaging test that uses sound waves to produce real-time images of the body’s carotid arteries that carry blood from the heart to the brain.
The major purpose of a carotid ultrasound scan is to check for blockages and carotid arteries narrowing. A doppler ultrasound is an important part of the carotid ultrasound this is because the doppler ultrasound is used to evaluate movements of minerals and blood flow in the veins and arteries.
A carotid ultrasound is done to guide against conditions such as stenosis which may increase the risk of stroke.
Uses/Reasons for Performing Carotid Ultrasound
The major reason for performing a carotid ultrasound is to check for narrowing or blockage of the carotid arteries which may increase the patient’s risk of having a stroke.
Carotid ultrasound may also be performed on patients who have an abnormal sound in the neck(carotid bruit) or high blood pressure and patients who are being prepared for coronary artery bypass surgery.
Other reasons for performing a carotid ultrasound include
- Hematoma: A collection of blood clotted within tissues that can slow down blood flow and eventually stop blood flow.
- To verify the positioning of a metal stent placed in the carotid to maintain blood flow.
- To check the carotid artery after surgery and to restore normal blood flow.
Reasons for using a doppler ultrasound along side the carotid ultrasound
- 1. To check blood flow and blockages such as clot.
- To check for increased blood flow which could be a sign of an infection.
- Monitor blood flow during surgery.
- To monitor the narrowing of vessels in the carotid.
- To reduce blood flow to some organs such as ovary and testes.
- Predict a high risk of stroke in children who suffers from sickle cell disease.
- Detect blood vessel abnormalities in children.
Who Performs the Carotid Ultrasound
Carotid ultrasound is performed by an ultrasound technologist or technician. A diagnostic radiologist or sonographer is a medical professional who is trained to interpret ultrasound images.
They specialize in interpreting medical imaging tests including MRI scans, ultrasound, and CT scans.
Procedures of a Carotid Ultrasound
Carotid ultrasound is performed in a hospital. The procedure of the Carotid ultrasound takes less than 60mins generally. Steps include;
- Lying down face-up on a table in the ultrasound room which usually has dark or dimly lighted, to enable easy reading of the ultrasound images on the ultrasound screen. Ensure to keep your shoulder and arms down.
- A special water-based gel will be applied to the area under examination to reduce friction and help the transducer slide across your skin. It is the transducer that sends and receives soundwaves to produce the image on the ultrasound screen.
- The technologist will move the transducer back and forth on your temple and both sides of your neck while looking at the ultrasound screen.
- The technologist will occasionally press the transducer down. While he’s doing this, you might be asked to hold your breath or change your position for a short while. This will enable the technologist to have a clear and improve imaging that will help diagnose your condition.
- The water-based gel is then wiped off from your skin.
- You may be asked to wait for a short while. Then the diagnostic radiologist will check if the imaging was complete.
- After an imaging test, the patient is usually asked to go home.
What you may experience during and after a Carotid ultrasound
During a carotid ultrasound, you may experience minimal or no discomfort as the transducer pressed against your skin. After the carotid ultrasound, you will be asked to dress and sit for a while as the result is being reviewed.
You may be given the results or asked to return to the hospital in a few days and should be able to resume normal activities after an ultrasound scan.
Merits/Benefits of Carotid Ultrasound
Some known benefits of carotid ultrasound are listed below:
- It is not painful although it may be uncomfortable temporarily.
- It is a noninvasive scan which means that there are no injections or needles.
- It is less expensive and easy to use compared to other imaging methods.
- It is widely available compared to other imaging methods.
- It is completely safe and it uses soundwaves, not radiation.
- It provides a more clear picture of soft tissues that did not show up clearly on the x-ray.
- It can show a narrowing of one or both carotid arteries.
Demerits/Limitation of Carotid Ultrasound
Though the ultrasound scan is painless and has no known harmful effect on the human body, it has a few limitations. These limitations include;
- Some patients may be difficult to exam because of the size of the neck.
- Surgical scars or wounds in the neck can also make it difficult for a carotid ultrasound examination.
- Carotid ultrasound alone cannot be used to visualize the total length of the neck vessels because a portion of the carotid artery travels through a bone at the base of the skull.
- Some plaques that produce low echo may not be noticed.