You are having your bath one fine day when you notice a bump around your anus. You ponder on it and write it off as one of those ingrown hairs caused by the recent shoddy shave job that you did, and since you don’t feel pain – only a slight itching – you ignore it and hope the body repairs itself as it always does. Little do you know that you have anal warts.
Anal warts (also known as Condyloma acuminata) are a condition that affects the area in and around the anus. Anal warts are a form of genital wart, and sometimes they develop around the genital region.
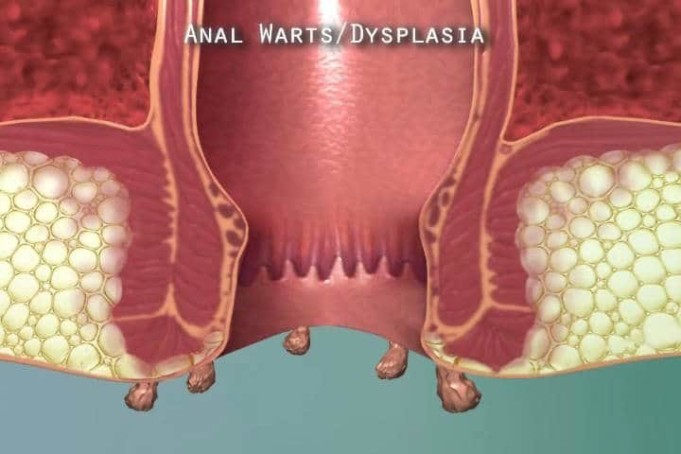
These warts can begin as small, almost unnoticeable pin-head size bump that can eventually grow to large pea sized bumps that cover the entire area.
What are the signs and symptoms of anal warts?
As mentioned earlier, these warts start as small in sized bumps that eventually grow bigger. They may develop some cauliflower-like appearance as they grow or when several bumps are bunched together.
Warts may be peach-coloured, pink, yellow, brown, or the appearance may even blend with your skin tone. Warts can also grow in your anal canal.
Anal warts are more often than not painless. Some people may not be aware that they have them long after they are infected.
However, the primary symptom of warts is soft, moist bumps near the anus. Other symptoms include:
- Itching
- Mucus discharge
- Bleeding
- Feeling like there is a lump in your rectum
Asides your anus, warts may occur on other parts of your body at the same time. Genital warts in women can be observed in the vagina, vulva or cervix while men can develop it on the penis, scrotum, groin or thighs.
Causes
Condyloma acuminata is caused by the Human Papilloma Virus (HPV). HPV is a sexually transmitted disease but can also spread by direct contact.
HPV often goes away on its own after a while without showing any signs or symptoms, but as with many sexually transmitted infections, it can linger in the body. HPV is very contagious especially among sexually active people.
Although anal intercourse is a method by which one can be exposed to HPV, it is not the only method. The disease can infect one through hand contact or secretions from an infected person.
The risk of getting infected increases when one has unprotected sex. Also, someone with a weak immune system caused by certain medications or diseases such as HIV is likely to contract the infection.
Risk factors that may predispose one to HPV include having multiple sexual partners, use of oral contraceptives, engaging in sexual intercourse at an early age and smoking.
Doctors visibly diagnose anal warts. The examination involves the use of a tool called anoscope to look for anal warts in the anal canal for men. Anal warts can be diagnosed with the aid of pap smear in women.
Treatment
It is possible for anal warts to become bigger and multiply if left untreated by a medical professional. Anal sex can lead to anal cancer although this is quite rare.
Treatment is proscribed based on size and location of the warts. Treatment includes:
- The use of topical medication: These include creams and lotion, and they work best if the warts are visibly located around the anus. They include imiquimod (Aldara, Zyclara), podofilox (Condylox), bichloroacetic acid (BCA), and trichloroacetic acid (TCA).
- Use of liquid nitrogen: This is used to freeze the warts in a process called cryotherapy. The warts fall off after freezing.
- Electrocautery: This is a procedure that involves the use of electric current to cauterize or burn off the warts.
- Laser Therapy: This treatment uses energy transmitted from intense light. This procedure is for particularly difficult cases.
- Surgery: When the warts are extensive and cannot be easily removed by the options above, a surgical procedure may be required. This would the localized use of anaesthesia on the affected area then the warts can be surgically removed. Treatment of anal warts may come in stages if the warts are extensive.
Prevention methods
The best method to prevent yourself from getting infected by anal warts is the use of safe sex methods. Abstaining from individuals who are infected with anal wart is very important.
However, since some individuals do not show symptoms of the infections, the use of condoms, sexual abstinence and limiting sexual contact to one partner cannot be overemphasized.
Although the use of condoms may be the best choice for sexually active people and will reduce the chances of getting HPV, it may not completely eliminate it as HPV can be spread through direct contact.
Therefore, as a protection measure, regular sexual partners need to be checked regularly for HPV and even other sexually transmitted infections.
There is hope however as Gardasil; the vaccine used to prevent HPV has been approved by the U.S Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is now available. It can be used in patients aged 9-26 prior to HPV exposure.